【重走Android之路】【Java面向对象基础(一)】数据类型与运算符
【重走Android之路】【基础篇(一)】【Java面向对象基础】数据类型与运算符
1、数据类型介绍
在Java中,数据类型分为两种:基本数据类型和引用类型。
基本数据类型共8种,见下表:
| 基本数据类型 | 字节数 | 二进制位数 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 默认值 |
| byte | 1 | 8-bit | -2^7 | +2^7 - 1 | 0 |
| short | 2 | 16-bit | -2^15 | +2^15 - 1 | 0 |
| int | 4 | 32-bit | -2^31 | +2^31 - 1 | 0 |
| long | 8 | 64-bit | -2^63 | +2^63 - 1 | 0 |
| float | 4 | 32-bit | IEEE754 | IEEE754 | 0.0f |
| double | 8 | 64-bit | IEEE754 | IEEE754 | 0.0d |
| char | 2 | 16-bit | \u0000 | \uFFFF | \u0000 |
| boolean | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | false |
| void |
需要指出的是:
- boolean这个类型比较特殊,Javadoc中这样描述:
-
boolean: The
booleandata type has only two possible values:trueandfalse. Use this data type for simple flags that track true/false conditions. This data type represents one bit of information, but its "size" isn't something that's precisely defined.
即:boolean类型只有两个值:true和false。使用这个类型来作为true/false分支的简单标识。这个类型只包含一个bit的信息,但是其所占空间并未精确定义 -
- void 也被放在了表中,但其实它不属于基本数据类型,准确的说它是伪类型,是一种无返回值类型。具体不必深究。
- 引用类型默认值为null。
- String作为参数传递时和其他引用类型不一样,即只传字符串值而非引用地址。
2、两种数据类型的区别
从以下三个方面分别对这两种数据类型进行对比:含义、处理、赋值。
2.1 含义
基本数据类型,其变量代表的是一个具体的值,可以是一个字符、一个数字或者一个布尔值等。
引用数据类型,其变量代表的是一个内存地址,该地址指向一块内存空间,在内存空间内存储着该变量所对应的一个或者一组值。
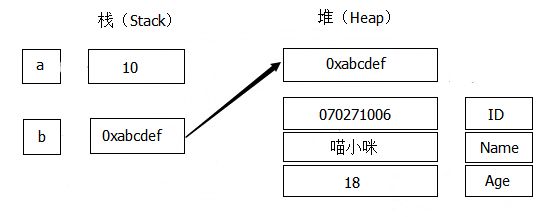
在Java中,基本数据类型的值和引用数据类型的地址信息是放在栈(Stack)中的,引用数据类型的值放在堆(Heep)中。例:
1 class Student { 2 String ID; 3 String Name; 4 int Age; 5 public Student(String id, String name, int age) { 6 ID = id; 7 Name = name; 8 Age = age; 9 } 10 } 11 12 int a = 10; 13 Student b = new Student("070271006", "喵小咪", 18);
上述变量的堆栈对应情况如下图:
2.2 处理
基本数据类型在声明的同时已经赋予空间,所以可以直接操作。例如:
1 int a = 10; 2 int b = a + 20;
一般情况下,引用类型在声明的时候,只是创建了一个变量,其具体的空间并没有分配。需要使用关键字new来开辟空间存储数据。
例如:
1 Student student = null; // 此时只是声明了一个Student变量 2 // student.toString(); // 这时候使用该变量访问就会出错:该行会报空指针异常 3 student = new Student("070271006", "喵小咪", 18);// 此时会告知JVM开辟空间存储数据
上述两行代码的空间分配JVM是这样处理的:
- 在栈中创建一个名为student的变量,其变量值为空;
- 在堆中为Student开辟一块空间,并分别为ID、Name、Age三个成员变量设置默认值;
- 根据Student构造方法的定义,为三个成员变量分别赋值:"070271006", "喵小咪", 18
- 把Student对象在堆中的地址赋值给栈中的student变量。
经过上述流程,student就可以访问堆中的成员变量。
还有一种比较特殊的情况,就是String类型的使用,其详细分析见下篇文章。
2.3 赋值
基本数据类型的赋值操作确实是实际意义上的“赋值”,比如:
1 int a = 10; 2 int b = a; // 此时,b的值就是10 3 // 如果修改a的值,b的值不会发生变化。 4 a = 100; // 此时a的值是100,b的值还是10
一般情况下,引用类型的赋值传递的是堆内存地址,例如:
1 Student stuMiao = new Student("070271006", "喵小咪", 18); 2 Student stuNodin = stuMiao;
上述赋值操作并没有新创建对象,而是在栈中声明了一个名为stuNodin的变量,其变量值和stuMiao这个变量的值相同,都是指向Student这个对象的堆内存的地址。形象的比喻,就像是同一个人的两个名字一样。
如果修改stuMiao这个引用对应的数据,则stuNodin这个引用的数据会同时发生改变。
1 stuMiao.Age = 16; // 此时,stuMiao.Age 等于 16;stuNodin.Age 等于 16;
同样地,String作为一种特殊类型,仍然不适用上述规则。详见下篇文章。
3、运算符
这里只提供Java中的运算符总览,不再赘述,详见下表:
| 算数运算符 | +,-,×,/,%取余 ,++,--,- 取反 |
| 关系运算符 | >,<,>=,<=,!=,== |
| 逻辑运算符 | !非, &与,|或,^异或,&& 短路与,|| 短路或 |
| 按位运算符 | ~按位取反, &按位与, |按位或, ^按位异或 |
| 移位运算符 | << 左移 ,>>带符号右移, >>>不带符号右移 |
| 三目条件运算符 | D=表达式1?表达式2 :表达式3 |
| 赋值运算符 | = ,+=,-= |
4、循环
Java中基本的循环有两种,即for循环和do-while循环,这里不再赘述。
从J2SE 1.5开始,Java引入了一种for的变型循环:foreach循环。并不是说foreach是类似for的关键字,而是便于理解起的一个名字,其作用就是“Each(逐个)”遍历。基本结构基于for循环,详细如下:
1 for (元素类型t 元素变量 x : 遍历对象list) { 2 引用了x的java语句; 3 }
foreach是一种for的简化版本,主要用于数组和集合的简单遍历操作。但是其也有局限性,其只提供遍历功能,不能进行删除、替换等操作,对于需要记录并使用索引的循环,foreach本身也无法实现(可以自己记录实现)。所以无法替代for循环,但是都可以转换为对应的for循环。
1 // 实例一,遍历数组: 2 int[] arrays = new int[] {1, 2, 3}; 3 for (int i : arrays) { 4 System.out.println(i); 5 } 6 7 //实例二,遍历集合: 8 List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); 9 for (String item : list) { 10 System.out.println(item); 11 }
【Nodin's Tips】
本篇主要介绍了Java中的数据类型、运算符和循环,这些都是Java非常基础的知识。但是越是基础的知识越不可小视,俗话说“千里之堤毁于蚁穴”,基础掌握不好难成大器。在基础讲解的同时,对两种数据类型的区别进行了较为详细的分析,是对数据类型的进一步认知,也为我们下篇文章对String进行更详细的分析打下基础。
本文系Nodin原创,转载请注明出处!http://www.cnblogs.com/monodin/p/3841185.html