Opencv+C++之人脸识别二
这两天课比较多,上次的两步法人脸识别代码一直没有补充完整,今天将整个实验代码show一下,同时将该方法的主要思想介绍下:
上一节我们已经将图片进行降维处理,这样做的目的就是要在保持对象间差异的同时降低处理数据量。除了PCA外,LDA也是一种比较简单实用的降维方法,大家可以对比两种降维方法;基于PCA降维后的数据,我们接着要做的是用训练数据将测试数据表示出来

接着通过以下的误差判别式来找到M近邻(误差值越小说明该训练样本跟测试样本的相似度越大)
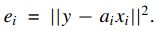
以上就完成了两步法中的第一步,第二步中用M近邻样本将测试样本再次标出(实际上这里的本质还是稀疏表示的方法,但是改进之处是单纯的稀疏法中稀疏项不确定,两步法中通过第一步的误差筛选确定了贡献度较大的训练样本)
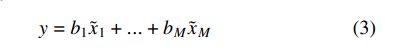
在M近邻中包含多个类的训练样本,我们要将每个类的训练样本累加起来,分别同测试样本做误差对比,将测试样本判定给误差最下的类

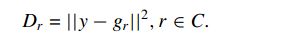
OK,主要思想介绍了,下面就看代码实现
/************************************************************************/ /* ZhaoChaofeng */ 2013.4.16 /************************************************************************/ #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> #include <fstream> #include <sstream> #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace cv; using namespace std; const double u=0.01f; const double v=0.01f;//the global parameter const int MNeighbor=40;//the M nearest neighbors // Number of components to keep for the PCA const int num_components = 100; //the M neighbor mats vector<Mat> MneighborMat; //the class index of M neighbor mats vector<int> MneighborIndex; //the number of object which used to training const int Training_ObjectNum=40; //the number of image that each object used const int Training_ImageNum=7; //the number of object used to testing const int Test_ObjectNum=40; //the image number const int Test_ImageNum=3; // Normalizes a given image into a value range between 0 and 255. Mat norm_0_255(const Mat& src) { // Create and return normalized image: Mat dst; switch(src.channels()) { case 1: cv::normalize(src, dst, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC1); break; case 3: cv::normalize(src, dst, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC3); break; default: src.copyTo(dst); break; } return dst; } // Converts the images given in src into a row matrix. Mat asRowMatrix(const vector<Mat>& src, int rtype, double alpha = 1, double beta = 0) { // Number of samples: size_t n = src.size(); // Return empty matrix if no matrices given: if(n == 0) return Mat(); // dimensionality of (reshaped) samples size_t d = src[0].total(); // Create resulting data matrix: Mat data(n, d, rtype); // Now copy data: for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // if(src[i].empty()) { string error_message = format("Image number %d was empty, please check your input data.", i); CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, error_message); } // Make sure data can be reshaped, throw a meaningful exception if not! if(src[i].total() != d) { string error_message = format("Wrong number of elements in matrix #%d! Expected %d was %d.", i, d, src[i].total()); CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, error_message); } // Get a hold of the current row: Mat xi = data.row(i); // Make reshape happy by cloning for non-continuous matrices: if(src[i].isContinuous()) { src[i].reshape(1, 1).convertTo(xi, rtype, alpha, beta); } else { src[i].clone().reshape(1, 1).convertTo(xi, rtype, alpha, beta); } } return data; } //convert int to string string Int_String(int index) { stringstream ss; ss<<index; return ss.str(); } ////show the element of mat(used to test