Java——(十)网络编程
------Java培训、Android培训、iOS培训、.Net培训、期待与您交流! -------
一、Java的基本网络支持
Java为网络支持提供了java.net包,该包下的URL和URLConnection等类提供了以编程方式访问Web服务的功能,
而URLDecoder和URLEncoder则提供了普通字符串和application/x-www-form-urlencoded MIME相互转换的静态
方法。
1.使用InetAdress
Java提供了InetAdress类来代表IP地址,InetAdress下还有两个子类:Inet4Address、Inet6Adress。InetAdress
类没有提供构造器,而是提供了如下两个静态方法来获取InetAdress实例。
1)getByName(String host):根据主机获取对应的InetAdress对象。
2)getByAddress(byte[] addr):根据原始IP地址来获取对应的InetAdress对象。
3)getLocalHost():根据本机IP地址来获取对应的InetAdress对象。
InetAdress还提供了如下三个方法来获取InetAdress实例对应的IP地址和主机名。
3)String getCanonicalHostName():获取此IP地址的全限定域名。
4)String getHostAddress():返回该InetAdress实例对应的IP地址字符串。
5)String getHostName():获取此IP地址的主机名。
6)boolean isReachable(int timeout):用于测试是否可到达该地址。
下面程序测试了InetAdress类的简单用法。
1 package com.socket; 2 3 import java.net.InetAddress; 4 5 public class InetAddressTest { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 8 9 // 根据主机名来获取对应的InetAddress实例 10 InetAddress ipAddress = InetAddress 11 .getByName("www.4399.com"); 12 //判断是否可达 13 System.out.println("4399网址是否可达:" + ipAddress.isReachable(2000)); 14 //获取该InetAdress实例的IP字符串 15 System.out.println(ipAddress.getHostAddress()); 16 //获取本机IP地址对应的InetAdress实例 17 System.out.println("本机IP:"+ InetAddress.getLocalHost()); 18 //根据原始IP地址来获取对应的InetAdress实例 19 InetAddress local = InetAddress.getByAddress(new byte[]{127,0,0,1}); 20 System.out.println("本机是否可达:" + local.isReachable(3000)); 21 //获取该InetAdress实例对应的全限定域名 22 System.out.println(local.getCanonicalHostName()); 23 } 24 25 }
运行结果:
4399网址是否可达:true 175.43.124.195 本机IP:XiongXueSong/192.168.1.113 本机是否可达:true 127.0.0.1
2.使用URLDecoder和URLEncoder
URLDecoder和URLEncoder用于完成普通字符串和application/x-www-form-urlencoded MIME字符串之间的
相互转换。
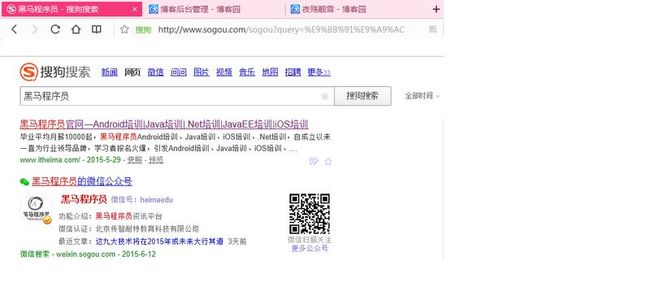
在介绍application/x-www-form-urlencoded MIME字符串之前,现在浏览器搜索关键字“黑马程序员”,将看到
下图所示界面。
从图中可以看出当我们所示的关键字包含中文时,这些关键字就会变成如上图所示的“乱码”——这就是所谓的
application/x-www-form-urlencoded MIME字符串。
当URL地址里包含非西欧字符的字符串时,系统就会将这些非西欧字符串转换成上图所示的特殊字符串。这就
需要使用URLDecoder和URLEncoder类。
1)URLDecoder类包含一个decode(String s, String enc)静态方法,它可以将看上去是乱码的特殊字符串转换
成普通字符串。
2)URLEncoder类包含一个encode(String s, String enc)静态方法,它可以将普通字符串转换成
application/x-www-form-urlencoded MIME字符串。
下面程序示范了将上图所示地址栏中的“乱码”转换成普通字符串,并示范了如何将普通字符串转换成
application/x-www-form-urlencoded MIME字符串。
1 package com.socket; 2 3 import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; 4 import java.net.URLDecoder; 5 import java.net.URLEncoder; 6 7 public class URLDecoderTest { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { 10 11 // 将application/x-www-form-urlencoded MIME字符串转换成普通字符串 12 String keyString = URLDecoder.decode( 13 "%E9%BB%91%E9%A9%AC%E7%A8%8B%E5%BA%8F%E5%91%98", "UTF-8"); 14 System.out.println(keyString); 15 //将普通字符串转换成application/x-www-form-urlencoded MIME字符串 16 String urlString = URLEncoder.encode("黑马程序员", "UTF-8"); 17 System.out.println(urlString); 18 } 19 20 }
运行结果:
黑马程序员 %E9%BB%91%E9%A9%AC%E7%A8%8B%E5%BA%8F%E5%91%98
提示:
包含中文字符串的普通字符串需要转换,转换方法是每个中文字符串栈2个字节,每个字节可以转换成
2个十六进制的数组,所以每个中文字符将转换成“%XX%XX”的形式。
3.使用URLhURLConnection
URL对象代表统一资源定位器,它是指向互联网“资源”的指针。资源可以是简单的文件或目录,也可以
是对更为复杂的引用。通常情况下,URL可以由协议名、主机、端口和资源组成,即满足如下格式:
protocol://host:port/resourceName
例如如下的URL地址:
http://www.4399.com
3.TCP编程
客户端:
1 package TCPDemo; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.io.InputStream; 6 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 7 import java.io.OutputStream; 8 import java.net.Socket; 9 10 public class TCPClient { 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 13 14 //创建TCP客户端服务 15 Socket s = new Socket("localhost", 8000); 16 // 17 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); 18 String line = null; 19 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { 20 if ("over".equals(line)) { 21 break; 22 } 23 OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream(); 24 out.write(line.getBytes()); 25 26 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; 27 InputStream in = s.getInputStream(); 28 in = s.getInputStream(); 29 int len = in.read(buf); 30 String text = new String(buf, 0, len); 31 String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress(); 32 System.out.println(ip + ": " + text); 33 } 34 35 36 } 37 38 }
服务端:
1 package TCPDemo; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.io.InputStream; 5 import java.io.OutputStream; 6 import java.net.ServerSocket; 7 import java.net.Socket; 8 9 public class TCPServer { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 12 13 //创建服务器套接字,端口号必须明确 14 ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8000); 15 16 //监听来自客户端的套接字 17 Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); 18 while (true) { 19 try { 20 21 String ip = socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress(); 22 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; 23 24 InputStream in = socket.getInputStream(); 25 int len = in.read(buf); 26 String text = new String(buf, 0, len); 27 System.out.println(ip + ":" + text); 28 29 OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream(); 30 out.write("已连接".getBytes()); 31 } catch (Exception e) { 32 // TODO: handle exception 33 System.out.println(e.toString()); 34 } 35 36 } 37 } 38 39 }
运行结果:
4.UDP编程
客户端
1 package TCPDemo; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.io.InputStream; 5 import java.io.OutputStream; 6 import java.net.ServerSocket; 7 import java.net.Socket; 8 9 public class TCPServer { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 12 13 //创建服务器套接字,端口号必须明确 14 ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8000); 15 16 while (true) { 17 //监听来自客户端的套接字 18 try { 19 Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); 20 21 String ip = socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress(); 22 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; 23 24 InputStream in = socket.getInputStream(); 25 int len = in.read(buf); 26 String text = new String(buf, 0, len); 27 System.out.println(ip + ":" + text); 28 29 OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream(); 30 out.write("已连接".getBytes()); 31 } catch (Exception e) { 32 // TODO: handle exception 33 System.out.println(e.toString()); 34 } 35 36 } 37 } 38 39 }
服务端
1 package UDPDemo; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.net.DatagramPacket; 5 import java.net.DatagramSocket; 6 7 public class UDPServer { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 10 System.out.println("开启Server。。。。。"); 11 12 //建立接收端的UDPSocket服务,必须明确端口号 13 DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(8888); 14 while (true) { 15 16 //创建数据包 17 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; 18 DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length); 19 //使用接收方法将接收到的数据存储到数据包中 20 ds.receive(dp); 21 //对数据进行解析 22 String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress(); 23 int port = dp.getPort(); 24 String text = new String(dp.getData(), 0 , dp.getLength()); 25 System.out.println(ip + ": " + port + ": " + text); 26 } 27 } 28 29 }
运行结果: