tomcat与spring-web
文章目录
-
-
- SpringServletContainerInitializer
- WebApplicationInitializer
-
- WebApplicationInitializer接口
- AbstractContextLoaderInitializer抽象类
- AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer抽象类
- AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer抽象类
- WebApplicationContext
- WebApplicationContextUtils
- ContextLoaderListener
-
- ContextLoader
- DispatcherServlet
-
SpringServletContainerInitializer
介绍
SpringServletContainerInitializer是spring-web jar包下的类,并且在jar包中的META-INF/services的特定文件中有如下配置:
org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer
这是利用了tomcat的3.0特性,因为tomcat会扫描类路径上的每个jar包中的META-INF/services中的这个指定名称的文件,并且读取这个文件中的类,比如这里的SpringServletContainerInitializer,这个类必须实现ServletContainerInitializer接口。然后这个类会被实例化,并且回调这个类的onStartup方法,并且还可以通过@HandleTypes注解传入感兴趣的类的子类作为第一个参数,ServletContxt作为第二个参数。利用这个特性可以给ServletContainer容器配置功能。
源码
/**
* 使用Servlet3.0的ServletContainerInitializer特性,可以使用基于java代码的方式配置servlet容器,而取代以前的web.xml
* 的配置方式。SpringServletContainerInitializer通过@HandleTypes,传入WebApplicationInitializer的实现类,来实现
* 对ServletContext初始化。也就是说,我们只要定义一个类实现WebApplicationInitializer这个接口,那么我们的这个类就能够
* 拿到ServletContext,并且往ServletContext中添加三大组件。
* Servlet 3.0 {@link ServletContainerInitializer} designed to support code-based
* configuration of the servlet container using Spring's {@link WebApplicationInitializer}
* SPI as opposed to (or possibly in combination with) the traditional
* {@code web.xml}-based approach.
*
* 只要把spring-web 这个jar包放在类路径上,那么就会使用到tomcat的这个servlet 3.0的特性,不需要这个功能,
* 那就移除这个jar包就行了。
* 因为spring-web 包有指定的这个文件META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer,
*
*
* Mechanism of Operation
* This class will be loaded and instantiated and have its {@link #onStartup}
* method invoked by any Servlet 3.0-compliant container during container startup assuming
* that the {@code spring-web} module JAR is present on the classpath. This occurs through
* the JAR Services API {@link ServiceLoader#load(Class)} method detecting the
* {@code spring-web} module's {@code META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer}
* service provider configuration file. See the
*
* JAR Services API documentation as well as section 8.2.4 of the Servlet 3.0
* Final Draft specification for complete details.
*
*
* In combination with {@code web.xml}
* A web application can choose to limit the amount of classpath scanning the Servlet
* container does at startup either through the {@code metadata-complete} attribute in
* {@code web.xml}, which controls scanning for Servlet annotations or through an
* {@code } element also in {@code web.xml}, which controls which
* web fragments (i.e. jars) are allowed to perform a {@code ServletContainerInitializer}
* scan. When using this feature, the {@link SpringServletContainerInitializer}
* can be enabled by adding "spring_web" to the list of named web fragments in
* {@code web.xml} as follows:
*
*
* {@code
*
* some_web_fragment
* spring_web
*
* }
*
* SpringServletContainerInitializer负责把用户定义的实现了WebApplicationInitializer接口的类实例化,并且把
* ServletContext传给用户自定义实现了WebApplicationInitializer接口的类对象的void onStartup(ServletContext)
* 方法,这样在tomcat初始化过程中,就可以配置servlet容器了。
*
* Relationship to Spring's {@code WebApplicationInitializer}
* Spring's {@code WebApplicationInitializer} SPI consists of just one method:
* {@link WebApplicationInitializer#onStartup(ServletContext)}. The signature is intentionally
* quite similar to {@link ServletContainerInitializer#onStartup(Set, ServletContext)}:
* simply put, {@code SpringServletContainerInitializer} is responsible for instantiating
* and delegating the {@code ServletContext} to any user-defined
* {@code WebApplicationInitializer} implementations. It is then the responsibility of
* each {@code WebApplicationInitializer} to do the actual work of initializing the
* {@code ServletContext}. The exact process of delegation is described in detail in the
* {@link #onStartup onStartup} documentation below.
*
* 一般性建议: 这个类用于支持框架, 用户可以自定义实现了WebApplicationInitializer接口的类,放在类路径上
* 来做定制化修改。
*
* General Notes
* In general, this class should be viewed as supporting infrastructure for
* the more important and user-facing {@code WebApplicationInitializer} SPI. Taking
* advantage of this container initializer is also completely optional: while
* it is true that this initializer will be loaded and invoked under all Servlet 3.0+
* runtimes, it remains the user's choice whether to make any
* {@code WebApplicationInitializer} implementations available on the classpath. If no
* {@code WebApplicationInitializer} types are detected, this container initializer will
* have no effect.
