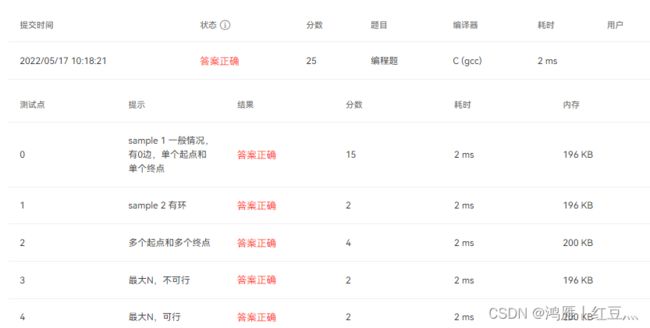
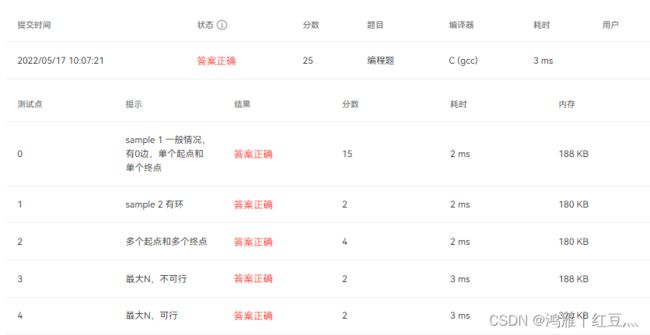
MOOC 数据结构 08-图8 How Long Does It Take——C语言
Given the relations of all the activities of a project, you are supposed to find the earliest completion time of the project.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts with a line containing two positive integers N (≤100), the number of activity check points (hence it is assumed that the check points are numbered from 0 to N−1), and M, the number of activities. Then M lines follow, each gives the description of an activity. For the i-th activity, three non-negative numbers are given: S[i], E[i], and L[i], where S[i] is the index of the starting check point, E[i] of the ending check point, and L[i] the lasting time of the activity. The numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, if the scheduling is possible, print in a line its earliest completion time; or simply output "Impossible".
Sample Input 1:
9 12
0 1 6
0 2 4
0 3 5
1 4 1
2 4 1
3 5 2
5 4 0
4 6 9
4 7 7
5 7 4
6 8 2
7 8 4
Sample Output 1:
18
Sample Input 2:
4 5
0 1 1
0 2 2
2 1 3
1 3 4
3 2 5
Sample Output 2:
Impossible思路和小结:
这是一道考察有向无环图DAG(Directed Acyclic Graph)的题,是一道基础的拓扑排序题。
我们可以稍微拓展下:如何确定是否无环,即从任一顶点出发遍历图,都不会回到该顶点;所以判断是否是DAG时,有两种方法,即BFS和DFS;
BFS方法就是老师讲的拓扑排序:有合理的拓扑序的图一定是无环图。
DFS方法就是在DFS一条路径时,不会回到该路径上的任何一个顶点;
下面就这两种方法分别解题:
1.拓扑排序(变种的BFS):增加一个数组,记录每个顶点的入度;将入度为0的顶点入队,开始BFS,每遍历一个顶点,它的邻接点入度-1,当入度为0时顶点入队;BFS完成后遍历了每个顶点,则是无环图;否则有环;
#include
#include
#include
typedef int Vertex; //顶点
typedef int WeightType; //边权
typedef struct _Edge{ //边
Vertex V1,V2;
WeightType Weight;
}Edge;
typedef struct _Adj Adj; //邻接点
struct _Adj{
Vertex AdjV;
WeightType weight;
Adj* Next;
};
typedef struct _LGraph{ //邻接表表示的图
int Nv;
int Ne;
Adj** G;
}LGraph;
typedef struct _Queue{ //TopSort用到的队列
Vertex* Data;
int front;
int rear;
}Queue;
LGraph* BuildGraph();
void InsertEdge( LGraph* Graph,Edge E );
void EarliestCompletionTime( LGraph* Graph );
bool TopSort( LGraph* Graph,int time[] );
void InitializeIndegree( LGraph* Graph,int Indegree[],int Len );
Queue* CreateQ( int N );
void AddQ( Queue* Q,Vertex V );
bool IsEmpty( Queue* Q );
Vertex DeleteQ( Queue* Q );
int Max( int time[],int N );
int main()
{
LGraph* Graph = BuildGraph();
EarliestCompletionTime( Graph );
return 0;
}
//建图
LGraph* BuildGraph()
{
LGraph* Graph = (LGraph*)malloc(sizeof(LGraph));
scanf("%d %d",&Graph->Nv,&Graph->Ne);
