深入浅出Mybatis系列(八)---mapper映射文件配置之select、resultMap
上篇《深入浅出Mybatis系列(七)---mapper映射文件配置之insert、update、delete》介绍了insert、update、delete的用法,本篇将介绍select、resultMap的用法。select无疑是我们最常用,也是最复杂的,mybatis通过resultMap能帮助我们很好地进行高级映射。下面就开始看看select 以及 resultMap的用法:
先看select的配置吧:
<select <!-- 1. id (必须配置) id是命名空间中的唯一标识符,可被用来代表这条语句。 一个命名空间(namespace) 对应一个dao接口, 这个id也应该对应dao里面的某个方法(相当于方法的实现),因此id 应该与方法名一致 --> id="selectPerson" <!-- 2. parameterType (可选配置, 默认为mybatis自动选择处理) 将要传入语句的参数的完全限定类名或别名, 如果不配置,mybatis会通过ParameterHandler 根据参数类型默认选择合适的typeHandler进行处理 parameterType 主要指定参数类型,可以是int, short, long, string等类型,也可以是复杂类型(如对象) --> parameterType="int" <!-- 3. resultType (resultType 与 resultMap 二选一配置) resultType用以指定返回类型,指定的类型可以是基本类型,可以是java容器,也可以是javabean --> resultType="hashmap" <!-- 4. resultMap (resultType 与 resultMap 二选一配置) resultMap用于引用我们通过 resultMap标签定义的映射类型,这也是mybatis组件高级复杂映射的关键 --> resultMap="personResultMap" <!-- 5. flushCache (可选配置) 将其设置为 true,任何时候只要语句被调用,都会导致本地缓存和二级缓存都会被清空,默认值:false --> flushCache="false" <!-- 6. useCache (可选配置) 将其设置为 true,将会导致本条语句的结果被二级缓存,默认值:对 select 元素为 true --> useCache="true" <!-- 7. timeout (可选配置) 这个设置是在抛出异常之前,驱动程序等待数据库返回请求结果的秒数。默认值为 unset(依赖驱动)--> timeout="10000" <!-- 8. fetchSize (可选配置) 这是尝试影响驱动程序每次批量返回的结果行数和这个设置值相等。默认值为 unset(依赖驱动)--> fetchSize="256" <!-- 9. statementType (可选配置) STATEMENT,PREPARED 或 CALLABLE 的一个。这会让 MyBatis 分别使用 Statement,PreparedStatement 或 CallableStatement,默认值:PREPARED--> statementType="PREPARED" <!-- 10. resultSetType (可选配置) FORWARD_ONLY,SCROLL_SENSITIVE 或 SCROLL_INSENSITIVE 中的一个,默认值为 unset (依赖驱动)--> resultSetType="FORWARD_ONLY">
配置看起来总是这么多,不过实际常用的配置也就那么几个, 根据自己的需要吧,上面都已注明是否必须配置。
下面还是上个demo及时练练手吧:
------------------------------------------------------------------------下面是针对select 的练手demo---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
数据库:新增两张表(t_course, t_student)
t_course:
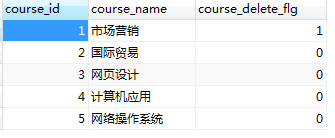
t_student:
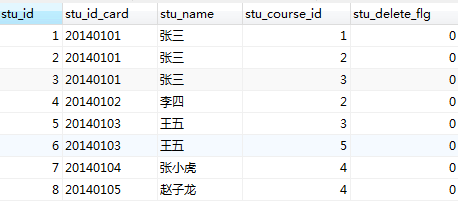
其中,1个student可选择多个course进行学习。
我们还是拿上篇文章的demo, 继续写:
增加后,项目目录如下所示:
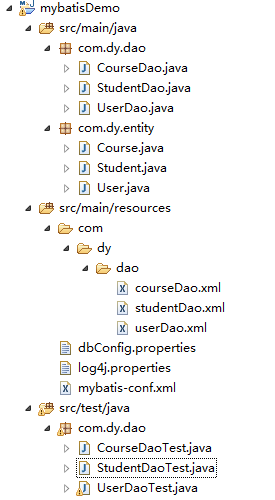
Course.java:

package com.dy.entity; public class Course { private int id; private String name; private int deleteFlag; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getDeleteFlag() { return deleteFlag; } public void setDeleteFlag(int deleteFlag) { this.deleteFlag = deleteFlag; } }
Student.java:

package com.dy.entity; import java.util.List; public class Student { private int id; private String idCard; private String name; private List<Course> courseList; private int deleteFlag; public Student(int id, String idCard, String name, List<Course> courseList, int deleteFlag) { this.id = id; this.idCard = idCard; this.name = name; this.courseList = courseList; this.deleteFlag = deleteFlag; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getIdCard() { return idCard; } public void setIdCard(String idCard) { this.idCard = idCard; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public List<Course> getCourseList() { return courseList; } public void setCourseList(List<Course> courseList) { this.courseList = courseList; } public int getDeleteFlag() { return deleteFlag; } public void setDeleteFlag(int deleteFlag) { this.deleteFlag = deleteFlag; } }
CourseDao.java:

package com.dy.dao; import com.dy.entity.Course; public interface CourseDao { public Course findCourseById(int courseId); }
StudentDao.java:

package com.dy.dao; import com.dy.entity.Student; public interface StudentDao { public Student findStudentById(String idCard); }
courseDao.xml:
<mapper namespace="com.dy.dao.CourseDao"> <!-- 1.此处直接将resultType 设置为course, 一看就知道我设置了别名吧,如果没有设置别名,那么resultType = com.dy.entity.Course。 2.可能细心的你会发现:Course.java中的属性名与数据库字段名不一致,下面,我就在sql语句中用了as, 使之匹配,当然方法不止一种, 在学习了resultMap之后,你能看到一种更直观优雅的方式去将javabean中的属性与数据库字段名保持一致 3.findCourseById 与CourseDao中findCourseById方法对应, 那么传入的参数名称以及类型也应该保持对应关系。 4.可以看到,在sql语句中,通过#{}表达式可以获取参数。 5.下面这条sql语句,实际上的形式是怎么样的?还记得之前说过,mybatis默认为preparedStatement吧,那么,用我们jdbc代码来看,它其实就是: select course_id as id, course_name as name, course_delete_flg as deleteFlag from t_course where course_id=? --> <select id="findCourseById" resultType="course" > select course_id as id, course_name as name, course_delete_flg as deleteFlag from t_course where course_id=#{courseId} </select> </mapper>
CourseDaoTest.java:

package com.dy.dao; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import org.junit.Test; import com.dy.entity.Course; public class CourseDaoTest { @Test public void findCourseById() { SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSessionFactory(); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); CourseDao courseDao = sqlSession.getMapper(CourseDao.class); Course course = courseDao.findCourseById(1); } //Mybatis 通过SqlSessionFactory获取SqlSession, 然后才能通过SqlSession与数据库进行交互 private static SqlSessionFactory getSessionFactory() { SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = null; String resource = "mybatis-conf.xml"; try { sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources .getResourceAsReader(resource)); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return sessionFactory; } }
上面的示例,我们针对course, 简单演示了 select的用法, 不过有个问题值得思考: 一个student可以对应多个course, 那么,在mybatis中如何处理这种一对多, 甚至于多对多,一对一的关系呢?
这儿,就不得不提到 resultMap 这个东西, mybatis的resultMap功能可谓十分强大,能够处理复杂的关系映射, 那么resultMap 该怎么配置呢? 别急,这就来了:
resultMap的配置:
<!-- 1.type 对应类型,可以是javabean, 也可以是其它 2.id 必须唯一, 用于标示这个resultMap的唯一性,在使用resultMap的时候,就是通过id指定 --> <resultMap type="" id=""> <!-- id, 唯一性,注意啦,这个id用于标示这个javabean对象的唯一性, 不一定会是数据库的主键(不要把它理解为数据库对应表的主键) property属性对应javabean的属性名,column对应数据库表的列名 (这样,当javabean的属性与数据库对应表的列名不一致的时候,就能通过指定这个保持正常映射了) --> <id property="" column=""/> <!-- result与id相比, 对应普通属性 --> <result property="" column=""/> <!-- constructor对应javabean中的构造方法 --> <constructor> <!-- idArg 对应构造方法中的id参数 --> <idArg column=""/> <!-- arg 对应构造方法中的普通参数 --> <arg column=""/> </constructor> <!-- collection,对应javabean中容器类型, 是实现一对多的关键 property 为javabean中容器对应字段名 column 为体现在数据库中列名 ofType 就是指定javabean中容器指定的类型 --> <collection property="" column="" ofType=""></collection> <!-- association 为关联关系,是实现N对一的关键。 property 为javabean中容器对应字段名 column 为体现在数据库中列名 javaType 指定关联的类型 --> <association property="" column="" javaType=""></association> </resultMap>
好啦,知道resutMap怎么配置后,咱们立即接着上面的demo来练习一下吧:
------------------------------------------------------------------下面是用resultMap处理一对多关系的映射的示例-------------------------------------------------------------
一个student对应多个course, 典型的一对多,咱们就来看看mybatis怎么配置这种映射吧:
studentDao.xml:

