(pytorch-深度学习)实现稠密连接网络(DenseNet)
稠密连接网络(DenseNet)
ResNet中的跨层连接设计引申出了数个后续工作。稠密连接网络(DenseNet)与ResNet的主要区别在于在跨层连接上的主要区别:
- ResNet使用相加
- DenseNet使用连结
ResNet(左)与DenseNet(右):
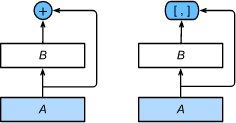
图中将部分前后相邻的运算抽象为模块 A A A和模块 B B B。
- DenseNet里模块 B B B的输出不是像ResNet那样和模块 A A A的输出相加,而是在通道维上连结。
- 这样模块 A A A的输出可以直接传入模块 B B B后面的层。在这个设计里,模块 A A A相当于直接跟模块 B B B后面的所有层直接连接在了一起。这也是它被称为“稠密连接”的原因。
DenseNet的主要构建模块是稠密块(dense block)和过渡层(transition layer)。
- 稠密块定义了输入和输出是如何连结的
- 过渡层用来控制通道数,控制其大小
稠密块
DenseNet使用了ResNet改良版的“批量归一化、激活和卷积”结构:
import time
import torch
from torch import nn, optim
import torch.nn.functional as F
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
def conv_block(in_channels, out_channels):
blk = nn.Sequential(nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1))
return blk
- 稠密块由多个conv_block组成,每块使用相同的输出通道数。
- 在前向计算时,我们将每块的输入和输出在通道维上连结。
class DenseBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_convs, in_channels, out_channels):
super(DenseBlock, self).__init__()
net = []
for i in range(num_convs):
in_c = in_channels + i * out_channels
net.append(conv_block(in_c, out_channels))
self.net = nn.ModuleList(net)
self.out_channels = in_channels + num_convs * out_channels # 计算输出通道数
def forward(self, X):
for blk in self.net:
Y = blk(X)
X = torch.cat((X, Y), dim=1) # 在通道维上将输入和输出连结
return X
定义一个有2个输出通道数为10的卷积块。
- 使用通道数为3的输入时,我们会得到通道数为 3 + 2 × 10 = 23 3+2\times 10=23 3+2×10=23的输出。
- 卷积块的通道数控制了输出通道数相对于输入通道数的增长,因此也被称为增长率(growth rate)。
blk = DenseBlock(2, 3, 10)
X = torch.rand(4, 3, 8, 8)
Y = blk(X)
Y.shape # torch.Size([4, 23, 8, 8])
过渡层
- 每个稠密块都会带来通道数的增加,使用过多则会带来过于复杂的模型。
- 过渡层用来控制模型复杂度。它通过 1 × 1 1\times1 1×1卷积层来减小通道数,并使用步幅为2的平均池化层减半高和宽,从而进一步降低模型复杂度。
def transition_block(in_channels, out_channels):
blk = nn.Sequential(
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))
return blk
对上例中稠密块的输出,使用通道数为10的过渡层。此时输出的通道数减为10,高和宽均减半。
blk = transition_block(23, 10)
blk(Y).shape # torch.Size([4, 10, 4, 4])
DenseNet模型
DenseNet首先使用和ResNet一样的单卷积层和最大池化层。
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
- 接着使用4个稠密块。
- 同ResNet一样,我们可以设置每个稠密块使用多少个卷积层(这里设成4)。
- 稠密块里的卷积层通道数(即增长率)设为32,所以每个稠密块将增加128个通道。
ResNet里通过步幅为2的残差块在每个模块之间减小高和宽。DenseNet则使用过渡层来减半高和宽,并减半通道数。
num_channels, growth_rate = 64, 32 # num_channels为当前的通道数
num_convs_in_dense_blocks = [4, 4, 4, 4]
for i, num_convs in enumerate(num_convs_in_dense_blocks):
DB = DenseBlock(num_convs, num_channels, growth_rate)
net.add_module("DenseBlosk_%d" % i, DB)
# 上一个稠密块的输出通道数
num_channels = DB.out_channels
# 在稠密块之间加入通道数减半的过渡层
if i != len(num_convs_in_dense_blocks) - 1:
net.add_module("transition_block_%d" % i, transition_block(num_channels, num_channels // 2))
num_channels = num_channels // 2
- 最后接上全局池化层和全连接层来输出。
class GlobalAvgPool2d(nn.Module):
# 全局平均池化层可通过将池化窗口形状设置成输入的高和宽实现
def __init__(self):
super(GlobalAvgPool2d, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return F.avg_pool2d(x, kernel_size=x.size()[2:])
class FlattenLayer(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(FlattenLayer, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x): # x shape: (batch, *, *, ...)