code) //void showMat(Mat RainMat) //{ // for (int i=0;i<RainMat.rows;i++) // { // for (int j=0;j<RainMat.cols;j++) // { // cout<<RainMat.at<float>(i,j)<<" "; // } // cout<<endl; // } //} // ////show the element of vector //void showVector(vector<int> index) //{ // for (int i=0;i<index.size();i++) // { // cout<<index[i]<<endl; // } //} // //void showMatVector(vector<Mat> neighbor) //{ // for (int e=0;e<neighbor.size();e++) // { // showMat(neighbor[e]); // } //} //Training function void Trainging() { // Holds some training images: vector<Mat> db; // This is the path to where I stored the images, yours is different! for (int i=1;i<=Training_ObjectNum;i++) { for (int j=1;j<=Training_ImageNum;j++) { string filename="s"+Int_String(i)+"/"+Int_String(j)+".pgm"; db.push_back(imread(filename,IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)); } } // Build a matrix with the observations in row: Mat data = asRowMatrix(db, CV_32FC1); // Perform a PCA: PCA pca(data, Mat(), CV_PCA_DATA_AS_ROW, num_components); // And copy the PCA results: Mat mean = pca.mean.clone(); Mat eigenvalues = pca.eigenvalues.clone(); Mat eigenvectors = pca.eigenvectors.clone(); // The mean face: //imshow("avg", norm_0_255(mean.reshape(1, db[0].rows))); // The first three eigenfaces: //imshow("pc1", norm_0_255(pca.eigenvectors.row(0)).reshape(1, db[0].rows)); //imshow("pc2", norm_0_255(pca.eigenvectors.row(1)).reshape(1, db[0].rows)); //imshow("pc3", norm_0_255(pca.eigenvectors.row(2)).reshape(1, db[0].rows)); ////get and save the training image information which decreased on dimensionality Mat mat_trans_eigen; Mat temp_data=data.clone(); Mat temp_eigenvector=pca.eigenvectors.clone(); gemm(temp_data,temp_eigenvector,1,NULL,0,mat_trans_eigen,CV_GEMM_B_T); //save the eigenvectors FileStorage fs(".\\eigenvector.xml", FileStorage::WRITE); fs<<"eigenvector"<<eigenvectors; fs<<"TrainingSamples"<<mat_trans_eigen; fs.release(); } //Line combination of test sample used by training samples //parameter:y stand for the test sample column vector; //x stand for the training samples matrix Mat LineCombination(Mat y,Mat x) { //the number of training samples size_t col=x.cols; //the result mat Mat result=cvCreateMat(col,1,CV_32FC1); //the transposition of x and also work as a temp matrix Mat trans_x_mat=cvCreateMat(col,col,CV_32FC1); //construct the identity matrix Mat I=Mat::ones(col,col,CV_32FC1); //solve the Y=XA //result=x.inv(DECOMP_SVD); //result*=y; Mat temp=(x.t()*x+u*I); Mat temp_one=temp.inv(DECOMP_SVD); Mat temp_two=x.t()*y; result=temp_one*temp_two; return result; } //Error test //parameter:y stand for the test sample column vector; //x stand for the training samples matrix //coeff stand for the coefficient of training samples void ErrorTest(Mat y,Mat x,Mat coeff) { //the array store the coefficient map<double,int> Efficient; //compute the error for (int i=0;i<x.cols;i++) { Mat temp=x.col(i); double coefficient=coeff.at<float>(i,0); temp=coefficient*temp; double e=norm((y-temp),NORM_L2); Efficient[e]=i;//insert a new element } //select the minimum w col as the w nearest neighbors map<double,int>::const_iterator map_it=Efficient.begin(); int num=0; //the map could sorted by the key one while (map_it!