Graph->G = malloc(Graph->Nv*sizeof(Adj*));
Vertex V;
for(V=0;VNv;V++){
Graph->G[V] = NULL;
}
Edge E;
int i;
for(i=0;iNe;i++){
scanf("%d %d %d",&E.V1,&E.V2,&E.Weight);
InsertEdge( Graph,E );
}
return Graph;
}
void InsertEdge( LGraph* Graph,Edge E )
{
Adj* NewNode = (Adj*)malloc(sizeof(Adj));
NewNode->AdjV = E.V2;
NewNode->weight = E.Weight;
NewNode->Next = Graph->G[E.V1];
Graph->G[E.V1] = NewNode;
}
//解题
void EarliestCompletionTime( LGraph* Graph )
{
int time[Graph->Nv]; //记录各个顶点最早完成时间
Vertex V; //time初始化
for(V=0;VNv;V++){
time[V] = 0;
}
bool IsDAG = TopSort( Graph,time ); //拓扑排序得出是否是DAG,并计算各顶点的time值
if(IsDAG){
printf("%d\n",Max( time,Graph->Nv));
}else{
printf("Impossible\n");
}
}
//拓扑排序,同时计算time
bool TopSort( LGraph* Graph,int time[] )
{
int Indegree[Graph->Nv]; //各个顶点的入度值
InitializeIndegree( Graph,Indegree,Graph->Nv );
Queue* Q = CreateQ(Graph->Nv);
Vertex V;
for(V=0;VNv;V++){
if(Indegree[V] == 0){
AddQ( Q,V );
}
}
int cnt = 0; //计数器,记录已排序的顶点个数
Adj* p; //临时指针
while(!IsEmpty( Q )){
V = DeleteQ( Q );
cnt++;
for(p=Graph->G[V];p;p=p->Next){ //V的每个邻接点
Indegree[p->AdjV]--;
if(Indegree[p->AdjV] == 0){
AddQ( Q,p->AdjV );
}
if(time[V] + p->weight > time[p->AdjV]){ //更新time值
time[p->AdjV] = time[V] + p->weight;
}
}
}
bool IsDAG = true; //判断是否是DAG
if(cnt != Graph->Nv){
IsDAG = false;
}
return IsDAG;
}
void InitializeIndegree( LGraph* Graph,int Indegree[],int Len )
{
Vertex V;
for(V=0;VG[V];p;p=p->Next){
Indegree[p->AdjV]++;
}
}
}
//队列相关操作集
Queue* CreateQ( int N )
{
Queue* Q = (Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
Q->Data = malloc(N*sizeof(int));
Q->front = Q->rear = -1;
return Q;
}
void AddQ( Queue* Q,Vertex V )
{
Q->rear++;
Q->Data[Q->rear] = V;
}
bool IsEmpty( Queue* Q )
{
return Q->front == Q->rear?true:false;
}
Vertex DeleteQ( Queue* Q )
{
Q->front++;
return Q->Data[Q->front];
}
//求最早完成时间
int Max( int time[],int N )
{
int i,EariestCompletionTime = time[N-1];
for(i=0;i EariestCompletionTime){
EariestCompletionTime = time[i];
}
}
return EariestCompletionTime;
} 2.DFS:增加一个数组visited[ ],确保每个顶点都遍历到;在深度遍历某一条具体路径时,如果又回到了该路径的上任一顶点,那么必定有环,所以增加一个数组collected[ ],标记DFS时某一条路径上的每个顶点,递归到这条路径的终点时,表示无环,初始化这个数组,然后继续深度遍历下一条路径;
#include
#include
#include
typedef int Vertex;
typedef int WeightType;
typedef struct _Edge{
Vertex V1,V2;
WeightType Weight;
}Edge;
typedef struct _Adj Adj;
struct _Adj{
Vertex AdjV;
WeightType weight;
Adj* Next;
};
typedef struct _LGraph{
