【MySQl】MyISAM和InnoDB索引对比
部分内容转自:http://www.2cto.com/database/201211/172380.html
比较好的文章:http://www.cnblogs.com/hustcat/archive/2009/10/28/1591648.html
MyISAM
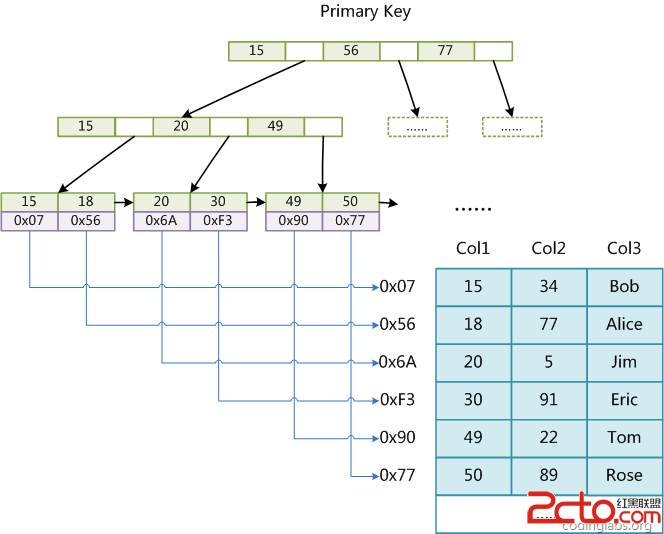
MyISAM引擎使用B+Tree作为索引结构,叶节点的data域存放的是数据记录的地址。下图是MyISAM索引的原理图:
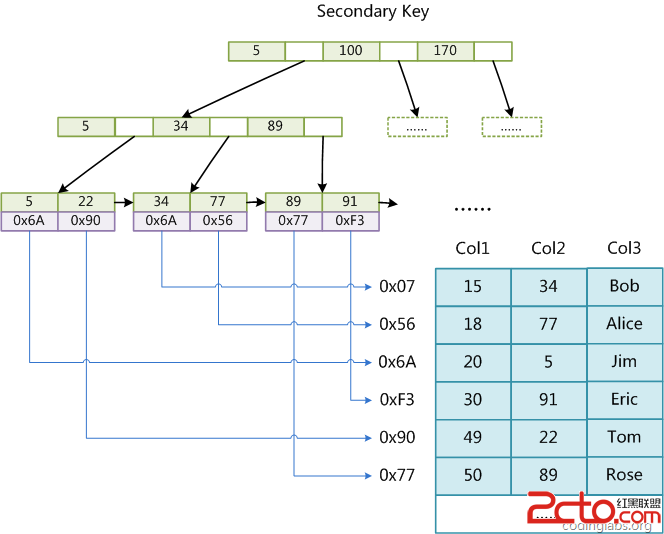
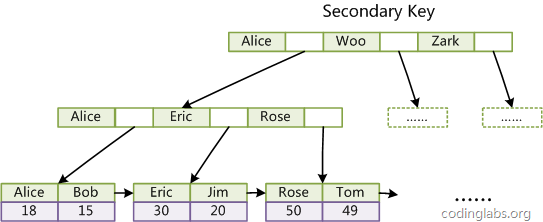
这里设表一共有三列,假设我们以Col1为主键,则上图是一个MyISAM表的主索引(Primary key)示意。可以看出MyISAM的索引文件仅仅保存数据记录的地址。在MyISAM中,主索引和辅助索引(Secondary key)在结构上没有任何区别,只是主索引要求key是唯一的,而辅助索引的key可以重复。如果我们在Col2上建立一个辅助索引,则此索引的结构如下图所示:
InnoDB
mysql> show create table t2; +-------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Table | Create Table | +-------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | t2 | CREATE TABLE `t2` ( `column_a` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `column_b` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `column_c` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `column_d` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL, KEY `index_a_b_c` (`column_a`,`column_b`,`column_c`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 | +-------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> show index from t2 \G *************************** 1. row *************************** Table: t2 Non_unique: 1 Key_name: index_a_b_c Seq_in_index: 1 Column_name: column_a Collation: A Cardinality: 9 Sub_part: NULL Packed: NULL Null: YES Index_type: BTREE Comment: Index_comment: *************************** 2. row *************************** Table: t2 Non_unique: 1 Key_name: index_a_b_c Seq_in_index: 2 Column_name: column_b Collation: A Cardinality: 9 Sub_part: NULL Packed: NULL Null: YES Index_type: BTREE Comment: Index_comment: *************************** 3. row *************************** Table: t2 Non_unique: 1 Key_name: index_a_b_c Seq_in_index: 3 Column_name: column_c Collation: A Cardinality: 9 Sub_part: NULL Packed: NULL Null: YES Index_type: BTREE Comment: Index_comment: 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select count(*) from t2; +----------+ | count(*) | +----------+ | 9 | +----------+ 1 row in set (0.01 sec)
show index语法的说明:
1、Table:索引所在的表名。 2、Non_unique:非唯一的索引,可以看到primary key是0,因为必须是唯一的。 3、Key_name:索引的名称,我们可以通过这个名称来drop index。 4、Seq_in_index:索引中该列的位置,如果看联合索引就比较直观。(例如上面例子) 5、Column_name:索引的列。 6、Collation:列以什么方式存储在索引中。可以是‘A’或者NULL。B+树索引总是A,即排序的。如果使用了Heap存储索引,并且建立了Hash索引,这里就会显示NULL。因为Hash根据Hash桶来存放索引数据,而不是对数据进行排序。 7、Cardinality:非常关键的值,表示索引中唯一值得数目的估计值,优化器会根据这个值来判断查询是否使用这个索引。Cardinality/表的行数的比值应尽可能接近1,如果非常小,那么需要考虑是否还需要建这个索引。这个值不是实时更新的,因为开销会很大,可以通过运行ANALYZE TABLE或myisamchk -a可以更新这个值。 8、Sub_part:是否是列的部分被索引。假设如果看index_a这个索引,这里显示10,表示只索引a列的前10个字符。如果索引整个列,则该字段为NULL。 9、Packed:关键字如何被压缩。如果没有被压缩,则为NULL。 10、Null:是否索引的列含有NULL值。可以看到index_a_b_c这里为YES,因为我们定义的a、b、c列允许NULL值。 11、Index_type:索引的类型。InnoDB存储引擎只支持B+树索引,所以这里显示的都是BTREE。 12、Comment:注释。
