AtomicLong简介及其用法
1. 什么是AtomicLong?
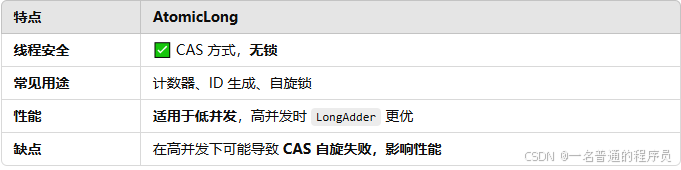
AtomicLong是java并发包(java.util.concurrent.atomic)中的一个类,用于在多线程环境下对long类型变量进行原子操作。它提供了线程安全的更新操作,避免了显示锁的使用,适合在高并发的场景下使用。
特点:
原子性:支持原子性递增、递减、修改,所有操作都是原子的,线程安全。
无锁:基于CAS(Compare-And-Swap)实现,性能优于锁机制,比synchronized更高效
可见性:保证变量的修改对所有线程可见。
适用于高并发场景,如计数器,唯一id的生成。
2. 常用方法
2.1 构造方法
AtomicLong():初始值为0
AtomicLong(long initialValue):指定初始值
2.2 常用方法
long get(): 获取当前值。
void set(long newValue): 设置新值。
long getAndSet(long newValue): 获取当前值并设置新值。
boolean compareAndSet(long expect ,long update): 如果当前值等于expect,则更新为update,成功返回true。
long getAndIncrement(): 获取当前值并自增1。
long getAndDecrement(): 获取当前值并自减1。
long getAndAdd(long delta): 获取当前值并加上delta。
long incrementAndGet(): 自增1并返回新值。
long decrementAndGet(): 自减1并返回新值。
long addAndGet(long delta): 加上delta并返回新值。
示例:
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
public class AtomicLongExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建 AtomicLong 实例,初始值为 0
AtomicLong atomicLong = new AtomicLong(0);
// 获取当前值
System.out.println("Initial Value: " + atomicLong.get()); // 输出: 0
// 设置新值
atomicLong.set(10);
System.out.println("After set(10): " + atomicLong.get()); // 输出: 10
// 获取当前值并自增
long oldValue = atomicLong.getAndIncrement();
System.out.println("getAndIncrement(): " + oldValue); // 输出: 10
System.out.println("After getAndIncrement(): " + atomicLong.get()); // 输出: 11
// 自增并获取新值
long newValue = atomicLong.incrementAndGet();
System.out.println("incrementAndGet(): " + newValue); // 输出: 12
// 比较并设置
boolean success = atomicLong.compareAndSet(12, 20);
System.out.println("compareAndSet(12, 20): " + success); // 输出: true
System.out.println("After compareAndSet: " + atomicLong.get()); // 输出: 20
// 获取当前值并加上 delta
long result = atomicLong.getAndAdd(5);
System.out.println("getAndAdd(5): " + result); // 输出: 20
System.out.println("After getAndAdd(5): " + atomicLong.get()); // 输出: 25
}
}3. AtomicLong 在多线程环境下的应用
3.1 计数器
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
public class AtomicCounter {
private final AtomicLong counter = new AtomicLong(0);
public void increment() {
counter.incrementAndGet();
}
public long getCount() {
return counter.get();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicCounter counter = new AtomicCounter();
// 模拟 1000 个线程并发自增
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
new Thread(counter::increment).start();
}
// 等待线程执行完(实际应用中应使用 CountDownLatch)
try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) {}
System.out.println("最终计数值: " + counter.getCount());
}
}
优势:无需 synchronized,避免锁竞争,提高性能
3.2 生成全局唯一ID
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
public class UniqueIDGenerator {
private static final AtomicLong ID_GENERATOR = new AtomicLong(1000);
public static long getNextId() {
return ID_GENERATOR.incrementAndGet();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("生成 ID: " + getNextId());
System.out.println("生成 ID: " + getNextId());
}
}
适用场景:订单号、日志 ID、数据库主键 生成等
3.3 CAS 自旋锁(避免 synchronized 造成的阻塞)
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
public class SpinLock {
private final AtomicLong lock = new AtomicLong(0);
public void lock() {
while (!lock.compareAndSet(0, 1)) {
// 自旋等待
}
}
public void unlock() {
lock.set(0);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpinLock spinLock = new SpinLock();
new Thread(() -> {
spinLock.lock();
System.out.println("线程 1 获取锁");
try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) {}
spinLock.unlock();
System.out.println("线程 1 释放锁");
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
spinLock.lock();
System.out.println("线程 2 获取锁");
spinLock.unlock();
}).start();
}
}
原理:通过 compareAndSet(0, 1) 方式,实现 非阻塞自旋锁。
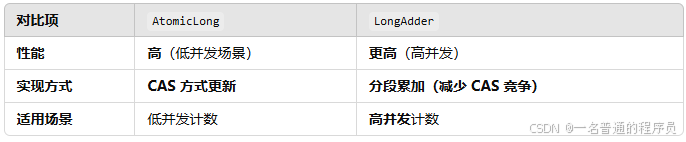
3.4 AtomicLong vs. LongAdder
在高并发情况下,AtomicLong 可能会成为性能瓶颈,可以考虑 LongAdder(Java 8 引入)。
LongAdder 示例:
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAdder;
public class LongAdderExample {
private static final LongAdder counter = new LongAdder();
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
new Thread(counter::increment).start();
}
try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) {}
System.out.println("最终计数值: " + counter.sum());
}
}
LongAdder 更适合高并发场景(如 Web 请求统计)。
5. 总结
- 低并发(如单个计数器)✅ 选
AtomicLong - 高并发(如大规模计数统计)✅ 选
LongAdder - 涉及复杂修改逻辑 ✅
AtomicLong.updateAndGet(x -> x * 2)