JAVA中包装类和泛型 通配符
目录
1. 包装类
1.1 基本数据类型和对应的包装类
1.2 装箱和封箱
1.3 自动自动装箱和封箱
2. 什么是泛型
3. 引出泛型
3.1 语法
4. 泛型类的使⽤
4.1 语法
4.2 ⽰例
4.3 类型推导(Type Inference)
5 泛型的上界
5.1 语法
6. 通配符
6.1 通配符解决什么问题
6.2 通配符上界
6.3 通配符下界
1. 包装类
在Java中,由于基本类型不是继承⾃Object,为了在泛型代码中可以⽀持基本类型,Java给每个基本类型都对应了⼀个包装类型。
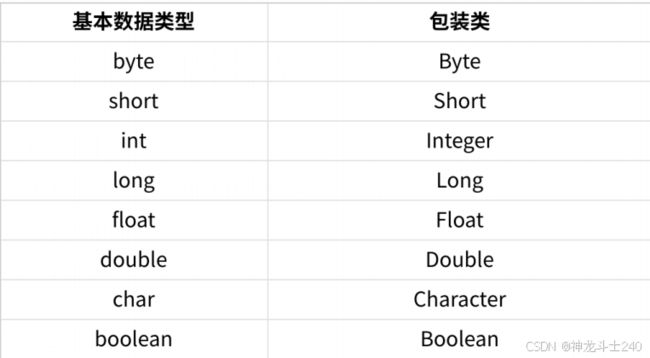
1.1 基本数据类型和对应的包装类
出了Integer和Characterr,其余基本类型的包装类都是⾸字⺟⼤写。
1.2 装箱和封箱
虽然包装类,确实是类。在使用的时候,进行算数运算的时候,还需要转换成内置类型进行计算。
包装类和内置类型转换
内置类型 ————》 包装类 装箱
包装类 ————》 内置类型 拆箱
1.3 自动自动装箱和封箱
从JAVA8开始就可以实现自动装箱和拆箱。
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//内置类型,复制给包装类,自动装箱
Integer a = 10;
//包装类,赋值给内置类型,自动拆箱
int b = a;
}
}
进行算数运算
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// //内置类型,复制给包装类,自动装箱
// Integer a = 10;
// //包装类,赋值给内置类型,自动拆箱
// int b = a;
Integer a = 10;
Integer b = 20;
System.out.println(a+b);
}
}这里的a+b是针对两个Integr先进行转换成int,在进行计算。自动拆箱(其实就是隐士类型转换)。
对于包装类来说直接拿过来用即可。当作内置类型。不过有些地方只能用包装类,不能用内置类型。
2. 什么是泛型
⼀般的类和⽅法,只能使⽤具体的类型: 要么是基本类型,要么是⾃定义的类。如果要编写可以应⽤于多种类型的代码,这种刻板的限制对代码的束缚就会很⼤
----- 来源《Java编程思想》对泛型的介绍。
泛型是在JDK1.5引⼊的新的语法,通俗讲泛型:就是适⽤于许多许多类型。从代码上讲,就是对类型实现了参数化。
3. 引出泛型
实现⼀个类,类中包含⼀个数组成员,使得数组中可以存放任何类型的数据,也可以根据成员⽅法返回数组中某个下标的值
1. 我们以前学过的数组,只能存放指定类型的元素。
例如:
int[] array = new int[10];
String[] strs = new String[10];
3.1 语法
基础写法:
class 泛型类名称<类型形参列表> {
// 这⾥可以使⽤类型参数
}
class ClassName {
} 其他写法:
class 泛型类名称<类型形参列表> extends 继承类/* 这⾥可以使⽤类型参数 */ {
// 这⾥可以使⽤类型参数
}
class ClassName extends ParentClass {
// 可以只使⽤部分类型参数
} 4. 泛型类的使⽤
4.1 语法
泛型类<类型实参> 变量名; // 定义⼀个泛型类引⽤
new 泛型类<类型实参>(构造⽅法实参); // 实例化⼀个泛型类对象4.2 ⽰例
MyArray list = new MyArray(); 注意:泛型只能接受类,所有的基本数据类型必须使⽤包装类!
//就是“参数类型”
//T就是一个类型,相当于是:“形参”
class ArrayTemplate {
//此时arr是T[]类型,T是类型?还不知道,得在后边实例化的时候才能知道。
//由于T类型未知,不能直接new T[] 类型转换
private T[]arr = (T[]) new Object[10];
public T get(int index){
return arr[index];
}
public void set (int index ,T value){
arr[index] = value;
}
}
public class Test2 {
//针对上述ArrayTemplate进行实例化
//反省参数类型T就指定为Integer
//针对arr1来说,只能储存Integer类型的数据
ArrayTemplate arr1 = new ArrayTemplate();
//泛型参数类型 T 就指定为String
//针对Arr2 来说,就只能存储 String 类型的数据
ArrayTemplate arr2 = new ArrayTemplate();
//针对arr3来说,就只能存储Book类型
ArrayTemplate arr3 = new ArrayTemplate();
}
针对泛型参数来说,只能指定引用类型,不能指定内置类型。
4.3 类型推导(Type Inference)
当编译器可以根据上下⽂推导出类型实参时,可以省略类型实参的填写
MyArray list = new MyArray<>(); // 可以推导出实例化需要的类型实参为Integer ⼩结:
1. 泛型是将数据类型参数化,进⾏传递
2. 使⽤ 表⽰当前类是⼀个泛型类。
3. 泛型⽬前为⽌的优点:数据类型参数化,编译时⾃动进⾏类型检查和转换
5 泛型的上界
在定义泛型类时,有时需要对传⼊的类型变量做⼀定的约束,可以通过类型边界来约束。
5.1 语法
class 泛型类名称<类型形参 extends 类型边界> {
...
}实例:
public class MyArray {
...
} 只接受 Number 的⼦类型作为 T 的类型实参
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test3 t1 = new Test3<>();
Test3 t2 = new Test3<>();
Test3 t3 = new Test3<>();
//String类型不是Number的子类
// Test3 t4 = new Test3<>();
}
}
6. 通配符
? ⽤于在泛型的使⽤,即为通配符
6.1 通配符解决什么问题
在"?"的基础上⼜产⽣了两个⼦通配符:
? extends 类:设置通配符上限
? super 类:设置通配符下限
6.2 通配符上界
语法:
//可以传⼊的实参类型是Number或者Number的⼦类public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test4 t = new Test4<>();
//
// t = new Test4();
//这个情况,T来说,无论是啥参数类型 ,都可以通过t来指向
//此处 ? 称为通配符。
// Test4 t = new Test4<>();
//
// t = new Test4();
//指定了通配符的上界
//此时的t 可以指向泛型参数为Number 及其子类的情况
Test4 t = new Test4<>();
t = new Test4();
// 错误写法,String不是NUmber的子类
t = new Test4();
}
}
6.3 通配符下界
语法
//代表 可以传⼊的实参的类型是Integer或者Integer的⽗类类型