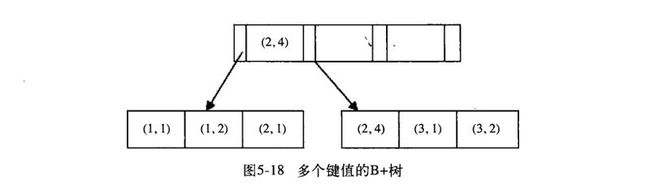
联合索引形象的说明可以比喻成手机中的电话薄,因为联合索引是多个键值的B+树情况,和单列索引的键值顺序排序相同,使用联合索引也是通过叶节点逻辑上的顺序地读出所有数据,比如表中column1和column2要建一个index_1_2,那这个联合索引会先按照column1顺序存放,在column1值相同的数据,再使用coiumn2顺序存放。例如:(1,1),(1,2),(2,1),(2,4),(3,1),(3,2),按照(column1,column2)的顺序进行存放:
mysql> explain select * from t2 where column_a=1 and column_b=2 and column_c=3; +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------------------+------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------------------+------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | ref | index_a_b_c | index_a_b_c | 15 | const,const,const | 1 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------------------+------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from t2 where column_a=1 and column_b=2; +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------------+------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------------+------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | ref | index_a_b_c | index_a_b_c | 10 | const,const | 1 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------------+------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from t2 where column_a=1; +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------+------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------+------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | ref | index_a_b_c | index_a_b_c | 5 | const | 1 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------+------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
另外针对column_a和column_c两列的查询,实际上只是用到了组合索引中的column_a部分:
mysql> explain select * from t2 where column_a=1 and column_c=3; +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------+------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------+------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | ref | index_a_b_c | index_a_b_c | 5 | const | 2 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------+------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
可以看到key_len是5,查询通过索引index_a_b_c的column_a中找到相应column_a=1行的叶子节点逻辑位置区域,但是由于条件column_c无法被使用到索引,遍历了column_a=1的所有行。
所以大家习惯说的联合索引的"最左前缀"的原则,简单的理解就是只从联合索引组合的最左侧的列开始的组合顺序组合。
理解了联合索引机制,什么用不到就更好理解:
mysql> explain select * from t2 where column_b=2 and column_c=3; +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 9 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from t2 where column_b=2; +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 9 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from t2 where column_c=3; +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 9 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)