*
* 这个容器初始化器,并没有要求一定要使用springmvc, 它允许你只要实现了 WebApplicationInitializer这个接口,那么
* 你从这个接口的方法里拿到ServletContext后,可以做你任何想要添加的servlet, listener, or filter这些组件,并不一定
* 是spring的组件。
*
* Note that use of this container initializer and of {@code WebApplicationInitializer}
* is not in any way "tied" to Spring MVC other than the fact that the types are shipped
* in the {@code spring-web} module JAR. Rather, they can be considered general-purpose
* in their ability to facilitate convenient code-based configuration of the
* {@code ServletContext}. In other words, any servlet, listener, or filter may be
* registered within a {@code WebApplicationInitializer}, not just Spring MVC-specific
* components.
*
*
This class is neither designed for extension nor intended to be extended.
* It should be considered an internal type, with {@code WebApplicationInitializer}
* being the public-facing SPI.
*
*
See Also
* See {@link WebApplicationInitializer} Javadoc for examples and detailed usage
* recommendations.
*
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @since 3.1
* @see #onStartup(Set, ServletContext)
* @see WebApplicationInitializer
*/
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class) // 感兴趣的类是 WebApplicationInitializer接口的子类
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
@Override // classpath路径上的所有类只要是@HandlesTypes注解标注的类,都会传过来,即WebApplicationInitializer
public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = new LinkedList<WebApplicationInitializer>();
// 把传过来的类实例化(不能被实例化的就不管了),添加到initializers集合中
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
for (Class<?> waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
// Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes,
// no matter what @HandlesTypes says...
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer) waiClass.newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class",
ex);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath");
return;
}
servletContext.log(initializers.size() +
" Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
// 对这些initializers进行一个排序,排序可以通过实现Ordered接口,或者使用@Order注解
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
}
WebApplicationInitializer
介绍
通过SpringServletContainerInitializer的介绍,我们知道了spring-web模块能够把类路径上实现了WebApplicationInitializer这个接口的类给例化,并且把ServletContext给传过来给onStartup方法,那么我们就可以自己往ServletContext中添加web的三大组建了。
我们先看下常规的web.xml配置
<web-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" version="3.0">
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListenerlistener-class>
listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xmlparam-value>
context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvcservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xmlparam-value>
init-param>
<load-on-startup>1load-on-startup>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvcservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/url-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
web-app>
源码
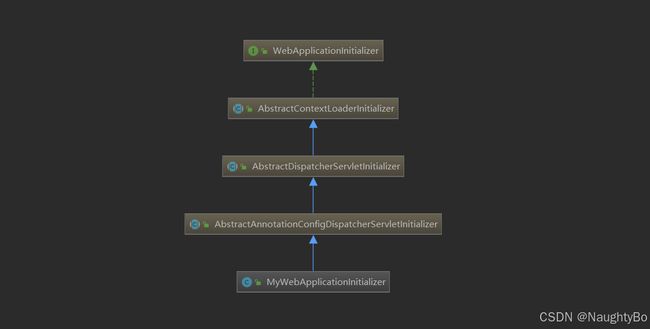
通过看上面的继承关系图,我们来看下它们的源码
WebApplicationInitializer接口
public interface WebApplicationInitializer {
/**
* 实现了这个接口的类可以往传过来的servletContext中注入servlets, filters, listeners三大组件
* 这个接口方法的回调是由SpringServletContainerInitializer负责的
*
* Configure the given {@link ServletContext} with any servlets, filters, listeners
* context-params and attributes necessary for initializing this web application. See
* examples {@linkplain WebApplicationInitializer above}.
* @param servletContext the {@code ServletContext} to initialize
* @throws ServletException if any call against the given {@code ServletContext}
* throws a {@code ServletException}
*/
void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException;
}
AbstractContextLoaderInitializer抽象类
/**
* 这个类实现了WebApplicationInitializer,目的是往ServlvetContext中添加ContextLoaderListener,
* 这跟我们在web.xml 中配置ContextLoaderListener监听器是一样的
*
* Convenient base class for {@link WebApplicationInitializer} implementations
* that register a {@link ContextLoaderListener} in the servlet context.
*
* The only method required to be implemented by subclasses is
* {@link #createRootApplicationContext()}, which gets invoked from
* {@link #registerContextLoaderListener(ServletContext)}.
*
* @author Arjen Poutsma
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.2
*/
public abstract class AbstractContextLoaderInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
/** Logger available to subclasses */
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
/*
* 这个重写接口的方法负责使用servletContext注册ContextLoaderListener监听器
*/
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
registerContextLoaderListener(servletContext);
}
/**
*
* 1.创建spring容器,准确的说应该是spring的根容器,并且把这个spring的根容器设置给了ContextLoaderListener监听器,
* 2.getRootApplicationContextInitializers()方法获取到ApplicationContextInitializer实例,这个在此处是可以
* 在当前这个类的这个模板方法里自定义返回ApplicationContextInitializer实例的。这个对应到web.xml中做的如下配置
*
* contextInitializerClasses
* com.zzhua.initializer.MyApplicationContextInitializer
*
* 这里返回的 ApplicationContextInitializer 实例用于对spring的根容器的修改,并且可以返回不止1个,
* 可以使用@Order注解或者实现Order接口来做一个排序,按顺序对spring根容器修改。
* 这个ApplicationContextInitializer的回调是发生在ContextLoader的
* configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext()方法中调用customizeContext(sc, wac)方法时。
*
*
* Register a {@link ContextLoaderListener} against the given servlet context. The
* {@code ContextLoaderListener} is initialized with the application context returned
* from the {@link #createRootApplicationContext()} template method.