=Efficient.end() && num<MNeighbor) { MneighborMat.push_back(x.col(map_it->second)); MneighborIndex.push_back(map_it->second); ++map_it; ++num; } //return MneighborMat; } //error test of two step //parameter:MneighborMat store the class information of M nearest neighbor samples int ErrorTest_Two(Mat y,Mat x,Mat coeff) { int result; bool flag=true; double minimumerror; // map<int,vector<Mat>> ErrorResult; //count the class of M neighbor for (int i=0;i<x.cols;i++) { //compare //Mat temp=x.col(i)==MneighborMat[i]; //showMat(temp); //if (temp.at<float>(0,0)==255) //{ int classinf=MneighborIndex[i]; double coefficient=coeff.at<float>(i,0); Mat temp=x.col(i); temp=coefficient*temp; ErrorResult[classinf/Training_ImageNum].push_back(temp); //} } // map<int,vector<Mat>>::const_iterator map_it=ErrorResult.begin(); while(map_it!=ErrorResult.end()) { vector<Mat> temp_mat=map_it->second; int num=temp_mat.size(); Mat temp_one; temp_one=Mat::zeros(temp_mat[0].rows,temp_mat[0].cols,CV_32FC1); while (num>0) { temp_one+=temp_mat[num-1]; num--; } double e=norm((y-temp_one),NORM_L2); if (flag) { minimumerror=e; result=map_it->first+1; flag=false; } if (e<minimumerror) { minimumerror=e; result=map_it->first+1; } ++map_it; } return result; } //testing function //parameter:y stand for the test sample column vector; //x stand for the training samples matrix int testing(Mat x,Mat y) { // the class that test sample belongs to int classNum; //the first step: get the M nearest neighbors Mat coffecient=LineCombination(y.t(),x.t()); //cout<<"the first step coffecient"<<endl; //showMat(coffecient); //map<Mat,int> MneighborMat=ErrorTest(y,x,coffecient); ErrorTest(y.t(),x.t(),coffecient); //cout<<"the M neighbor index"<<endl; //showVector(MneighborIndex); //cout<<"the M neighbor mats"<<endl; //showMatVector(MneighborMat); //the second step: //construct the W nearest neighbors mat int row=x.cols;//should be careful Mat temp(row,MNeighbor,CV_32FC1); for (int i=0;i<MneighborMat.size();i++) { Mat temp_x=temp.col(i); if (MneighborMat[i].isContinuous()) { MneighborMat[i].convertTo(temp_x,CV_32FC1,1,0); } else { MneighborMat[i].clone().convertTo(temp_x,CV_32FC1,1,0); } } //cout<<"the second step mat"<<endl; //showMat(temp); Mat coffecient_two=LineCombination(y.t(),temp); //cout<<"the second step coffecient"<<endl; //showMat(coffecient_two); classNum=ErrorTest_Two(y.t(),temp,coffecient_two); return classNum; } int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) { //the number which test true int TrueNum=0; //the Total sample which be tested int TotalNum=Test_ObjectNum*Test_ImageNum; //if there is the eigenvector.xml, it means we have got the training data and go to the testing stage directly; FileStorage fs(".\\eigenvector.xml", FileStorage::READ); if (fs.isOpened()) { //if the eigenvector.xml file exist,read the mat data Mat mat_eigenvector; fs["eigenvector"] >> mat_eigenvector; Mat mat_Training; fs["TrainingSamples"]>>mat_Training; for (int i=1;i<=Test_ObjectNum;i++) { int ClassTestNum=0; for (int j=Training_ImageNum+1;j<=Training_ImageNum+Test_ImageNum;j++) { string filename="s"+Int_String(i)+"/"+Int_String(j)+".pgm"; Mat TestSample=imread(filename,IMREAD_GRAYSCALE); Mat TestSample_Row; TestSample.reshape(1,1).convertTo(TestSample_Row,CV_32FC1,1,0);//convert to row mat Mat