C/C++算法编程竞赛标准模板库(STL)篇:队列(queue)
目录
前言
这个栏目是对我算法学习过程的同步记录,我也希望能够通过这个专栏加深自己对编程的理解以及帮助到更多像我一样想从零学习算法并参加竞赛的同学。在这个专栏的文章中我会结合在编程过程中遇到的各种问题并提出相应的解决方案。当然,如果屏幕前的你有更好的想法或者发现的错误也欢迎交流和指出!不喜勿喷!不喜勿喷!不喜勿喷!这章的内容非常重要!!那么事不宜迟,我们马上开始吧!
一、queue队列
1.基本介绍
2.queue的常用函数
二、priority_queue优先队列(堆)
1.基本介绍
2.priority_queue的常用函数
3.priority_queue修改比较函数
三、deque双端队列
1.基本介绍
2.deque的常用函数
四、综合练习
1.例题一:lanqiao OJ 1113
2.例题二:lanqiao OJ 741
总结
我也从没想过STL中的queue还有这么多的花样。总而言之,如果你觉得这篇文章还不错,劳烦多多支持一下!码字不易,感谢你的观看!
前言
这个栏目是对我算法学习过程的同步记录,我也希望能够通过这个专栏加深自己对编程的理解以及帮助到更多像我一样想从零学习算法并参加竞赛的同学。在这个专栏的文章中我会结合在编程过程中遇到的各种问题并提出相应的解决方案。当然,如果屏幕前的你有更好的想法或者发现的错误也欢迎交流和指出!不喜勿喷!不喜勿喷!不喜勿喷!这章的内容非常重要!!那么事不宜迟,我们马上开始吧!
一、queue队列
1.基本介绍
queue是一种先进先出(FIFO)的数据结构。queue提供了一组函数来操作和访问元素,但它的功能相对简单。
其中蓝色标识的是双端队列的函数操作,红色标识的是单向队列的函数操作。
queue的定义和结构如下:
template >
class queue; T表示存储在queue中元素的类型。
Container:表示底层容器的类型,默认为deque,也可以使用其他容器类型,如list,queue的内部实现了用底层容器来存储元素,并且只能通过特定的函数来访问和操作元素。
2.queue的常用函数
queue的常用函数表如下所示:
| 函数 | 描述 | 时间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|
| push(x) | 在队尾弹出x | O(1) |
| pop() | 弹出队首元素 | O(1) |
| front() | 返回队首元素 | O(1) |
| back() | 返回队尾元素 | O(1) |
| empty() | 检查队列是否为空 | O(1) |
| size() | 返回队列中元素的个数 | O(1) |
二、priority_queue优先队列(堆)
1.基本介绍
priority_queue与普通的queue不同,其元素是按照一定的优先级进行排序的。默认情况下,priority_queue按照元素的值从大到小进行排序,即最大元素位于队列的前面。
priorty_queue的定义域结构如下,我们仅做了解即可。
template ,
class Compare = less>
class priority_queue; T表示存储在priority_queue中元素的类型。
Container:表示底层容器的类型,默认为vector,也可以使用其他容器类型,如deque。
Compare:表示元素之间的比较函数对象的类型,默认为less,即按照元素的值进行比较。priority_queue的内部实现了用底层容器来存储元素,并且只能通过特定的函数来访问和操作元素。
PS:priority_queue是一个十分重要的数据结构,考察频率极高。
2.priority_queue的常用函数
priority_queue的常用函数表如下所示:
| 函数 | 描述 | 时间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|
| push(x) | 在栈顶推入元素x | O(logN) |
| pop() | 弹出栈顶元素 | O(logN) |
| top() | 返回栈顶元素 | O(1) |
| empty() | 检查栈是否为空 | O(1) |
| size() | 返回栈中元素的个数 | O(1) |
3.priority_queue修改比较函数
(1)通过仿函数修改比较函数,代码如下所示:
#include
using namespace std;
struct Compare
{
//重载()
bool operator()(int a, int b)
{
//自定义的比较函数,按照从小到大(逆序)排列
return a > b;
}
};