int Nv;
int Ne;
Adj** G;
}LGraph;
LGraph* BuildGraph();
void InsertEdge( LGraph* Graph,Edge E );
void EarliestCompletionTime( LGraph* Graph );
bool DFS( LGraph* Graph,Vertex X,int time[],bool visited[],bool collected[] );
int Max( int time[],int N );
int main()
{
LGraph* Graph = BuildGraph();
EarliestCompletionTime( Graph );
return 0;
}
//建图
LGraph* BuildGraph()
{
LGraph* Graph = (LGraph*)malloc(sizeof(LGraph));
scanf("%d %d",&Graph->Nv,&Graph->Ne);
Graph->G = malloc(Graph->Nv*sizeof(Adj*));
Vertex V;
for(V=0;VNv;V++){
Graph->G[V] = NULL;
}
Edge E;
int i;
for(i=0;iNe;i++){
scanf("%d %d %d",&E.V1,&E.V2,&E.Weight);
InsertEdge( Graph,E );
}
return Graph;
}
void InsertEdge( LGraph* Graph,Edge E )
{
Adj* NewNode = (Adj*)malloc(sizeof(Adj));
NewNode->AdjV = E.V2;
NewNode->weight = E.Weight;
NewNode->Next = Graph->G[E.V1];
Graph->G[E.V1] = NewNode;
}
void EarliestCompletionTime( LGraph* Graph )
{
int time[Graph->Nv];
bool visited[Graph->Nv];
bool collected[Graph->Nv];
Vertex V;
for(V=0;VNv;V++){
time[V] = 0;
visited[V] = false;
collected[V] = false;
}
bool IsDAG = true;
for(V=0;VNv;V++){ //确保有多个起点(入度为0)时,不会遗漏任何一个
if(!visited[V] && IsDAG){
IsDAG = DFS( Graph,V,time,visited,collected );
}
}
if(IsDAG){
printf("%d\n",Max( time,Graph->Nv));
}else{
printf("Impossible\n");
}
}
bool DFS( LGraph* Graph,Vertex X,int time[],bool visited[],bool collected[] )
{
bool IsDAG = true;
visited[X] = true;
if(Graph->G[X] == NULL){
//递归到某条路径的终点时,初始化collected;
Vertex V;
for(V=0;VNv;V++){
collected[V] = false;
}
return true;
}
Adj* p;
for(p=Graph->G[X];p;p=p->Next){
collected[X] = true; //某条路径开始的起点,标记一下
if(IsDAG == false){ //如果已经发现有环,退出递归;
return false;
}
if(collected[p->AdjV] == true){
IsDAG = false;
break;
}else{
if(time[X] + p->weight > time[p->AdjV]){
time[p->AdjV] = time[X] + p->weight;
}
IsDAG = DFS( Graph,p->AdjV,time,visited,collected );
}
}
return IsDAG;
}
int Max( int time[],int N )
{
int i,EariestCompletionTime = time[N-1];
for(i=0;i EariestCompletionTime){
EariestCompletionTime = time[i];
}
}
return EariestCompletionTime;
} 可以参考我写的判断DAG的方法的文章
数据结构 拓扑排序拓展 如何判断DAG_鸿雁丨红豆灬的博客-CSDN博客有向无环图 DAG(Directed Acyclic Graph)在学习拓扑排序的时候,我们知道如果一个有向图存在合理的拓扑序,那么这个图一定是DAG;以下是拓扑排序的伪码描叙:伪码描叙: void TopSort(){for(图中的每一个顶点V){ if(Indegree[V]==0){ AddQ( Q,V );}}while(IsEmpty( Q )){V = DeleteQ( Q );输出V,或者记录V的输出序号;cnt++;for(V 的https://blog.csdn.net/h465705089/article/details/124818968