De_deminsion_test; gemm(TestSample_Row,mat_eigenvector,1,NULL,0,De_deminsion_test,CV_GEMM_B_T);// get the test sample which decrease the dimensionality //cout<<"the test sample"<<endl; //showMat(De_deminsion_test.t()); //cout<<"the training samples"<<endl; //showMat(mat_Training); int result=testing(mat_Training,De_deminsion_test); //cout<<"the result is"<<result<<endl; if (result==i) { TrueNum++; ClassTestNum++; } MneighborIndex.clear(); MneighborMat.clear();//及时清除空间 } cout<<"第"<<Int_String(i)<<"类测试正确的图片数: "<<Int_String(ClassTestNum)<<endl; } fs.release(); } else { Trainging(); } // Show the images: waitKey(0); // Success! return 0; }
在以上的实现中,有些opencv的实现需要特别注意一下:
(1)坑爹的Mat类型,它虽然可以方便的让我们实现图像数据的矩阵化,并给出了一系列的操作方法,但是,在调试中,它却不能像一般变量一样,让我们直观的看到;我用一个比较笨的方法:自己写一个方法,在调试中调用,呈现关键矩阵的数据
(2)另外一个就是将训练数据做一个保存,用到了opencv中的FileStorage类;有关对中间数据的存储通常会用到.xml或者.yml文件,以下对其做个简单介绍
新版本的OpenCV的C++接口中,imwrite()和imread()只能保存整数数据,且需要以图像格式。当需要保存浮点数据或者XML/YML文件时,之前的C语言接口cvSave()函数已经在C++接口中被删除,代替它的是 FileStorage类。这个类非常的方便,封装了很多数据结构的细节,编程的时候可以根据统一的接口对数据结构进行保存。
1. FileStorage类写XML/YML文件
• 新建一个FileStorage对象,以FileStorage::WRITE的方式打开一个文件。
• 使用 << 操作对该文件进行操作。
• 释放该对象,对文件进行关闭。
例子如下:
FileStorage fs("test.yml", FileStorage::WRITE); fs << "frameCount" << 5; time_t rawtime; time(&rawtime); fs << "calibrationDate" << asctime(localtime(&rawtime)); Mat cameraMatrix = (Mat_<double>(3,3) << 1000, 0, 320, 0, 1000, 240, 0, 0, 1); //又一种Mat初始化方式 Mat distCoeffs = (Mat_<double>(5,1) << 0.1, 0.01, -0.001, 0, 0); fs << "cameraMatrix" << cameraMatrix << "distCoeffs" << distCoeffs; //features为一个大小为3的向量,其中每个元素由随机数x,y和大小为8的uchar数组组成 fs << "features" << "["; for( int i = 0; i < 3; i++ ) { int x = rand() % 640; int y = rand() % 480; uchar lbp = rand() % 256; fs << "{:" << "x" << x << "y" << y << "lbp" << "[:"; for( int j = 0; j < 8; j++ ) fs << ((lbp >> j) & 1); fs << "]" << "}"; } fs << "]"; fs.release();
2. FileStorage类读XML/YML文件
FileStorage对存储内容在内存中是以层次的节点组成的,每个节点类型为FileNode,FileNode可以使单个的数值、数组或者一系列FileNode的集合。FileNode又可以看做是一个容器,使用iterator接口可以对该节点内更小单位的内容进行访问,例如访问到上面存储的文件中"features"的内容。步骤与写文件类似:
• 新建FileStorage对象,以FileStorage::READ 方式打开一个已经存在的文件
• 使用FileStorage::operator []()函数对文件进行读取,或者使用FileNode和FileNodeIterator
• 使用FileStorage::release()对文件进行关闭
例子如下:
FileStorage fs("test.yml", FileStorage::READ); //方式一: []操作符 int frameCount = (int)fs["frameCount"]; //方式二: FileNode::operator >>() string date; fs["calibrationDate"] >> date; Mat cameraMatrix2, distCoeffs2; fs["cameraMatrix"] >> cameraMatrix2; fs["distCoeffs"] >> distCoeffs2; //注意FileNodeIterator的使用,似乎只能用一维数组去读取里面所有的数据 FileNode features = fs["features"]; FileNodeIterator it = features.begin(), it_end = features.end(); int idx = 0; std::vector<uchar> lbpval; for( ; it != it_end; ++it, idx++ ) { cout << "feature #" << idx << ": "; cout << "x=" << (int)(*it)["x"] << ", y=" << (int)(*it)["y"] << ", lbp: ("; (*it)["lbp"] >> lbpval; //直接读出一维向量 for( int i = 0; i < (int)lbpval.size(); i++ ) cout << " " << (int)lbpval[i]; cout << ")" << endl; } fs.release();
另外,注意在新建FileStorage对象之后,并以READ或WRITE模式打开文件之后,可以用FileStorage::isOpened()查看文件状态,判断是否成功打开了文件。
有关FileStorage类的相关内容引用自:http://www.cnblogs.com/summerRQ/articles/2524560.html
我使用的是opencv2.4.0版本实现的方法,opencv有个欠缺的地方就是版本间的兼容性,虽然做了些工作,但是使用起来还是有些不流畅。不过,值得称赞的是其将OOP的思想应用到库的开发中,很多核心对象和相关操作被封装起来,方便使用。