<mapper namespace="com.dy.dao.StudentDao"> <!-- 这儿定义一个resultMap --> <resultMap type="student" id="studentMap"> <!-- 数据库中主键是id, 但是我这儿却是指定idCard为主键,为什么? 刚刚讲了,id用来表示唯一性, 我们可以认为只要idCard一样,那么他就是同一个学生。 如果此处用数据库中id, 那么mybatis将会认为数据库中每条记录都是一个student, 这显然不符合逻辑 --> <id property="idCard" column="stu_id_card"/> <result property="id" column="stu_id"/> <result property="name" column="stu_name"/> <result property="deleteFlag" column="stu_delete_flg"/> <!-- 这儿就是实现一对多的关键。 在Student中,courseList为List<Course>, 因此,ofType也应该与之对应(当然,我用了别名,不然要蛋疼的写全名了)。 collection的子标签是在指定Course的映射关系(由于Course的javabean的属性名与数据库的列名不一致) --> <collection property="courseList" column="stu_course_id" ofType="Course"> <id property="id" column="course_id"/> <result property="name" column="course_name"/> <result property="deleteFlag" column="course_delete_flg"/> </collection> </resultMap> <!-- 这儿将返回类型设置成了上面指定的studentMap --> <select id="findStudentById" resultMap="studentMap"> SELECT s.*, c.* FROM t_student s LEFT JOIN t_course c ON s.stu_course_id=c.course_id WHERE s.stu_id_card=#{idCard} </select> </mapper>
StudentDaoTest.java:

package com.dy.dao; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.List; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import org.junit.Test; import com.dy.entity.Course; import com.dy.entity.Student; public class StudentDaoTest { @Test public void findCourseById() { SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSessionFactory(); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); StudentDao studentDao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class); Student student = studentDao.findStudentById("20140101"); List<Course> courseList = student.getCourseList(); for (Course course: courseList) { System.out.println(course.getId() + " " + course.getName()); } } //Mybatis 通过SqlSessionFactory获取SqlSession, 然后才能通过SqlSession与数据库进行交互 private static SqlSessionFactory getSessionFactory() { SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = null; String resource = "mybatis-conf.xml"; try { sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources .getResourceAsReader(resource)); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return sessionFactory; } }
相信通过以上demo, 大家也能够使用mybatis的select 和 resultMap的用法了。上面demo只演示了一对多的映射,其实多对一、多对多也与它类似,所以我就没演示了,有兴趣的可以自己动手再做做。
好啦,本次就写到这儿了。(PS,生病一周了,所以到现在才更新博客)。
另附上demo, 需要的童鞋可以前往下载:
demo 下载地址:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1qWjsDzA
