Linux: ASoC 声卡硬件参数的设置过程简析
文章目录
- 1. 前言
- 2. ASoC 声卡设备硬件参数
-
- 2.1 将 DAI、Machine 平台的硬件参数添加到声卡
- 2.2 打开 PCM 流时将声卡硬件参数配置到 PCM 流
- 2.3 应用程序对 PCM 流参数进行修改调整
1. 前言
限于作者能力水平,本文可能存在谬误,因此而给读者带来的损失,作者不做任何承诺。
2. ASoC 声卡设备硬件参数
ASoC(ALSA System-on-Chip) 声卡驱动框架如下图所示:
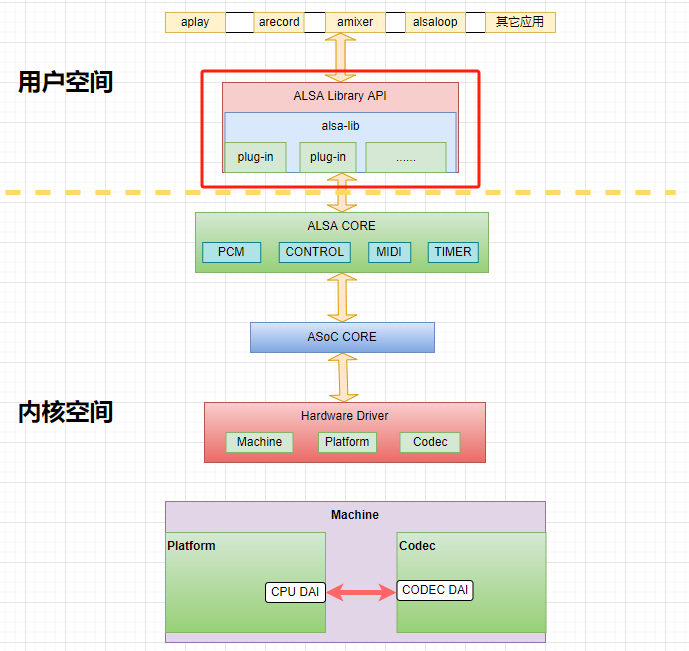
整个声卡驱动由 CPU DAI 驱动、CODEC DAI 驱动、Machine 驱动(胶水粘合驱动) 这 3 者拼接构成,所以声卡硬件参数,自然也同时受这 3 者的共同约束。
声卡的硬件参数管理过程包括以下两步:
1. 将 DAI (CPU 侧 + CODEC 侧)、Machine 平台的 声卡硬件参数 添加到声卡
2. 打开 PCM 流时,将 声卡的硬件参数 配置到 PCM 流
3. 应用程序在硬件参数允许的范围内,对 PCM 流参数进行修改调整
2.1 将 DAI、Machine 平台的硬件参数添加到声卡
声卡硬件参数主要包括:通道数,数据格式(S16_LE,S32_LE,...),采样率,period 大小,FIFO 大小 等。这些声卡硬件参数来自于 DAI 接口驱动、Machine 平台驱动,用数据结构 struct snd_soc_pcm_stream 描述:
/* SoC PCM stream information */
struct snd_soc_pcm_stream {
const char *stream_name;
/* 支持的数据格式。如 S16_LE, ... */
u64 formats; /* SNDRV_PCM_FMTBIT_* */
/* 支持的采样率 */
unsigned int rates; /* SNDRV_PCM_RATE_* */
unsigned int rate_min; /* min rate */
unsigned int rate_max; /* max rate */
/* 支持的最小通道数 */
unsigned int channels_min; /* min channels */
/* 支持的最大通道数 */
unsigned int channels_max; /* max channels */
unsigned int sig_bits; /* number of bits of content */
};
这里以 CPU 侧 DAI 驱动硬件参数为例,来剖析声卡硬件参数的添加过程。如:
static struct snd_soc_dai_driver sun4i_i2s_dai = {
.probe = sun4i_i2s_dai_probe,
.capture = {
.stream_name = "Capture",
.channels_min = 2,
.channels_max = 2,
.rates = SNDRV_PCM_RATE_8000_192000,
.formats = SNDRV_PCM_FMTBIT_S16_LE,
},
.playback = {
.stream_name = "Playback",
.channels_min = 2,
.channels_max = 2,
.rates = SNDRV_PCM_RATE_8000_192000,
.formats = SNDRV_PCM_FMTBIT_S16_LE,
},
.ops = &sun4i_i2s_dai_ops,
.symmetric_rates = 1,
};
上面示例代码中的 capture,playback 为 struct snd_soc_pcm_stream 类型,定义了 SoC CPU 一侧 DAI 接口 I2S 支持的通道数、数据格式、采样率,然后通过接口 snd_soc_register_component() ,将声卡 DAI 组件注册到系统,即添加到声卡组件对象(struct snd_soc_component)全局列表 component_list :
devm_snd_soc_register_component(&pdev->dev,
&sun4i_i2s_component,
&sun4i_i2s_dai, 1)
snd_soc_register_component()
struct snd_soc_component *component;
...
component = kzalloc(sizeof(*component), GFP_KERNEL);
...
ret = snd_soc_component_initialize(component, component_driver, dev);
...
snd_soc_component_add(component)
...
list_add(&component->list, &component_list); /* (1) 添加到声卡组件全局列表 @component_list */
然后在注册声卡时,将声卡组件对象(struct snd_soc_component)添加到声卡(声卡组件对象(struct snd_soc_component)作为声卡的一部分),这一过程也将包含在 DAI 驱动内的 DAI 硬件参数添加到了声卡:
snd_soc_register_card()
snd_soc_instantiate_card()
soc_bind_dai_link()
static int soc_bind_dai_link(struct snd_soc_card *card,
struct snd_soc_dai_link *dai_link)
{
...
/* 集成 CPU 一侧 DAI (驱动) 到声卡 */
rtd->cpu_dai = snd_soc_find_dai(&cpu_dai_component);
snd_soc_rtdcom_add(rtd, rtd->cpu_dai->component);
...
/* Find CODEC from registered CODECs */
codec_dais = rtd->codec_dais;
for (i = 0; i < rtd->num_codecs; i++) { /* 集成 CODEC 一侧 DAI (驱动) 到声卡 */
codec_dais[i] = snd_soc_find_dai(&codecs[i]); // 查找 DAI
...
snd_soc_rtdcom_add(rtd, codec_dais[i]->component); // 添加 DAI 到声卡(包括 DAI 携带的硬件参数)
}
...
}
struct snd_soc_dai *snd_soc_find_dai(
const struct snd_soc_dai_link_component *dlc)
{
...
/* Find CPU DAI from registered DAIs*/
list_for_each_entry(component, &component_list, list) {
// 匹配 DAI
...
list_for_each_entry(dai, &component->dai_list, list) {
...
return dai; // 返回匹配的 DAI
}
}
...
}
static int snd_soc_rtdcom_add(struct snd_soc_pcm_runtime *rtd,
struct snd_soc_component *component)
{
...
list_add_tail(&new_rtdcom->list, &rtd->component_list);
...
}
2.2 打开 PCM 流时将声卡硬件参数配置到 PCM 流
先看一下 PCM 流 DAI 相关的硬件参数的数据结构:
/* include/sound/pcm.h */
struct snd_pcm_substream {
...
struct snd_pcm_runtime *runtime; /* PCM 流运行时参数 */
...
};
/*
* Hardware (lowlevel) section
*/
struct snd_pcm_hardware {
unsigned int info; /* SNDRV_PCM_INFO_* */
u64 formats; /* SNDRV_PCM_FMTBIT_* */
unsigned int rates; /* SNDRV_PCM_RATE_* */
unsigned int rate_min; /* min rate */
unsigned int rate_max; /* max rate */
unsigned int channels_min; /* min channels */
unsigned int channels_max; /* max channels */
size_t buffer_bytes_max; /* max buffer size */
size_t period_bytes_min; /* min period size */
size_t period_bytes_max; /* max period size */
unsigned int periods_min; /* min # of periods */
unsigned int periods_max; /* max # of periods */
size_t fifo_size; /* fifo size in bytes */
};
struct snd_pcm_hw_constraints {
struct snd_mask masks[SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_LAST_MASK -
SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_FIRST_MASK + 1]; /* 掩码类参数 */
struct snd_interval intervals[SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_LAST_INTERVAL -
SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_FIRST_INTERVAL + 1]; /* 区间值类参数 */
unsigned int rules_num; /* 当前约束总条数 */
/*
* 当前 @rules 可容纳的约束总数:
* 一旦当前约束条数 @rules_num 增长到大于当前 @rules 可容纳的
* 调试(即 @rules_num >= @rules_all), 则动态重新分配空间到 @rules,
* 同时也调整 @rules_all 为新空间大小.
*/
unsigned int rules_all;
/*
* snd_pcm_hw_rule_add() 注册的 对参数变量(SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_FORMAT, ...)
* 的 约束规则.
*/
struct snd_pcm_hw_rule *rules;
};
struct snd_pcm_runtime {
...
/* -- hardware description -- */
struct snd_pcm_hardware hw;
/*
* 硬件参数 @hw 分类后的组织形式,分为 mask 类参数约束、区间类参数约束、rule 约束。
* 这也是应用程序初始化 PCM 后,用户空间对硬件参数的读写都是通过 @hw_constraints 。
*/
struct snd_pcm_hw_constraints hw_constraints;
...
};
再来看一下将声卡硬件参数配置到 PCM 流的代码细节:
open("/dev/snd/pcmC%dD%dp", ...)
...
snd_pcm_playback_open() / snd_pcm_capture_open()
snd_pcm_open()
snd_pcm_open_file()
snd_pcm_open_substream()
struct snd_pcm_runtime {
...
struct snd_pcm_hardware hw;
struct snd_pcm_hw_constraints hw_constraints;
...
};
int snd_pcm_open_substream(struct snd_pcm *pcm, int stream,
struct file *file,
struct snd_pcm_substream **rsubstream)
{
...
// 将 DAI 等的硬件参数 配置到 PCM 流
if ((err = substream->ops->open(substream)) < 0) // ASoC 架构下: soc_pcm_open()
goto error;
...
// 将 参数 转换为 约束参数形式
err = snd_pcm_hw_constraints_complete(substream);
...
}
// 将 DAI 等的硬件参数 配置到 PCM 流
soc_pcm_open() // ASoC 架构下
soc_pcm_init_runtime_hw()
static void soc_pcm_init_runtime_hw(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream)
{
struct snd_pcm_runtime *runtime = substream->runtime;
struct snd_pcm_hardware *hw = &runtime->hw;
...
struct snd_soc_pcm_stream *codec_stream;
struct snd_soc_pcm_stream *cpu_stream;
...
// CPU DAI
if (substream->stream == SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK)
cpu_stream = &cpu_dai_drv->playback; // &sun4i_i2s_dai.playback
else
cpu_stream = &cpu_dai_drv->capture; // &sun4i_i2s_dai.capture
...
/* 配置声卡 DAI 的参数到 PCM 流 */
hw->channels_min = max(chan_min, cpu_stream->channels_min);
hw->channels_max = min(chan_max, cpu_stream->channels_max);
if (hw->formats)
hw->formats &= formats & cpu_stream->formats;
else
hw->formats = formats & cpu_stream->formats;
...
}
int snd_pcm_hw_constraints_complete(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream)
{
struct snd_pcm_runtime *runtime = substream->runtime;
struct snd_pcm_hardware *hw = &runtime->hw;
...
...
err = snd_pcm_hw_constraint_mask(runtime, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_ACCESS, mask);
...
err = snd_pcm_hw_constraint_mask64(runtime, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_FORMAT, hw->formats);
...
err = snd_pcm_hw_constraint_minmax(runtime, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_CHANNELS,
hw->channels_min, hw->channels_max);
...
err = snd_pcm_hw_constraint_minmax(runtime, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_PERIODS,
hw->periods_min, hw->periods_max);
...
err = snd_pcm_hw_constraint_minmax(runtime, SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_BUFFER_BYTES,
hw->period_bytes_min, hw->buffer_bytes_max);
...
}
int snd_pcm_hw_constraint_minmax(struct snd_pcm_runtime *runtime, snd_pcm_hw_param_t var,
unsigned int min, unsigned int max)
{
struct snd_pcm_hw_constraints *constrs = &runtime->hw_constraints;
struct snd_interval t;
t.min = min;
t.max = max;
t.openmin = t.openmax = 0;
t.integer = 0;
return snd_interval_refine(constrs_interval(constrs, var), &t);
}
小结一下:
在应用程序通过 `open()` 打开 PCM 流时,将来自 `DAI` 的硬件参数 `struct snd_soc_pcm_stream`
(例子中是 `sun4i_i2s_dai.playback, sun4i_i2s_dai.capture`),配置到了 PCM 运行时数据
`struct snd_pcm_runtime::hw` 和 `struct snd_pcm_runtime::hw_constraints`,之后用户空间
对硬件参数的读写都是和 `snd_pcm_runtime::hw_constraints` 交互。
2.3 应用程序对 PCM 流参数进行修改调整
在 2.2 小节中,在 open("/dev/snd/pcmC%dD%dp", ...) 打开 PCM 流时,设置了 PCM 的默认硬件参数,但这并不一定符合用户的预期,譬如采样率,通道数,数据格式等,这时候用户空间可以通过 ioctl(fd, SNDRV_PCM_IOCTL_HW_PARAMS, &hwparams) 来进行调整:
sys_ioctl()
...
snd_pcm_ioctl()
snd_pcm_common_ioctl()
snd_pcm_hw_params_user()
snd_pcm_hw_params()
static int snd_pcm_hw_params_user(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream,
struct snd_pcm_hw_params __user * _params)
{
struct snd_pcm_hw_params *params;
...
/* 复制用户空间参数到内核空间 */
params = memdup_user(_params, sizeof(*params));
...
/* 按用户请求参数 @_params,对当前设置的参数做可能的调整 */
err = snd_pcm_hw_params(substream, params);
...
/* 修改后的参数,从 @_params 返回用户空间 */
if (copy_to_user(_params, params, sizeof(*params)))
err = -EFAULT;
end:
kfree(params);
return err;
}
static int snd_pcm_hw_params(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream,
struct snd_pcm_hw_params *params)
{
struct snd_pcm_runtime *runtime;
...
params->rmask = ~0U;
err = snd_pcm_hw_refine(substream, params); /* 对 所有 硬件参数,按用户请求参数 @params,做可能的调整 */
...
/* 更新 用户参数 @params 到 PCM 流 */
runtime->access = params_access(params);
runtime->format = params_format(params);
runtime->subformat = params_subformat(params);
runtime->channels = params_channels(params);
runtime->rate = params_rate(params);
runtime->period_size = params_period_size(params);
runtime->periods = params_periods(params);
runtime->buffer_size = params_buffer_size(params);
runtime->info = params->info;
runtime->rate_num = params->rate_num;
runtime->rate_den = params->rate_den;
...
return 0;
_error:
...
}
int snd_pcm_hw_refine(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream,
struct snd_pcm_hw_params *params)
{
...
/* 对所有 掩码类型参数 做可能的调整 */
err = constrain_mask_params(substream, params);
...
/* 对所有 区间类型参数 做可能的调整 */
err = constrain_interval_params(substream, params);
...
/* 对 所有类型(掩码类 + 区间类) 的所有参数 按 约束规则 做可能的调整 */
err = constrain_params_by_rules(substream, params);
...
}
这里只看 constrain_interval_params() 的调整参数的过程,其它的类似:
static int constrain_interval_params(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream,
struct snd_pcm_hw_params *params)
{
// 这里的 ,正是前面 2.2 分析 PCM 打开过程中, snd_pcm_hw_constraint_minmax() 设置的
struct snd_pcm_hw_constraints *constrs =
&substream->runtime->hw_constraints;
struct snd_interval *i;
unsigned int k;
...
for (k = SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_FIRST_INTERVAL; k <= SNDRV_PCM_HW_PARAM_LAST_INTERVAL; k++) {
i = hw_param_interval(params, k);
...
/* 对区间类型参数做可能的调整 */
changed = snd_interval_refine(i, constrs_interval(constrs, k));
...
}
return 0;
}
到此,对声卡硬件参数管理设置过程分析已毕。可以看到,一如前面 2.2 小结的那样,ioctl(SNDRV_PCM_IOCTL_HW_PARAMS) 是和 snd_pcm_runtime::hw_constraints 交互,影响 PCM 运行时如下所示的硬件参数:
struct snd_pcm_runtime {
...
/* -- HW params -- */
snd_pcm_access_t access; /* access mode: SNDRV_PCM_ACCESS_RW_INTERLEAVED, ... */
snd_pcm_format_t format; /* SNDRV_PCM_FORMAT_*: SNDRV_PCM_FORMAT_S16_LE, ... */
snd_pcm_subformat_t subformat; /* subformat: SNDRV_PCM_SUBFORMAT_STD, ... */
unsigned int rate; /* rate in Hz */
unsigned int channels; /* channels */
snd_pcm_uframes_t period_size; /* period size */
unsigned int periods; /* periods */
snd_pcm_uframes_t buffer_size; /* buffer size */
snd_pcm_uframes_t min_align; /* Min alignment for the format */
size_t byte_align;
unsigned int frame_bits;
unsigned int sample_bits;
unsigned int info;
unsigned int rate_num;
unsigned int rate_den;
...
/* -- hardware description -- */
//struct snd_pcm_hardware hw;
/*
* 硬件参数 @hw 分类后的组织形式,分为 mask 类参数约束、区间类参数约束、rule 约束。
* 这也是应用程序初始化 PCM 后,用户空间对硬件参数的读写都是通过 @hw_constraints 。
*/
struct snd_pcm_hw_constraints hw_constraints;
...
};
对应硬件参数,声卡还有软件参数,对这部分感兴趣的读者,可自行阅读相关源码。