* @param servletContext the servlet context to register the listener against
*/
protected void registerContextLoaderListener(ServletContext servletContext) {
WebApplicationContext rootAppContext = createRootApplicationContext();
if (rootAppContext != null) {
// spring容器被设置给了ContextLoaderListener的父类ContextLoader的WebApplicationContext属性
// 说明ContextLoaderListener是持有spring根容器的
ContextLoaderListener listener = new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext);
listener.setContextInitializers(getRootApplicationContextInitializers());
servletContext.addListener(listener);
}
else {
logger.debug("No ContextLoaderListener registered, as " +
"createRootApplicationContext() did not return an application context");
}
}
/**
* Create the "root" application context to be provided to the
* {@code ContextLoaderListener}.
* The returned context is delegated to
* {@link ContextLoaderListener#ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext)} and will
* be established as the parent context for any {@code DispatcherServlet} application
* contexts. As such, it typically contains middle-tier services, data sources, etc.
* @return the root application context, or {@code null} if a root context is not
* desired
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer
*/
protected abstract WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext();
/**
* Specify application context initializers to be applied to the root application
* context that the {@code ContextLoaderListener} is being created with.
* @since 4.2
* @see #createRootApplicationContext()
* @see ContextLoaderListener#setContextInitializers
*/
protected ApplicationContextInitializer<?>[] getRootApplicationContextInitializers() {
return null;
}
}
AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer抽象类
/**
*
* 这个类同样使用WebApplicationInitializer接口, 用于往ServletContext中注册 DispatcherServlet,
* 并且对DispatcherServlet做相关的配置
*
* Base class for {@link org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer}
* implementations that register a {@link DispatcherServlet} in the servlet context.
*
* Concrete implementations are required to implement
* {@link #createServletApplicationContext()}, as well as {@link #getServletMappings()},
* both of which get invoked from {@link #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)}.
* Further customization can be achieved by overriding
* {@link #customizeRegistration(ServletRegistration.Dynamic)}.
*
*
Because this class extends from {@link AbstractContextLoaderInitializer}, concrete
* implementations are also required to implement {@link #createRootApplicationContext()}
* to set up a parent "root" application context. If a root context is
* not desired, implementations can simply return {@code null} in the
* {@code createRootApplicationContext()} implementation.
*
* @author Arjen Poutsma
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @since 3.2
*/
public abstract class AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer extends AbstractContextLoaderInitializer {
/**
* The default servlet name. Can be customized by overriding {@link #getServletName}.
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_SERVLET_NAME = "dispatcher";
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
// 先调用父类的方法,即先创建spring的父容器
super.onStartup(servletContext);
// 注册DispatcherServlet到ServletContext中,在此过程中,会创建spring容器,即spring子容器
registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext);
}
/**
*
* 创建spring的web子容器, 创建方法是模板方法,交给子类实现,
* new了一个DispatcherServlet,并且把上面创建的spring子容器传给了DispatcherServlet
* 获取到ApplicationContextInitializer的实例,获取方法是模板方法。获取的这些实例将应用于初始化spring的web子容器
* 获取实例的过程,对应于web.xml中的servlet标签下的如下配置
*
* contextInitializerClasses
* com.zzhua.initializer.MyAppContextInitializer,
*
* 加上 下面这个配置也会对spring的web子容器初始化
*
* contextInitializerClasses
* com.zzhua.initializer.MyApplicationContextInitializer
*
* 这些初始化的调用是在DispatcherServlet的父类FrameworkServlet中的
* configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法调用applyInitializers(wac);时被调用
*
* Register a {@link DispatcherServlet} against the given servlet context.
* This method will create a {@code DispatcherServlet} with the name returned by
* {@link #getServletName()}, initializing it with the application context returned
* from {@link #createServletApplicationContext()}, and mapping it to the patterns
* returned from {@link #getServletMappings()}.
*
Further customization can be achieved by overriding {@link
* #customizeRegistration(ServletRegistration.Dynamic)} or
* {@link #createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext)}.
* @param servletContext the context to register the servlet against
*/
protected void registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext servletContext) {
String servletName = getServletName();
Assert.hasLength(servletName, "getServletName() must not return empty or null");
// 创建一个spring的web容器, 这个创建方法是个模板方法,实现交给子类
WebApplicationContext servletAppContext = createServletApplicationContext();
Assert.notNull(servletAppContext,
"createServletApplicationContext() did not return an application " +
"context for servlet [" + servletName + "]");
// 将创建的spring的web子容器作为创建DispatcherServlet的构造参数,从而创建DispatcherServlet,
// 这说明,DispatcherServlet持有WebApplicationContext的,并且是在父类FrameWorkServlet中属性持有的
FrameworkServlet dispatcherServlet = createDispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
// 将Initializers设置给dispatcherServlet,用于初始化spring的web子容器
dispatcherServlet.setContextInitializers(getServletApplicationContextInitializers());
// 将DispatcherServlet注册给ServletContext
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet(servletName,
dispatcherServlet);
Assert.notNull(registration,
"Failed to register servlet with name '" + servletName + "'." +
"Check if there is another servlet registered under the same name.");
// 立即初始化
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
// 设置前端控制器DispatcherServlet的映射路径
registration.addMapping(getServletMappings());
// 异步支持
registration.setAsyncSupported(isAsyncSupported());
// 获取到filter,获取方法时模板方法,
// 这个filter只拦截的servlet-name就是前端控制器DispatcherServlet
Filter[] filters = getServletFilters();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(filters)) {
for (Filter filter : filters) {
registerServletFilter(servletContext, filter);
}
}
// 自定义registration方法, 模板方法,让用户继续自定义registration
customizeRegistration(registration);
}
/**
*
* 默认就是: servletName
*
* Return the name under which the {@link DispatcherServlet} will be registered.
