数据结构~AVL树
文章目录
-
- 一、AVL树的概念
- 二、AVL树的定义
- 三、AVL树的插入
- 四、AVL树的平衡
- 五、AVL树的验证
- 六、AVL树的删除
- 七、完整代码
- 八、总结
一、AVL树的概念
- AVL树是最先发明的自平衡二叉查找树,AVL是⼀颗空树,或者具备下列性质的二叉搜索树:它的左右子树都是AV树,且左右子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。AVL树是⼀颗高度平衡搜索二叉树,通过控制高度差去控制平衡。
- AVL树得名于它的发明者G. M. Adelson-Velsky和E. M. Landis是两个前苏联的科学家,他们在1962年的论文《An algorithm for the organization of information》中发表了它。
- AVL树实现这里引入⼀个平衡因子(balance factor)的概念,每个结点都有⼀个平衡因子,任何结点的平衡因子等于右子树的高度减去左子树的高度,也就是说任何结点的平衡因子等于0/1/-1,AVL树并不是必须要平衡因子,但是有了平衡因子可以更方便去进行观察和控制树是否平衡,就像⼀个风向标⼀样。
- 为什么AVL树是高度平衡搜索⼆叉树,要求高度差不超过1,而不是高度差是0呢 0不是更好的平衡吗?画画图分析发现,不是不想这样设计,而是有些情况是做不到高度差是0的。比如⼀棵树是2个结点,4个结点等情况下,高度差最好就是1,无法作为高度差是0
- AVL树整体结点数量和分布和完全二叉树类似,高度可以控制在logN ,那么增删查改的效率也可以控制在O(logN) ,相比二叉搜索树有了本质的提升。
二、AVL树的定义
定义了一个 AVL 树的数据结构。它包含了一个结构体AVLTreeNode和一个AVLTree。
- AVLTreeNode结构体:
成员变量:
_kv:存储键值对的数据成员,类型为pair
_left、_right和_parent:分别指向左子树、右子树和父节点的指针。
_bf:表示平衡因子,用于判断树的平衡性。
构造函数:接受一个pair
- AVLTree类:
成员变量:
_root:指向 AVL 树的根节点的指针。
公有接口:代码中省略了公有接口的具体实现,但通常会包含插入、删除、查找等操作的函数声明。
私有成员:仅包含根节点指针_root。
template<class K, class V>
struct AVLTreeNode
{
// 需要parent指针,后续更新平衡因⼦可以看到
pair<K, V> _kv;
AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;
int _bf; // balance factor
AVLTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
:_kv(kv)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _bf(0)
{}
};
template<class K, class V>
class AVLTree
{
typedef AVLTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
//...
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
pair
pair在C++map里面讲过:map
pair可以将两个数据组成一组元素,因此对于key/value模型这种需要用到两个数据为一组的元素时就可以使用,内部的成员变量为first和second,其主要使用方法为:
pair<T1, T2> p1(v1, v2); //输入两个数据创建pair类型变量
make_pair(v1, v2); //输入两个数据通过函数创建pair类型变量
p1.first //访问p1的第一个数据
p1.second //访问p1的第二个数据
三、AVL树的插入
AVL树插入一个值的过程
- 插入一个值按⼆叉搜索树规则进行插入。
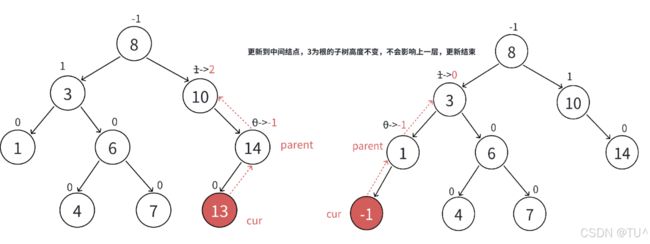
- 新增结点以后,只会影响祖先结点的高度,也就是可能会影响部分祖先结点的平衡因子,所以更新从新增结点->根结点路径上的平衡因子,实际中最坏情况下要更新到根,有些情况更新到中间就可以停止了,具体情况下面再详细分析。
- 更新平衡因子过程中没有出现问题,则插入结束
- 更新平衡因子过程中出现不平衡,对不平衡子树旋转,旋转后本质调平衡的同时,本质降低了子树的高度,不会再影响上⼀层,所以插入结束。
平衡因子更新
- 平衡因子=右子树高度-左子树高度
- 只有子树高度变化才会影响当前结点平衡因子。
- 插入结点,会增加高度,所以新增结点在parent的右子树,parent的平衡因子++,新增结点在parent的左子树,parent平衡因子- -
- parent所在子树的高度是否变化决定了是否会继续往上更新
更新停止条件
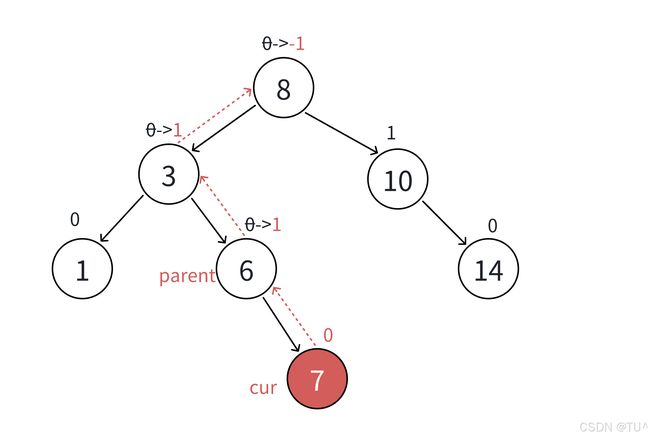
- 更新后parent的平衡因子等于0,更新中parent的平衡因子变化为-1->0或者1->0,说明更新前parent子树⼀边高⼀边低,新增的结点插入在低的那边,插入后parent所在的子树高度不变,不会影响parent的父亲结点的平衡因子,更新结束。
- 更新后parent的平衡因子等于1或-1,更新前更新中parent的平衡因子变化为0->1或者0->-1,说明更新前parent子树两边⼀样高,新增的插入结点后,parent所在的子树⼀边高⼀边低,parent所在的子树符合平衡要求,但是高度增加了1,会影响arent的父亲结点的平衡因子,所以要继续向上更新。
- 更新后parent的平衡因子等于2或-2,更新前更新中parent的平衡因子变化为1->2或者-1->-2,说明更新前parent子树⼀边高⼀边低,新增的插入结点在高的那边,parent所在的子树高的那边更高了,破坏了平衡,parent所在的子树不符合平衡要求,需要旋转处理,旋转的目标有两个:1、把parent子树旋转平衡。2、降低parent子树的⾼度,恢复到插⼊结点以前的高度。所以旋转后也不需要继续往上更新,插⼊结束。
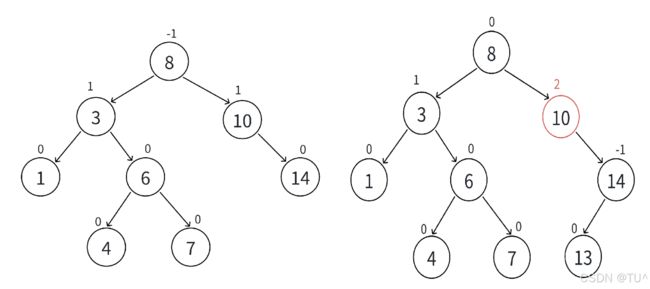
更新到10结点,平衡因子为2,10所在的子树已经不平衡,需要旋转处理
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kv.first > cur->_kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kv.first < cur->_kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(kv);
if (parent->_kv.first > cur->_kv.first)
parent->_right = cur;
else
parent->_left = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
while (parent)
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
parent->_bf--;
else
parent->_bf++;
if (parent->_bf == 0)
{
break;
}
else if (parent->_bf == 1 || parent->_bf == -1)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 || parent->_bf == -2)
{
if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == -1)
{
RotateR(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == 1)
{
RotateL(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == 1)
{
RotateLR(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == -1)
{
RotateRL(parent);
}
else
{
assert(false);
}
}
else
{
assert(false);
}
}
return true;
}
四、AVL树的平衡
旋转
旋转的原则
1.保持搜索树的规则
2. 让旋转的树从不满足变平衡,其次降低旋转树的高度
旋转总共分为四种,左单旋/右单旋/左右双旋/右左双旋。
说明:下面的图中,有些结点我们给的是具体值,如10和5等结点,这里是为了讲解,实际中是什么值都可以,只要大小关系符合搜索树的规则即可。
右单旋
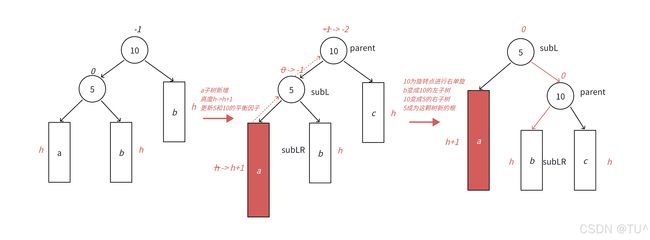
- 下面图展示的是10为根的树,有a/b/c抽象为三棵高度为h的子树(h>=0),a/b/c均符合AVL树的要求。10可能是整棵树的根,也可能是⼀个整棵树中局部的子树的根。这里a/b/c是高度为h的子树,是⼀种概括抽象表示,他代表了所有右单旋的场景,实际右单旋形态有很多种
- 在a子树中插入⼀个新结点,导致a子树的高度从h变成h+1,不断向上更新平衡因子,导致10的平衡因子从-1变成-2,10为根的树左右高度差超过1,违反平衡规则。10为根的树左边太高了,需要往右边旋转,控制两棵树的平衡。
- 旋转核心步骤,因为5
右单旋代码实现
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
Node* pParent = parent->_parent;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = subL;
subL->_parent == nullptr;
}
else
{
if (pParent->_left == parent)
{
pParent->_left = subL;
}
else
{
pParent->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = parent;
}
subL->_bf = 0;
parent->_bf = 0;
}
左单旋
本图展示的是10为根的树,有a/b/c抽象为三棵高度为h的子树(h>=0),a/b/c均符合AVL树的要求。10可能是整棵树的根,也可能是⼀个整棵树中局部的子树的根。这里a/b/c是高度为h的子树,是⼀种概括抽象表示,他代表了所有右单旋的场景,实际右单旋形态有很多种,具体跟上面左旋类似。
• 在a子树中插入⼀个新结点,导致a子树的高度从h变成h+1,不断向上更新平衡因子,导致10的平衡因子从1变成2,10为根的树左右高度差超过1,违反平衡规则。10为根的树右边太高了,需要往左边旋转,控制两棵树的平衡。
• 旋转核心步骤,因为10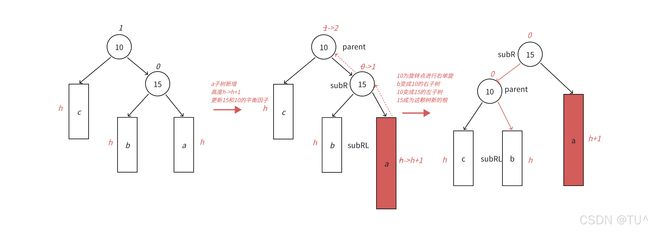
左单旋代码实现
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
Node* pParent = parent->_parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (_root == parent)
{
_root = subR;
subR->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (pParent->_left == parent)
pParent->_left = subR;
else
pParent->_right = subR;
subR->_parent = parent;
}
parent->_bf = 0;
subR->_bf = 0;
}
左右双旋
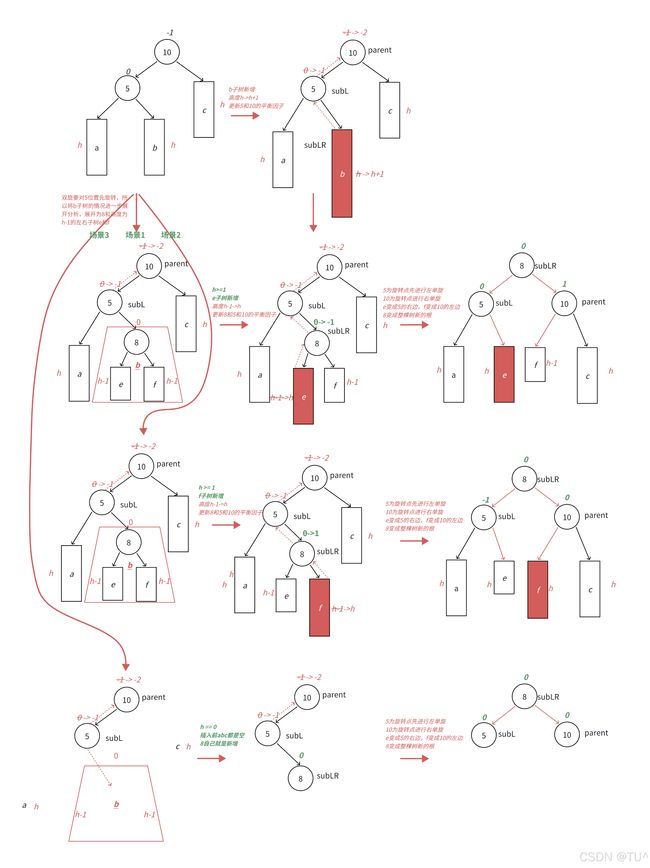
通过图情况1和图情况2可以看到,左边高时,如果插入位置不是在a子树,而是插入在b子树,b子树高度从h变成h+1,引发旋转,右单旋无法解决问题,右单旋后,我们的树依旧不平衡。右单旋解决的纯粹的左边高,但是插入在b子树中,10为跟的⼦树不再是单纯的左边高,对于10是左边高,但是对于5是右边高,需要用两次旋转才能解决,以5为旋转点进行⼀个左单旋,以10为旋转点进行⼀个右单旋,这棵树这棵树就平衡了。
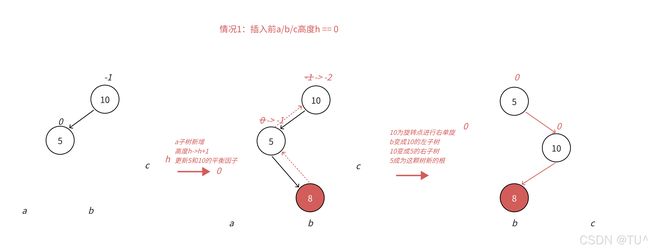
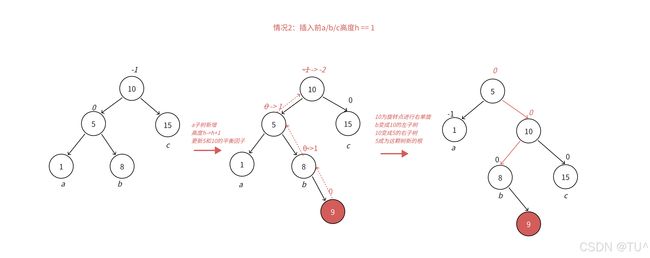
图情况1和图情况2分别为左右双旋中hc = =0和h= =1具体场景分析,下⾯我们将a/b/c子树抽象为高度h的AVL子树进行分析,另外我们需要把b子树的细节进⼀步展开为8和左子树高度为h-1的e和f子树,因为我们要对b的父亲5为旋转点进行左单旋,左单旋需要动b树中的左子树。b子树中新增结点的位置不同,平衡因子更新的细节也不同,通过观察8的平衡因子不同,这里我们要分三个场景讨论。
场景1:h>=1时,新增结点插入在e子树,子树高度从h-1并为h并不断更新8->5->10平衡因子,引发旋转,其中8的平衡因⼦为-1,旋转后8和5平衡因子为0,10平衡因子为1。
场景2:h>=1时,新增结点插⼊在f子树,f子树高度从h-1变为h并不断更新8->5->10平衡因子,引发旋转,其中8的平衡因⼦为1,旋转后8和10平衡因⼦为0,5平衡因子为-1。
场景3:h==0时,a/b/c都是空树,b自己就是⼀个新增结点,不断更新5->10平衡因子,引发旋转,其中8的平衡因⼦为0,旋转后8和10和5平衡因⼦均为0。
左右双旋代码实现
void RotateLR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
int bf = subLR->_bf;
RotateL(parent->_left);
RotateR(parent);
if (bf == -1)
{
subL->_bf = 0;
subLR->_bf = 0;
parent->_bf = 1;
}
else if (bf == 1)
{
subL->_bf = 0;
subLR->_bf = -1;
parent->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == 0)
{
subL->_bf = 0;
subLR->_bf = 0;
parent->_bf = 0;
}
else
{
assert(false);
}
}
右左双旋
跟左右双旋类似,下面将a/b/c⼦树抽象为高度h的AVL子树进行分析,另外我们需要把b子树的细节进⼀步展开为12和左⼦树高度为h-1的e和f子树,因为我们要对b的父亲15为旋转点进行右单旋,右单旋需要动b树中的右⼦树。b⼦树中新增结点的位置不同,平衡因子更新的细节也不同,通
过观察12的平衡因子不同,这里要分三个场景讨论。
• 场景1:h>=1时,新增结点入在e子树,e子树高度从h-1变为h并不断更新12->15->10平衡因子,引发旋转,其中12的平衡因子为-1,旋转后10和12平衡因子为0,15平衡因⼦为1。
• 场景2:h>=1时,新增结点插入在f子树,f子树高度从h-1变为h并不断更新12->15->10平衡因子,引发旋转,其中12的平衡因子为1,旋转后15和12平衡因⼦为0,10平衡因子为-1。
• 场景3:h= =0时,a/b/c都是空树,b自己就是⼀个新增结点,不断更新15->10平衡因子,引发旋转,其中12的平衡因子为0,旋转后10和12和15平衡因子均为0。
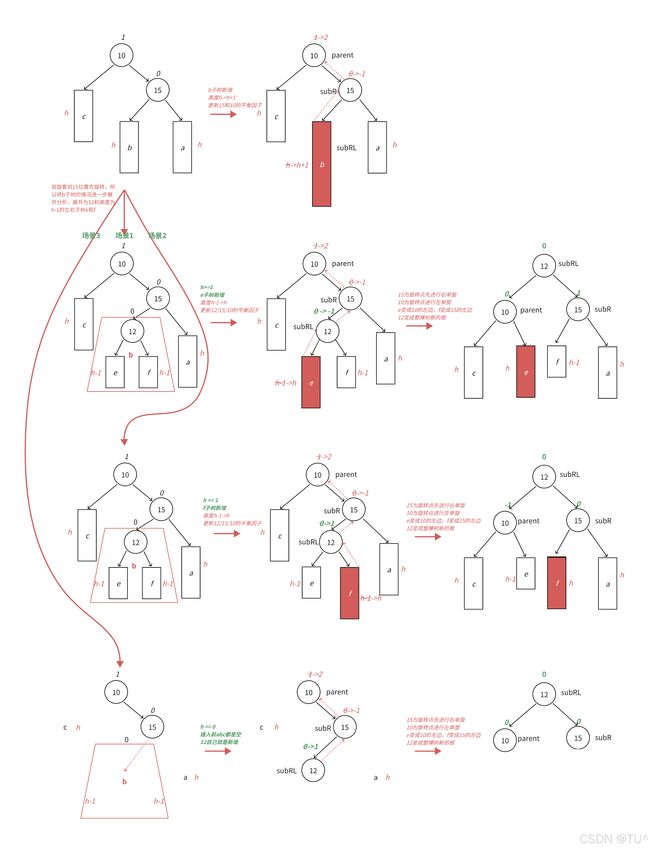
右左双旋代码实现
void RotateRL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
int bf = subRL->_bf;
RotateR(parent->_right);
RotateL(parent);
if (bf == 1)
{
subR->_bf = 0;
subRL->bf = 0;
parent->_bf = -1;
}
else if (bf == -1)
{
subR->_bf = 1;
subRL->bf = 0;
parent->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == 0)
{
subR->_bf = 0;
subRL->bf = 0;
parent->_bf = 0;
}
else
{
assert(false);
}
}
五、AVL树的验证
AVL树是否合格,我们通过检查左右子树高度差的的程序进行反向验证,同时检查⼀下结点的平衡因子更新是否出现了问题。
int _Height(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return 0;
}
int Heightleft = _Height(root->_left);
int Heightright = _Height(root->_right);
return Heightleft > Heightright ? Heightleft + 1 : Heightright + 1;
}
bool _IsBalanceTree(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return true;
int leftHeight = _Height(root->_left);
int rightHeight = _Height(root->_right);
int diff = rightHeight - leftHeight;
if (abs(diff) >= 2)
{
cout << "平衡因子异常:高度异常" << root->_kv.first << endl;
return false;
}
if (root->_bf != diff)
{
cout << "平衡因子异常:高度异常" << root->_kv.first << endl;
return false;
}
return _IsBalanceTree(root->_left) && _IsBalanceTree(root->_right);
}
_Height函数用于计算以给定节点为根的子树的高度。如果节点为空指针,则返回 0。否则,递归地计算左子树和右子树的高度,然后选择较大的子树高度加 1 作为当前子树的高度。
_IsBalanceTree函数用于判断以给定节点为根的子树是否为平衡树。如果节点为空指针,则返回true,表示空树是平衡树。对于非空节点,首先计算左子树和右子树的高度,然后计算它们的高度差。如果高度差大于等于 2,则说明该节点的子树不平衡,输出错误信息并返回false。接着,检查当前节点的平衡因子是否与计算得到的高度差一致,如果不一致,也输出错误信息并返回false。最后,递归地判断左子树和右子树是否为平衡树,只有当左右子树都为平衡树时,才返回true。
六、AVL树的删除
- 首先调用Find函数找到要删除的节点delNode。如果找不到指定的键值,则直接返回。
- 确定替换节点replaceNode:
如果delNode的左子树或右子树为空,那么delNode本身就是替换节点。
如果delNode有两个子树,那么找到delNode的后继节点作为替换节点。 - 确定替换节点的子节点child:
如果replaceNode的左子树不为空,那么child就是replaceNode的左子树。
否则,child就是replaceNode的右子树。 - 更新child的父指针:
如果child不为空,将其父指针设置为replaceNode的父节点。 - 更新树的结构:
如果replaceNode是根节点,那么将root指向child。
如果replaceNode是其父节点的左子树,那么将其父节点的左子树设置为child。
否则,将其父节点的右子树设置为child。 - 如果replaceNode不等于delNode,则将delNode的值更新为replaceNode的值。
- 从树中删除replaceNode,并释放其内存。
- 从replaceNode的父节点开始,向上遍历树,更新每个节点的平衡因子,并进行必要的旋转操作来保持树的平衡:
如果当前节点的平衡因子为 1 或 -1,继续向上遍历。
如果平衡因子为 0,结束遍历。
如果平衡因子为 2 或 -2,根据子树的情况进行相应的旋转操作。
void Remove(const K& key)
{
Node* delNode = Find(key);
if (delNode == nullptr)
return;
Node* replaceNode = nullptr;
if (delNode->_left == nullptr || delNode->_right == nullptr)
replaceNode = delNode;
else
{
replaceNode = GetSuccessor(delNode);
}
Node* child = nullptr;
if (replaceNode->_left != nullptr)
child = replaceNode->_left;
else
child = replaceNode->_right;
if (child != nullptr)
child->_parent = replaceNode->_parent;
if (replaceNode->_parent == nullptr)
_root = child;
else if (replaceNode == replaceNode->_parent->_left)
replaceNode->_parent->_left = child;
else
replaceNode->_parent->_right = child;
if (replaceNode != delNode)
delNode->_kv = replaceNode->_kv;
Node* parent = replaceNode->_parent;
while (parent)
{
if (replaceNode == parent->_left)
parent->_bf++;
else
parent->_bf--;
if (parent->_bf == 1 || parent->_bf == -1)
{
replaceNode = parent;
parent = replaceNode->_parent;
}
else if (parent->_bf == 0)
{
break;
}
else
{
if (parent->_bf == 2)
{
if (parent->_left->_bf >= 0)
{
RotateL(parent);
}
else
{
RotateLR(parent);
}
}
else
{
if (parent->_right->_bf <= 0)
{
RotateR(parent);
}
else
{
RotateRL(parent);
}
}
if (parent->_parent == nullptr)
_root = parent;
else
parent = parent->_parent;
}
}
delete replaceNode;
}
实现了从 AVL 树中删除指定键值的节点的功能。它通过一系列的操作来保持 AVL 树的平衡性质,包括找到要删除的节点、确定替换节点、调整树的结构以及更新平衡因子和进行必要的旋转操作。
注意事项
在进行旋转操作时,需要正确地更新节点的指针和平衡因子,以确保树的结构和平衡性质得到正确维护。
七、完整代码
#pragma once
#include八、总结
时间复杂度
- 搜索、插入和删除操作
在 AVL 树中,搜索、插入和删除操作的时间复杂度均为 O (log n),其中 n 为树中节点的个数。这是因为 AVL 树始终保持平衡,树的高度始终保持在 O (log n) 级别,相比于普通二叉搜索树(在最坏情况下可能退化为链表,时间复杂度为 O (n))具有更好的性能。
应用场景
- 数据库索引
AVL 树可用于数据库中的索引结构,能够快速地查找、插入和删除数据记录,提高数据库操作的效率。
有序数据存储与检索
在需要频繁进行查找、插入和删除操作的有序数据集合中,AVL 树是一种高效的数据结构选择,如某些文件系统中用于管理文件索引等。
AVL 树是一种自平衡二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree)。它以发明者 Adelson - Velsky 和 Landis 的名字命名。
对于 AVL 树中的任意节点,其左子树和右子树的高度差(平衡因子)的绝对值不超过1。
二叉搜索树的学习:数据结构~二叉搜索树