在程序中动态创建视图
一般Android各种视图(或者控件)的创建都是写定在.xml的布局文件中的,这样的好处是使用方便,创建视图的时候就能实时看到效果,管理也比较方便。但是,有的时候需要动态创建一些视图,其实.xml文件中的任何视图都是可以在程序中创建的,而每个视图的属性也都有对应的设置的方法。
下面有个小例子,可以横向滑动的多个选项卡,并且可以动态添加选项卡:
动态显示选项卡的主要代码:
public class MainActivity extends Activity{ private TextView addText = null; private LinearLayout lp = null; private int i = 0;public static String NAME = ""; public static String BIRTH = ""; public static int SEX = 1; //是否点击选项卡标志 public static boolean Click_Flag = false; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); addText = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.add); lp = (LinearLayout)findViewById(R.id.linear);//点击按钮添加一个新的选项卡 addText.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, InfoActivity.class); MainActivity.this.startActivity(intent); } }); } @Override protected void onResume() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onResume(); if(InfoActivity.added_FLAG == true) { add(i++); InfoActivity.added_FLAG = false; } } //添加选项卡的函数,参数是添加的位置 public void add(int i){ //在水平的LinearLayout lp里面添加一个垂直的LinearLayout ll final LinearLayout ll = new LinearLayout(MainActivity.this); //0是水平,1是垂直,默认水平 ll.setOrientation(1); ll.setBackgroundColor(Color.rgb(0x33, 0xb5, 0xe5)); final LinearLayout.LayoutParams llp = new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(DensityUtil.dip2px(this, 250),LinearLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT); llp.setMargins(1, 1, 1, 1); lp.addView(ll, i, llp); //在ll里面添加ImageView final ImageView im = new ImageView(MainActivity.this); im.setScaleType(ScaleType.CENTER_INSIDE); im.setImageResource(R.drawable.person); final LayoutParams imp = new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, DensityUtil.dip2px(this, 100)); ll.addView(im, 0, imp); //在ll里面添加TextView final TextView tv1 = new TextView(MainActivity.this); tv1.setText(getString(R.string.num)+":"+NUM); tv1.setTextSize(30); tv1.setTextColor(Color.BLACK); final LinearLayout.LayoutParams tvp1 = new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT,LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT); tvp1.setMargins(DensityUtil.dip2px(this, 20), 0, DensityUtil.dip2px(this, 20), 0); ll.addView(tv1, 1, tvp1); //在ll里面添加TextView final TextView tv2 = new TextView(MainActivity.this); tv2.setText(getString(R.string.name)+":"+NAME); tv2.setTextSize(30); tv2.setTextColor(Color.BLACK); final LinearLayout.LayoutParams tvp2 = new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT,LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT); tvp2.setMargins(DensityUtil.dip2px(this, 20), 0, DensityUtil.dip2px(this, 20), 0); ll.addView(tv2, 2, tvp2); //在ll里面添加TextView final TextView tv3 = new TextView(MainActivity.this); String sSEX; if(SEX == 1) sSEX = getString(R.string.male); else sSEX = getString(R.string.female); tv3.setText(getString(R.string.sex)+":"+sSEX); tv3.setTextSize(30); tv3.setTextColor(Color.BLACK); final LinearLayout.LayoutParams tvp3 = new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT,LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT); tvp3.setMargins(DensityUtil.dip2px(this, 20), 0, DensityUtil.dip2px(this, 20), 0); ll.addView(tv3, 3, tvp3); //在ll里面添加TextView final TextView tv4 = new TextView(MainActivity.this); tv4.setText(getString(R.string.birth)+":"+BIRTH); tv4.setTextSize(30); tv4.setTextColor(Color.BLACK); final LinearLayout.LayoutParams tvp4 = new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT,LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT); tvp4.setMargins(DensityUtil.dip2px(this, 20), 0, DensityUtil.dip2px(this, 20), 0); ll.addView(tv4, 4, tvp4); //内容描述,用于监听器的识别 ll.setContentDescription("Num"+NUM+":"+NAME); //为新添加的卡设置监听器 ll.setOnClickListener(new cardListener()); //改变按下效果的监听器 ll.setOnTouchListener(new cardTouchListener()); } //选项卡点击监听类 class cardListener implements OnClickListener { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Click_Flag = true;
//每个选项卡控件是用代码动态创建的,那怎么知道哪个选项卡触发了监听器呢,在这里用了一个内容描述,每次添加的时候都会有描述 OtherActivity.NUMANDNAME = v.getContentDescription(); finish(); } } //改变按下效果的监听器 class cardTouchListener implements OnTouchListener { @Override public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN || event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE){ //更改为按下时的图片 v.setBackgroundColor(Color.rgb(0x00, 0x33, 0xcc)); }else if(event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP || !v.hasFocus()){ //改为抬起时的图片 v.setBackgroundColor(Color.rgb(0x33, 0xb5, 0xe5)); } return false; } } }
布局文件如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#ffffff" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <HorizontalScrollView android:id="@+id/hsv" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:fillViewport="true" android:scrollbars="none" > <LinearLayout android:id="@+id/linear" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" > <TextView android:id="@+id/add" android:layout_width="250dp" android:layout_height="300dp" android:gravity="center" android:text="@string/add" android:background="#33b5e5" android:textSize="40sp" android:layout_margin="1dp" /> </LinearLayout> </HorizontalScrollView> <Button android:id="@+id/back" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:text="@string/back" android:textSize="20sp" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" /> </LinearLayout>
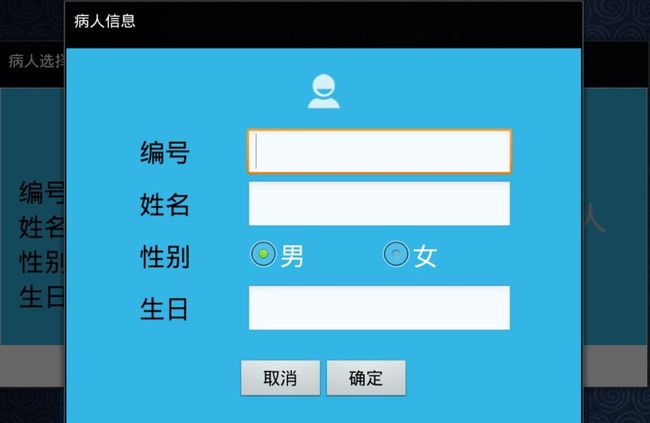
点击添加弹出另一个窗口,在新窗口中添加新信息然后返回并建立新的选项卡,新窗口的主要代码如下:
public class InfoActivity extends Activity{ private EditText numEdit = null; private EditText nameEdit = null; private RadioButton maleRadio = null; private RadioButton femaleRadio = null; private EditText birthEdit = null; private Button okButton = null; private Button cancelButton = null; //是否添加的标志,否代表点了取消 public static boolean added_FLAG = false; //选择过性别的标志 private boolean radiochacked_flag = false;
private String sNum; private String sName; private String sBirth; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.info); numEdit = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.et_num); nameEdit = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.et_name); birthEdit = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.et_birth); maleRadio = (RadioButton)findViewById(R.id.rb_male); maleRadio.setOnClickListener(new radioClickListener()); femaleRadio = (RadioButton)findViewById(R.id.rb_female); femaleRadio.setOnClickListener(new radioClickListener()); okButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.info_ok); cancelButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.info_cancel); cancelButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub added_FLAG = false; finish(); } }); okButton.setOnClickListener(new okButtonListener()); } class radioClickListener implements OnClickListener { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub radiochacked_flag = true; switch(v.getId()) { case R.id.rb_male: MainActivity.SEX = 1; break; case R.id.rb_female: MainActivity.SEX = 0; break; } } } class okButtonListener implements OnClickListener{
Toast toast = null; @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub added_FLAG = true; usednumber_flag = false; //没有选择性别则默认男 if(radiochacked_flag == false) MainActivity.SEX = 1; sNum = numEdit.getText().toString(); sName = nameEdit.getText().toString(); sBirth = birthEdit.getText().toString(); if(!"".equals(sNum.trim()) && !"".equals(sName.trim()) && !"".equals(sBirth.trim())) { PatientActivity.NUM = sNum; PatientActivity.NAME = sName; PatientActivity.BIRTH = sBirth; finish(); } else { toast = Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "信息填写不完整!", Toast.LENGTH_LONG); toast.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER, 0, 0); toast.show(); } } } }
具体效果如下:
有几个注意点:
1、在xml文件中,我们一般使用的视图长度单位是dp,这个单位是脱离具体像素的,对不同大小的屏幕有较好的适应性。但是在程序中,长度设置方法的参数是没有单位的,默认就是像素px,所以要进行dp到px的转化。我采用的转化方法是网上找的:
public class DensityUtil { /** * 根据手机的分辨率从 dp 的单位 转成为 px(像素) */ public static int dip2px(Context context, float dpValue) { final float scale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density; return (int) (dpValue * scale + 0.5f); } /** * 根据手机的分辨率从 px(像素) 的单位 转成为 dp */ public static int px2dip(Context context, float pxValue) { final float scale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density; return (int) (pxValue / scale + 0.5f); } }
2、我们在xml文件中创建视图的时候,如果要对某个视图使用监听器,则单独进行绑定即可,一般过程是先通过ID找到视图,然后绑定监听器SetOnClickListener()等,但是如果动态创建视图,就无法每个视图绑定不同的监听器,一般绑定同一个监听器,然后在监听器的类中进行判断是那个视图触发的监听器。判断可以采用内容描述,在动态创建视图时加上setContentDescription()这个方法,然后根据不同的内容描述进行判断,同样的思路也可以采用setID(),这样就和RadioButton的一般用法相似。