* Defaults to {@link #DEFAULT_SERVLET_NAME}.
* @see #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)
*/
protected String getServletName() {
return DEFAULT_SERVLET_NAME;
}
/**
* 模板方法,创建spring的web子容器的逻辑,交给子类来做
*
* Create a servlet application context to be provided to the {@code DispatcherServlet}.
* The returned context is delegated to Spring's
* {@link DispatcherServlet#DispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext)}. As such,
* it typically contains controllers, view resolvers, locale resolvers, and other
* web-related beans.
* @see #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)
*/
protected abstract WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext();
/**
* DispatcherServlet中传了spring的web子容器,说明dispatcherServlet是持有spring的web子容器的
* 这个子容器将传给前端控制器的父类FrameWorkServlet的webApplicationContext
*
* Create a {@link DispatcherServlet} (or other kind of {@link FrameworkServlet}-derived
* dispatcher) with the specified {@link WebApplicationContext}.
* Note: This allows for any {@link FrameworkServlet} subclass as of 4.2.3.
* Previously, it insisted on returning a {@link DispatcherServlet} or subclass thereof.
*/
protected FrameworkServlet createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext servletAppContext) {
return new DispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
}
/**
* 这里返回的初始化器,将应用于前端控制器创建时传入的spring的web容器的初始化
* Specify application context initializers to be applied to the servlet-specific
* application context that the {@code DispatcherServlet} is being created with.
* @since 4.2
* @see #createServletApplicationContext()
* @see DispatcherServlet#setContextInitializers
* @see #getRootApplicationContextInitializers()
*/
protected ApplicationContextInitializer<?>[] getServletApplicationContextInitializers() {
return null;
}
/**
* 设置前端控制器DispatcherServlet的处理请求的url-pattern
*
* Specify the servlet mapping(s) for the {@code DispatcherServlet} —
* for example {@code "/"}, {@code "/app"}, etc.
* @see #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)
*/
protected abstract String[] getServletMappings();
/**
* 指定拦截前端控制器DispatcherServlet的filter
*
* Specify filters to add and map to the {@code DispatcherServlet}.
* @return an array of filters or {@code null}
* @see #registerServletFilter(ServletContext, Filter)
*/
protected Filter[] getServletFilters() {
return null;
}
/**
* Add the given filter to the ServletContext and map it to the
* {@code DispatcherServlet} as follows:
*
* - a default filter name is chosen based on its concrete type
*
- the {@code asyncSupported} flag is set depending on the
* return value of {@link #isAsyncSupported() asyncSupported}
*
- a filter mapping is created with dispatcher types {@code REQUEST},
* {@code FORWARD}, {@code INCLUDE}, and conditionally {@code ASYNC} depending
* on the return value of {@link #isAsyncSupported() asyncSupported}
*
* If the above defaults are not suitable or insufficient, override this
* method and register filters directly with the {@code ServletContext}.
* @param servletContext the servlet context to register filters with
* @param filter the filter to be registered
* @return the filter registration
*/
protected FilterRegistration.Dynamic registerServletFilter(ServletContext servletContext,
Filter filter) {
// 这里就是在往ServletContext注册Filter用于拦截前端控制器DispatcherServlet
String filterName = Conventions.getVariableName(filter);
Dynamic registration = servletContext.addFilter(filterName, filter);
if (registration == null) {
int counter = -1;
while (counter == -1 || registration == null) {
counter++;
registration = servletContext.addFilter(filterName + "#" + counter, filter);
Assert.isTrue(counter < 100,
"Failed to register filter '" + filter + "'." +
"Could the same Filter instance have been registered already?");
}
}
registration.setAsyncSupported(isAsyncSupported());
registration.addMappingForServletNames(getDispatcherTypes(), false, getServletName());
return registration;
}
private EnumSet<DispatcherType> getDispatcherTypes() {
return (isAsyncSupported() ?
EnumSet.of(DispatcherType.REQUEST, DispatcherType.FORWARD,
DispatcherType.INCLUDE, DispatcherType.ASYNC) :
EnumSet.of(DispatcherType.REQUEST, DispatcherType.FORWARD, DispatcherType.INCLUDE));
}
/**
* 异步支持
* A single place to control the {@code asyncSupported} flag for the
* {@code DispatcherServlet} and all filters added via {@link #getServletFilters()}.
* The default value is "true".
*/
protected boolean isAsyncSupported() {
return true;
}
/**
* 留给用户自定义前端控制器的方法,
* Optionally perform further registration customization once
* {@link #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)} has completed.
* @param registration the {@code DispatcherServlet} registration to be customized
* @see #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)
*/
protected void customizeRegistration(ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration) {
}
}
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer抽象类
/**
*
* spring借助tomcat的3.0新特性SCI机制,提供的自动扫描 WebApplicationInitializer 接口实现类,
* 得到ServletContext,从而注册Servlet、listener、filter等web组件。
*
* 使用AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext支持使用@Configuration注解类作为spring容器的配置信息,创建spring容器
* servlet的spring的web子容器
* ServletContextListener的spring的根容器
*
* 作为这个类的具体实现,需要重写getRootConfigClasses()和getServletConfigClasses()方法,指定spring的配置类
*
* Base class for {@link org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer}
* implementations that register a
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet DispatcherServlet}
* configured with annotated classes, e.g. Spring's
* {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration @Configuration} classes.
*
* Concrete implementations are required to implement {@link #getRootConfigClasses()}
* and {@link #getServletConfigClasses()} as well as {@link #getServletMappings()}.
* Further template and customization methods are provided by
* {@link AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer}.
*
*
This is the preferred approach for applications that use Java-based
* Spring configuration.
*
* @author Arjen Poutsma
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 3.2
*/
public abstract class AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer
extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer {
/**
* 获取配置类创建spring的web子容器, 这里用的是 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
* {@inheritDoc}
* This implementation creates an {@link AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext},
* providing it the annotated classes returned by {@link #getRootConfigClasses()}.
* Returns {@code null} if {@link #getRootConfigClasses()} returns {@code null}.
*/
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
// 获取配置类
Class<?>[] configClasses = getRootConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
rootAppContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
// 注册给spring的配置文件,但并未刷新
rootAppContext.register(configClasses);
return rootAppContext;
}
else {
return null;
}
}
/**
* 获取配置类创建spring根容器,这里用的是 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
*
* {@inheritDoc}
* This implementation creates an {@link AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext},
* providing it the annotated classes returned by {@link #getServletConfigClasses()}.
*/
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext servletAppContext = new
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
// 获取配置类
Class<?>[] configClasses = getServletConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
// 把配置类注册给了spring容器,但并未刷新
servletAppContext.register(configClasses);
}
return servletAppContext;
}
/**
* 指定spring根容器使用的配置类,这个配置类需要使用@Configuration或者是@Component注解
* Specify {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration @Configuration}
* and/or {@link org.springframework.stereotype.Component @Component} classes to be
* provided to the {@linkplain #createRootApplicationContext() root application context}.
* @return the configuration classes for the root application context, or {@code null}
* if creation and registration of a root context is not desired
*/
protected abstract Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses();
/**
* 指定spring的web子容器使用的配置类,这个配置类需要使用@Configuration或者是@Component注解
* Specify {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration @Configuration}
* and/or {@link org.springframework.stereotype.Component @Component} classes to be
* provided to the {@linkplain #createServletApplicationContext() dispatcher servlet
* application context}.
* @return the configuration classes for the dispatcher servlet application context or
* {@code null} if all configuration is specified through root config classes.
*/
protected abstract Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses();
}
应用
从WebApplicationIntializer接口的继承体系和下面子类的实现来看,它主要是做好了准备工作,
- 创建Spring的根容器(注意此时并没有刷新spring容器),并且设置到了ContextLoaderListener当中,并且把ContextLoaderListener注册到了ServletContext中,等待tomcat回调ServletContextListener的ContextInitialized方法时,再刷新spring容器
- 创建Spring的web子容器(注意此时也未刷新该spring容器),并且设置到了DispatcherServlet当中,并且把DispatcherServlet注册到了ServletContext中,等待tomcat初始化Servlet时,回调servlet的init方法时,再刷新spring容器
那么 其实接下来就是要看tomcat回调ContextLoaderLisetener和DispatcherServlet的初始化方法,那么在初始化方法过程中,肯定就会被spring容器进行一个自定义,并且完成spring根容器和spring的web子容器的刷新。
示例:
RootConfig
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.zzhua",
excludeFilters = {@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION
,value = Controller.class)}
)
public class RootConfig { // 配置根容器中的bean
}
ServletConfig
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.zzhua",
includeFilters = {@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,
value = Controller.class)
},
useDefaultFilters = false)
public class ServletConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { // 配置spring的web子容器中的bean
}
MyWebApplicationInitializer
public class MyWebApplicationInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
// 把这个配置类设置给了ContextLoaderListener的父类ContextLoader持有的webApplicationContxt属性的配置类。
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{RootConfig.class};
}
// 把这个配置类设置给了DispacherServlet的父类FrameWorkServlet持有的webApplicationContxt属性的配置类。
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{ServletConfig.class};
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
super.onStartup(servletContext);
// 我们可以顺便注册一下其它的一些需要的组件
//注册组件 ServletRegistration
ServletRegistration.Dynamic servlet = servletContext.addServlet("userServlet",
new HelloServlet());
//配置servlet的映射信息
servlet.addMapping("/hello1");
}
}
WebApplicationContext
// Spring-web的WebApplicationContext继承了Spring的ApplicationContext,
// 也就是说WebApplicationContext具有了spring容器的功能
public interface WebApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext {
// 此处注意这个名字, 这个名字是创建了spring容器后, 将这个spring容器存到ServletContext的键,
// 通过这个键能拿到spring根容器
String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";
String SCOPE_REQUEST = "request";
String SCOPE_SESSION = "session";
String SCOPE_APPLICATION = "application";
String SERVLET_CONTEXT_BEAN_NAME = "servletContext";
String CONTEXT_PARAMETERS_BEAN_NAME = "contextParameters";
String CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTES_BEAN_NAME = "contextAttributes";
@Nullable // 从这个定义的方法, 可以看出WebApplicationContext(Spring容器)也能拿到SerlvetContext
ServletContext getServletContext();
}
WebApplicationContextUtils
public abstract class WebApplicationContextUtils {
// ...