return x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
net.add_module("BN", nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels))
net.add_module("relu", nn.ReLU())
net.add_module("global_avg_pool", GlobalAvgPool2d()) # GlobalAvgPool2d的输出: (Batch, num_channels, 1, 1)
net.add_module("fc", nn.Sequential(FlattenLayer(), nn.Linear(num_channels, 10)))
- 打印每个子模块的输出维度
X = torch.rand((1, 1, 96, 96))
for name, layer in net.named_children():
X = layer(X)
print(name, ' output shape:\t', X.shape)
0 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 48, 48])
1 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 48, 48])
2 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 48, 48])
3 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 24, 24])
DenseBlosk_0 output shape: torch.Size([1, 192, 24, 24])
transition_block_0 output shape: torch.Size([1, 96, 12, 12])
DenseBlosk_1 output shape: torch.Size([1, 224, 12, 12])
transition_block_1 output shape: torch.Size([1, 112, 6, 6])
DenseBlosk_2 output shape: torch.Size([1, 240, 6, 6])
transition_block_2 output shape: torch.Size([1, 120, 3, 3])
DenseBlosk_3 output shape: torch.Size([1, 248, 3, 3])
BN output shape: torch.Size([1, 248, 3, 3])
relu output shape: torch.Size([1, 248, 3, 3])
global_avg_pool output shape: torch.Size([1, 248, 1, 1])
fc output shape: torch.Size([1, 10])
- 获取数据
def load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=None, root='~/Datasets/FashionMNIST'):
"""Download the fashion mnist dataset and then load into memory."""
trans = []
if resize:
trans.append(torchvision.transforms.Resize(size=resize))
trans.append(torchvision.transforms.ToTensor())
transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose(trans)
mnist_train = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root=root, train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
mnist_test = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root=root, train=False, download=True, transform=transform)
if sys.platform.startswith('win'):
num_workers = 0 # 0表示不用额外的进程来加速读取数据
else:
num_workers = 4
train_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(mnist_train, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=num_workers)
test_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(mnist_test, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=num_workers)
return train_iter, test_iter
batch_size = 256
# 如出现“out of memory”的报错信息,可减小batch_size或resize
train_iter, test_iter = load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=96)
训练模型
def train(net, train_iter, test_iter, batch_size, optimizer, device, num_epochs):
net = net.to(device)
print("training on ", device)
loss = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
train_l_sum, train_acc_sum, n, batch_count, start = 0.0, 0.0, 0, 0, time.time()
for X, y in train_iter:
X = X.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_l_sum += l.cpu().item()
train_acc_sum += (y_hat.argmax(dim=1) == y).sum().cpu().item()
n += y.shape[0]
batch_count += 1
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(test_iter, net)
print('epoch %d, loss %.4f, train acc %.3f, test acc %.3f, time %.1f sec'
% (epoch + 1, train_l_sum / batch_count, train_acc_sum / n, test_acc, time.time() - start))
lr, num_epochs = 0.001, 5
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
train(net, train_iter, test_iter, batch_size, optimizer, device, num_epochs)
《动手学深度学习》