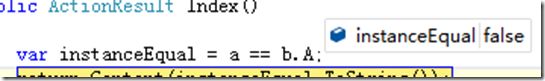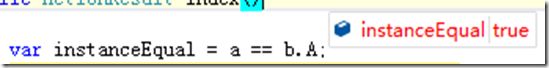autofac使用Common Serivce Locator跟随wcf,mvc,web api的实例控制
autofac本身只提供了基本的ioc容器的功能
要想在mvc,wcf,web api中使用,除了autofac本身,还需要引入对应的包(点击对应连接可查看文档)
除此之外,使用Common Service Locator 也可以用aotofac来做真正的容器
为了说明下面的实例管理,先准备2个类
public class ClassA { } public class ClassB { public ClassB(ClassA a) { this.A = a; } public ClassA A { get; set; } }
类A是一个最简单的类,类B有一个类A的属性
在global中构造ioc容器
var builder = new ContainerBuilder(); builder.RegisterType<ClassA>(); builder.RegisterType<ClassB>(); builder.RegisterControllers(Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly()); builder.RegisterApiControllers(Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly()); var container = builder.Build(); DependencyResolver.SetResolver(new AutofacDependencyResolver(container)); GlobalConfiguration.Configuration.DependencyResolver = new AutofacWebApiDependencyResolver(container);
为了之后说明在mvc和web api中的使用,我们需要设置一些与mvc和web api有关的代码。详细的可以查看官方文档
controller中的也很简单
private ClassA a; private ClassB b; public HomeController(ClassA a, ClassB b) { this.a = a; this.b = b; } public ActionResult Index() { var instanceEqual = a == b.A; return Content(instanceEqual.ToString()); }
在autofac的实例管理中(文档)。
最基本的(不做任何设置)为InstancePerDependency 也就是说,每个依赖,会创建一个新的实例
按照以上的代码,当在HomeController里需要ClassA的实例的时候,创建了一个新的,HomeController中还需要ClassB,此时会创建一个新的ClassB,而ClassB在创建时,也需要一个ClassA,当为InstancePerDependency的时候,ClassB需要的ClassA,是重新创建了一个ClassA的实例,而与HomeController中需要的那个,是不同的实例
可以看到,homecontroller中,a与b.A是不同的
另一种比较常用的实例管理方式为 Instance Per Lifetime Scope,意思是每一个生命周期内,只会存在一个。这个在UnitOfWork模式中是非常重要的
我们把ClassA的实例管理设置为仅一个
builder.RegisterType<ClassA>().InstancePerLifetimeScope();
可以看到,此时两个引用是同一个实例
有时候,我们从容器中获取实例,不是用构造注入,属性注入等方式,而是直接从容器中获取
到目前为止,运行的方式与我们预期的是一样的。
下面说当引入Common Service Locator时的情况
Common Service Locator是微软定义的一个基础接口,各大ico容器提供了各自的实现
我们根据Autofac官方网站上的说明设置
var csl = new AutofacServiceLocator(container); ServiceLocator.SetLocatorProvider(() => csl);
以上代码添加在global中
然后再controller里加入代码如下
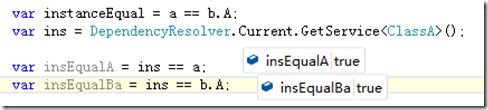
var insSL = ServiceLocator.Current.GetInstance<ClassA>(); var insSLEqualA = insSL == a; var insSLEqualBa = insSL == b.A;
为了简化,直接在controller调用common service locator,其实这个在写组件时时很好用的一种手段。
在我们的预期中,通过common service locator获取到的应该也是同一个实例,他也根据设置的InstancePerLiefttimeScope起作用。
很遗憾,并不是一个.
通过查看autofac相关的源码,发现
当有一个新的request请求时,autofac会自动的创建一个lifetime scope
/// <summary> /// Begin a new nested scope. Component instances created via the new scope /// will be disposed along with it. /// /// </summary> /// /// <returns> /// A new lifetime scope. /// </returns> ILifetimeScope BeginLifetimeScope();
之后的容器,是这个ILifetimeScope,而不是builder.Build()处理的那个container。
所以我们才可以通过DependencyResolver.Current取到正确的值。
而设置common service locator,我们给定的是固定的一个值,而这个值是根容器。
查看ServiceLocator的源码可以发现
public static class ServiceLocator { private static ServiceLocatorProvider currentProvider; /// <summary> /// The current ambient container. /// /// </summary> public static IServiceLocator Current { get { return ServiceLocator.currentProvider(); } } /// <summary> /// Set the delegate that is used to retrieve the current container. /// /// </summary> /// <param name="newProvider">Delegate that, when called, will return /// the current ambient container.</param> public static void SetLocatorProvider(ServiceLocatorProvider newProvider) { ServiceLocator.currentProvider = newProvider; } }
ServiceLocatorProvider是一个委托,而每次访问Current时,去执行这个委托。
我们之前按照autofac的官方文档中的写法
var csl = new AutofacServiceLocator(container); ServiceLocator.SetLocatorProvider(() => csl);
委托每次执行,返回的都是根容器,而不是与当前请求有关的ILifetimeScope。
改造一些这个委托的写法
var csl = new AutofacServiceLocator(container); ServiceLocator.SetLocatorProvider(() => { var httpContext = HttpContext.Current; if (httpContext.CurrentHandler is MvcHandler) { return new AutofacServiceLocator(AutofacDependencyResolver.Current.RequestLifetimeScope); } return csl; });
如果是一个mvc请求,则使用当前的请求scope去设置common service locator
看到,从common service locator中获取的,也是同样的一个实例了。
mvc对应的LifetimeScope可以从AutofacDependencyResolver.Current.RequestLifetimeScope获取
wcf对应的可以从AutofacInstanceContext.Current获取
而web api的有些麻烦
目前我找到的方式是
Request.GetDependencyScope().GetRequestLifetimeScope()
此处这个Request是ApiController里的那个Request属性,他的类型是HttpRequestMessage
在global里如果获得这个Request的实例呢
根据最新的release文档,我们可以发现,他提供了一个新的方法
builder.RegisterHttpRequestMessage(GlobalConfiguration.Configuration);
此方法的意思是,我们可以通过容器来获取当前的request
但是尝试了很多种方法,都无法正确的从容器中把它获取出来。
不过到是给我们提供了一种思路,可以通过自己添加一个MessageHandler来把Request变得可以访问。
public sealed class CommonServiceLocatorApiHandler : DelegatingHandler { public HttpRequestMessage Request { get; private set; } protected override System.Threading.Tasks.Task<HttpResponseMessage> SendAsync(HttpRequestMessage request, System.Threading.CancellationToken cancellationToken) { Request = request; return base.SendAsync(request, cancellationToken); } }
新建一个继承api的handler,把request保存下,用public公开出来
GlobalConfiguration.Configuration.MessageHandlers.Add(new CommonServiceLocatorApiHandler());
把刚建的添加到handlers里
var csl = new AutofacServiceLocator(container); ServiceLocator.SetLocatorProvider(() => { var httpContext = HttpContext.Current; if (httpContext.CurrentHandler is MvcHandler) { return new AutofacServiceLocator(AutofacDependencyResolver.Current.RequestLifetimeScope); } else if(httpContext.CurrentHandler is HttpControllerHandler) { var handler = GlobalConfiguration.Configuration.MessageHandlers.FirstOrDefault( x => x is CommonServiceLocatorApiHandler) as CommonServiceLocatorApiHandler; if (handler != null) { return new AutofacServiceLocator(handler.Request.GetDependencyScope().GetRequestLifetimeScope()); } } return csl; });