public static WebApplicationContext getWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
return getWebApplicationContext(
sc, // 从ServletContext中取出spring容器
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE // 引用了上面这个键
);
}
// ...
}
// 可以通过这种静态方法拿到spring容器, 所以只要能拿到ServletContext就能拿到Spring容器
// 源码可以参看ContextLoaderListener
ContextLoaderListener
ContextLoaderLisetener继承了ContextLoader,实现了ServletContextListener接口。ContextLoaderListener的大部分功能实现都在它的父类ContextLoader中实现,实现ServletContextListener接口,只是成为父类方法被tomcat容器调用的入口。
我们先看下ContextLoaderListener类
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
// 无参构造
public ContextLoaderListener() {
}
// 传入web版的spring的容器
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
// 这个方法很重要,这个方法将会被tomcat在生命周期中回调,并且将ServletContext传给了父类处理
// 我们不要忘了,我们把未刷新的spring容器放到了ContextLoaderListener中,并且保存在父类中,
// 下面就要看父类是如何处理的
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
/**
* Close the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}
ContextLoader
package org.springframework.web.context;
public class ContextLoader {
/** 作为内部维护的web版spring容器在ServletContext中的contextId
* Config param for the root WebApplicationContext id,
* to be used as serialization id for the underlying BeanFactory: {@value}
*/
public static final String CONTEXT_ID_PARAM = "contextId";
// spring容器刷新时用到的配置文件,我们应该还记得使用web.xml配置的时候,
// 会给该监听器配置一个ContextConfigLocation,来让spring容器根据这个配置文件刷新
/*
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
contextConfigLocation
classpath:applicationContext.xml
*/ // 这个context-param将会被tomcat读取到servletContext,而获取到servletContext后
// ,可以使用servletContext.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation")获取到对应的值
//
public static final String CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM = "contextConfigLocation";
// 获取web版的spring容器的实现类
/**
* Config param for the root WebApplicationContext implementation class to use: {@value}
* @see #determineContextClass(ServletContext)
*/
public static final String CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM = "contextClass";
// 用来定义初始化web版spring容器的initializer类(需要实现ApplicationContextInitializer接口),
// 这些类将会被实例化, 并且调用initializer.initialize(wac)来初始化spring容器
/**
* Config param for {@link ApplicationContextInitializer} classes to use
* for initializing the root web application context: {@value}
* @see #customizeContext(ServletContext, ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)
*/
public static final String CONTEXT_INITIALIZER_CLASSES_PARAM = "contextInitializerClasses";
// 定义全局的用来初始化spring容器的ApplicationContextInitializer接口实现类
/**
* Config param for global {@link ApplicationContextInitializer} classes to use
* for initializing all web application contexts in the current application: {@value}
* @see #customizeContext(ServletContext, ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)
*/
public static final String GLOBAL_INITIALIZER_CLASSES_PARAM = "globalInitializerClasses";
/**
* Optional servlet context parameter (i.e., "{@code locatorFactorySelector}")
* used only when obtaining a parent context using the default implementation
* of {@link #loadParentContext(ServletContext servletContext)}.
* Specifies the 'selector' used in the
* {@link ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator#getInstance(String selector)}
* method call, which is used to obtain the BeanFactoryLocator instance from
* which the parent context is obtained.
* The default is {@code classpath*:beanRefContext.xml},
* matching the default applied for the
* {@link ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator#getInstance()} method.
* Supplying the "parentContextKey" parameter is sufficient in this case.
*/
public static final String LOCATOR_FACTORY_SELECTOR_PARAM = "locatorFactorySelector";
/**
* Optional servlet context parameter (i.e., "{@code parentContextKey}")
* used only when obtaining a parent context using the default implementation
* of {@link #loadParentContext(ServletContext servletContext)}.
* Specifies the 'factoryKey' used in the
* {@link BeanFactoryLocator#useBeanFactory(String factoryKey)} method call,
* obtaining the parent application context from the BeanFactoryLocator instance.
* Supplying this "parentContextKey" parameter is sufficient when relying
* on the default {@code classpath*:beanRefContext.xml} selector for
* candidate factory references.
*/
public static final String LOCATOR_FACTORY_KEY_PARAM = "parentContextKey";
// 定义可以使用的初始化参数的分隔符
/**
* Any number of these characters are considered delimiters between
* multiple values in a single init-param String value.