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
priority_queue, Compare> pq;
return 0;
} (2)通过lambada表达式(匿名函数)修改比较函数。代码如下所示:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
auto compare = [](int a, int b)
{
return a > b;
};
priority_queue, decltype(compare)> pq(compare);
return 0;
} (3)如果priority_queue中的元素类型较简单,可以直接使用greater
代码如下所示:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
priority_queue, greater>pq;
return 0;
} std::greater函数对象定义在
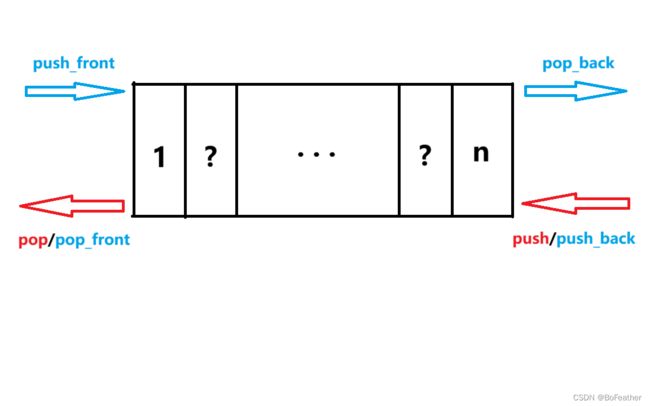
三、deque双端队列
1.基本介绍
deque(双端队列)是一种容器,它允许两端进行高效的插入和删除操作。后续算法中单调队列的实现需要依靠双端队列。单纯考察双端队列的题目并不多见。
2.deque的常用函数
deque(双端队列)的常用函数表如下所示:
| 函数 | 描述 | 时间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|
| push_back(x) | 在尾部插入元素x | 平摊O(1) |
| push_front(x) | 在头部插入元素x | 平摊O(1) |
| pop_back() | 弹出尾部元素 | 平摊O(1) |
| pop_front() | 弹出头部元素 | 平摊O(1) |
| front() | 返回头部元素 | O(1) |
| back() | 返回尾部元素 | O(1) |
| empty() | 检查deque是否为空 | O(1) |
| size() | 返回deque中的元素个数 | O(1) |
| clear() | 清空deque中的所有元素 | O(N) |
| insert(pos, x) | 在pos处插入元素x | 平摊O(N) |
| erase(pos) | 移除指定位置pos处的元素 | 平摊O(N) |
| erase(first, last) | 移除[first,last)范围内的元素 | 平摊O(N) |
PS:做后三个函数基本不会用到,感兴趣的可以自行了解。
四、综合练习
1.例题一:lanqiao OJ 1113
题目链接已给出:https://www.lanqiao.cn/problems/1113/learning/
参考代码如下:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
queueV,N;
int M;cin >> M;
while(M--)
{
string rec, name, channel;cin >> rec;
if(rec == "IN")
{
cin >> name >> channel;
if(channel == "V") V.push(name);
else if(channel == "N") N.push(name);
}
else if(rec == "OUT")
{
cin >> channel;
if(channel == "V")V.pop();
else N.pop();
}
}
while(V.size())
{
cout << V.front() << endl;
V.pop();
}
while(N.size())
{
cout << N.front() << endl;
N.pop();
}
return 0;
} 2.例题二:lanqiao OJ 741
题目链接已经给出:https://www.lanqiao.cn/problems/741/learning/
参考代码如下:
#include
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
priority_queue,greater>pq;
int n;cin >> n;
for(int i=0;i> x;
pq.push(x);
}
ll ans = 0;
while(pq.size()>=2)
{
ll x = pq.top();pq.pop();
ll y = pq.top();pq.pop();
ans += x + y;
pq.push(x + y);
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}