*/
private static final String INIT_PARAM_DELIMITERS = ",; \t\n";
// 在ContextLoader的同包下有ContextLoader.properties文件,里面定义了
// org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext\
// =org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
/**
* Name of the class path resource (relative to the ContextLoader class)
* that defines ContextLoader's default strategy names.
*/
private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "ContextLoader.properties";
// 默认策略的配置从默认的策略路径文件中读取
private static final Properties defaultStrategies;
static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
// by application developers.
try {
// 使用的是ClassPathResource来读取与ContextLoader同包下的ContextLoader.properties文件
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(
DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class);
// 使用PropertiesLoaderUtils的静态方法来读取resource
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': "
+ ex.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* Map from (thread context) ClassLoader to corresponding 'current' WebApplicationContext.
*/
private static final Map<ClassLoader, WebApplicationContext> currentContextPerThread =
new ConcurrentHashMap<ClassLoader, WebApplicationContext>(1);
/**
* The 'current' WebApplicationContext, if the ContextLoader class is
* deployed in the web app ClassLoader itself.
*/
private static volatile WebApplicationContext currentContext;
// 从这里我们可以看到ContextLoader维护的spring容器这个属性
// ,我们可以理解为,把spring容器存储到了tomcat的监听器中
/**
* The root WebApplicationContext instance that this loader manages.
*/
private WebApplicationContext context;
/**
* Holds BeanFactoryReference when loading parent factory via
* ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator.
*/
private BeanFactoryReference parentContextRef;
// contextInitializer将会被维护起来,它们将会用来初始化spring容器
/** Actual ApplicationContextInitializer instances to apply to the context */
private final
List<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>> contextInitializers =
new ArrayList<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>>();
// 无参构造方法
public ContextLoader() {
}
// 有参构造方法,
public ContextLoader(WebApplicationContext context) {
this.context = context;
}
// 添加到ContextLoader维护的List集合中
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void setContextInitializers(ApplicationContextInitializer<?>... initializers) {
if (initializers != null) {
for (ApplicationContextInitializer<?> initializer : initializers) {
this.contextInitializers.add
((ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>) initializer);
}
}
}
// 这是个很重要的方法,
// 如果在构造阶段传入了spring容器,那么就初始化它;
// 如果没有,那么就使用配置的contextClass以及contextConfigLocation来创建并刷新spring容器;
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
// spring的根容器都会放到ServletContext中并且以下面这个东西为键,并且只能放1个
if (servletContext.getAttribute
(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application"+
"context present - check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in"+
"your web.xml!");
}
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
// 记录开始时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
// 如果刚开始构造当前监听器的时候,并没有传入容器,那么就根据默认的策略创建spring容器
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
// 到这里,this.context就一定有值了
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
// isActive表示spring容器被刷新了,并且还没有关闭
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// 如果context没有父容器,那么就从servletContext中的loadParentContext方法中弄出来一个
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
// 给this.context找完父容器之后,开始配置并且刷新spring容器:this.context
// 这是个非常关键的方法,spring容器刷新是个非常重要的阶段
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
// spring容器刷新之后,将spring容器存到servletContext中,并且键如下
// ,这下我们可以看到为什么一进这个方法就判断这个键了
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE,
this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" +
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", err);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err);
throw err;
}
}
// 创建容器的方法,先从servletContext中配置的contextClass参数反射创建spring容器
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
// 确定contextClass
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
// 先从ServletContext中查找配置,配置找不到,那就使用默认策略的(ContextLoader.properteis配置的)
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
// 默认策略
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac,
ServletContext sc) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// spring容器的默认id就是 ObjectUtils.identityToString(this),
// 如果它没有被改变,那就根据已有的信息,做个修改
// 首先看servletContext有没有配置contextId, 不然的话就设置一个默认的
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
// 这里我们就知道了, web版的spring容器中保存了servletContext,
// 而servletContext也通过(域)一个键保存了spring容器
wac.setServletContext(sc);
// spring容器刷新前需要设置配置文件,首先看servletContext中有没有配置contextConfigLocation
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
// spring容器持有一个environment对象,environment对象有两个功能,一个是解析属性,二是对bean逻辑分组(profile)
// 这里获取environment的逻辑也简单,第一次获取,就创建并设置到spring容器的属性里
// ,这里创建的是StandardServletEnvironment,
// environment主要持有了一个propertySource的集合以及使用包装了propertySource的集合
// 的PropertySourcesPropertyResolver对象来作解析
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
// 将servletContext包装成ServletContextPropertySource设置到env的propertySource集合中
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);
}
// 刷新spring容器之前的最后一步
// 在这一步,我们可以将initializer配置给servletContext,
// 那么在这里就会获取到所有配置的initializer(ApplicationInitializer)对象,(servletContext+属性上的)
// 逐个对sprin根容器进行初始化,注意这些initializer对象是可以设置顺序的(@Order注解或者实现Order接口)
// 比如: 我们这个时候就可以往spring容器中注入我们的组件了,这是一个很好的时机
customizeContext(sc, wac);
// 准备工作都做好了,开始刷新spring容器
wac.refresh();
}
protected void customizeContext(ServletContext sc, ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
List<Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>>> initializerClasses =
determineContextInitializerClasses(sc);
for (Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>>
initializerClass : initializerClasses) {
Class<?> initializerContextClass =
GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(initializerClass,
ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
if (initializerContextClass != null && !initializerContextClass.isInstance(wac)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(String.format(
"Could not apply context initializer [%s] since its generic parameter [%s] " +
"is not assignable from the type of application context used by this " +
"context loader: [%s]", initializerClass.getName(),
initializerContextClass.getName(),
wac.getClass().getName()));
}
this.contextInitializers.add(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(initializerClass));
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.contextInitializers);
for (ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> initializer :
this.contextInitializers) {
initializer.initialize(wac);
}
}
protected List<Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>>>
determineContextInitializerClasses(ServletContext servletContext) {
List<Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>>> classes =
new ArrayList<Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>>>();
String globalClassNames = servletContext.getInitParameter(GLOBAL_INITIALIZER_CLASSES_PARAM);
if (globalClassNames != null) {
for (String className : StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(globalClassNames,
INIT_PARAM_DELIMITERS)) {
classes.add(loadInitializerClass(className));
}
}
String localClassNames = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_INITIALIZER_CLASSES_PARAM);
if (localClassNames != null) {
for (String className : StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(localClassNames,
INIT_PARAM_DELIMITERS)) {
classes.add(loadInitializerClass(className));
}
}
return classes;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>> loadInitializerClass(String className) {
try {
Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
if (!ApplicationContextInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Initializer class does not implement ApplicationContextInitializer interface: " + clazz);
}
return (Class<ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>>) clazz;
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to load context initializer class [" + className + "]", ex);
}
}
/**
* Template method with default implementation (which may be overridden by a
* subclass), to load or obtain an ApplicationContext instance which will be
* used as the parent context of the root WebApplicationContext. If the
* return value from the method is null, no parent context is set.
* The main reason to load a parent context here is to allow multiple root
* web application contexts to all be children of a shared EAR context, or
* alternately to also share the same parent context that is visible to
* EJBs. For pure web applications, there is usually no need to worry about
* having a parent context to the root web application context.
*
The default implementation uses
* {@link org.springframework.context.access.ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator},
* configured via {@link #LOCATOR_FACTORY_SELECTOR_PARAM} and
* {@link #LOCATOR_FACTORY_KEY_PARAM}, to load a parent context
* which will be shared by all other users of ContextsingletonBeanFactoryLocator
* which also use the same configuration parameters.
* @param servletContext current servlet context
* @return the parent application context, or {@code null} if none
* @see org.springframework.context.access.ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator
*/
protected ApplicationContext loadParentContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
ApplicationContext parentContext = null;
String locatorFactorySelector = servletContext.getInitParameter(LOCATOR_FACTORY_SELECTOR_PARAM);
String parentContextKey = servletContext.getInitParameter(LOCATOR_FACTORY_KEY_PARAM);
if (parentContextKey != null) {
// locatorFactorySelector may be null, indicating the default "classpath*:beanRefContext.xml"
BeanFactoryLocator locator = ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator.getInstance(locatorFactorySelector);
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Getting parent context definition: using parent context key of '" +
parentContextKey + "' with BeanFactoryLocator");
}
this.parentContextRef = locator.useBeanFactory(parentContextKey);
parentContext = (ApplicationContext) this.parentContextRef.getFactory();
}
return parentContext;
}
/**
* Close Spring's web application context for the given servlet context. If
* the default {@link #loadParentContext(ServletContext)} implementation,
* which uses ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator, has loaded any shared
* parent context, release one reference to that shared parent context.
* If overriding {@link #loadParentContext(ServletContext)}, you may have
* to override this method as well.
* @param servletContext the ServletContext that the WebApplicationContext runs in
*/
public void closeWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
servletContext.log("Closing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
try {
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
((ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context).close();
}
}
finally {
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = null;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.remove(ccl);
}
servletContext.removeAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
if (this.parentContextRef != null) {
this.parentContextRef.release();
}
}
}
/**
* Obtain the Spring root web application context for the current thread
* (i.e. for the current thread's context ClassLoader, which needs to be
* the web application's ClassLoader).
* @return the current root web application context, or {@code null}
* if none found
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.SpringBeanAutowiringSupport
*/
public static WebApplicationContext getCurrentWebApplicationContext() {
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl != null) {
WebApplicationContext ccpt = currentContextPerThread.get(ccl);
if (ccpt != null) {
return ccpt;
}
}
return currentContext;
}
}
DispatcherServlet
见 框架源码学习收藏汇总
- DispatcherServlet(上) - 继承体系与配置详解
- DispatcherServlet(下) - 处理请求流程
- SpringMvc-HandlerMapping(全)
- HandlerAdapter
- RequestMappingHandlerAdapter(上)
- RequestMappingHandlerAdatper(中)
- RequesetMappingHandlerAdatper(下)
- 视图解析器ViewResolver(上)
- 视图解析器ViewResolver(下)
- RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor
- 处理器方法参数解析器&参数校验
- @EnableWebMvc源码&内容协商管理器
- ResourceHttpRequestHandler指定静态资源文件夹