torch.nn中的非线性激活使用
1、神经网络中的非线性激活
在神经网络中,**非线性激活函数(Non-linear Activation Functions)**是引入非线性变换的关键组件,使神经网络能够学习并建模复杂的非线性关系。如果没有激活函数,无论神经网络有多少层,其整体表现仍等同于一个线性模型(如逻辑回归),无法解决非线性问题(如图像分类、自然语言处理等)。
为什么需要非线性激活?
- 打破线性限制:线性变换的叠加仍然是线性的(如矩阵乘法的结合律)。非线性激活允许网络学习输入数据中的非线性模式。
- 增强表达能力:通过非线性激活,神经网络可以逼近任意复杂函数(万能逼近定理)。
- 多层级联的有效性:深层网络的每一层通过非线性激活逐步提取更高阶的特征(如边缘→纹理→物体部件→完整物体)。
常见非线性激活函数
-
Sigmoid
公式: σ ( x ) = 1 1 + e − x \sigma(x) = \frac{1}{1 + e^{-x}} σ(x)=1+e−x1
输出范围:(0, 1)
用途:二分类输出层(概率输出)。
缺点:
梯度消失(梯度在两端接近0,深层网络难以训练)。
输出非零中心(可能影响梯度下降效率)。 -
Tanh(双曲正切)
公式: tanh ( x ) = e x − e − x e x + e − x \tanh(x) = \frac{e^x - e^{-x}}{e^x + e^{-x}} tanh(x)=ex+e−xex−e−x
输出范围:(-1, 1)
优点:零中心化(缓解梯度下降的震荡问题)。
缺点:梯度消失问题仍存在。 -
ReLU(Rectified Linear Unit)
公式: ReLU ( x ) = max ( 0 , x ) \text{ReLU}(x) = \max(0, x) ReLU(x)=max(0,x)
优点:
计算高效(无需指数运算)。
缓解梯度消失(正区间梯度恒为1)。
缺点:
Dead ReLU问题:负输入梯度为0,神经元可能永久失效(可通过Leaky ReLU或初始化优化缓解)。 -
Leaky ReLU
公式: LeakyReLU ( x ) = { x if x ≥ 0 α x if x < 0 \text{LeakyReLU}(x) = \begin{cases} x & \text{if } x \geq 0 \\ \alpha x & \text{if } x < 0 \end{cases} LeakyReLU(x)={xαxif x≥0if x<0
改进:负区间引入小斜率(如α=0.01),避免神经元死亡。 -
Swish
公式: Swish ( x ) = x ⋅ σ ( β x ) \text{Swish}(x) = x \cdot \sigma(\beta x) Swish(x)=x⋅σ(βx)(σ为Sigmoid,β可学习或固定)
特点:平滑且非单调,在某些任务中表现优于ReLU。 -
Softmax
公式:对输出层进行归一化, Softmax ( x i ) = e x i ∑ j e x j \text{Softmax}(x_i) = \frac{e^{x_i}}{\sum_j e^{x_j}} Softmax(xi)=∑jexjexi
用途:多分类输出层,输出概率分布。
如何选择激活函数?
- 隐藏层:通常首选 ReLU(简单高效),深层网络可尝试 Leaky ReLU 或 Swish。
- 输出层:
二分类:Sigmoid。
多分类:Softmax。
回归问题:线性激活(无激活函数)。
非线性激活的作用示例
假设一个简单的神经网络:
无激活函数:
Output = W 2 ( W 1 X + b 1 ) + b 2 = ( W 2 W 1 ) X + ( W 2 b 1 + b 2 ) \text{Output} = W_2(W_1X + b_1) + b_2 = (W_2W_1)X + (W_2b_1 + b_2) Output=W2(W1X+b1)+b2=(W2W1)X+(W2b1+b2)
等价于单层线性模型。
加入ReLU:
Output = W 2 ⋅ ReLU ( W 1 X + b 1 ) + b 2 \text{Output} = W_2 \cdot \text{ReLU}(W_1X + b_1) + b_2 Output=W2⋅ReLU(W1X+b1)+b2
非线性关系得以保留,模型能力显著提升。
总结
非线性激活函数是神经网络的核心,决定了模型的表达能力和训练动态。选择时需权衡梯度传播效率、计算成本和任务需求。现代深度学习框架(如PyTorch、TensorFlow)已内置多种激活函数,开发者可通过实验选择最佳方案。
2、torch.nn中的非线性激活
Non-linear Activations
使用方法见:torch.nn中的非线性激活介绍合集——Pytorch中的非线性激活
- nn.ELU——按元素应用 Exponential Linear Unit (ELU) 函数。
- nn.Hardshrink——按元素应用 Hard Shrinkage (Hardshrink) 函数。
- nn.Hardsigmoid——按元素应用 Hardsigmoid 函数。
- nn.Hardtanh——按元素应用 HardTanh 函数。
- nn.Hardswish——按元素应用 Hardswish 函数。
- nn.LeakyReLU——按元素应用 LeakyReLU 函数。
- nn.LogSigmoid——按元素应用 Logsigmoid 函数。
- nn.MultiheadAttention——允许模型共同关注来自不同表示子空间的信息。
- nn.PReLU——应用元素级 PReLU 函数。
- nn.ReLU——按元素应用修正的线性单元函数。
- nn.ReLU6——按元素应用 ReLU6 函数。
- nn.RReLU——按元素应用随机泄漏整流线性单元函数。
- nn.SELU——按元素应用 SELU 函数。
- nn.CELU——按元素应用 CELU 函数。
- nn.GELU——应用 Gaussian Error Linear Units 功能。
- nn.Sigmoid——按元素应用 Sigmoid 函数。
- nn.SiLU——按元素应用 Sigmoid 线性单元 (SiLU) 功能。
- nn.Mish——按元素应用 Mish 函数。
- nn.Softplus——按元素应用 Softplus 函数。
- nn.Softshrink——按元素应用软收缩功能。
- nn.Softsign——应用元素级 Softsign 函数。
- nn.Tanh——按元素应用 Hyperbolic Tangent (Tanh) 函数。
- nn.Tanhshrink——应用元素级 Tanhshrink 函数。
- nn.Threshold——对输入 Tensor 的每个元素进行阈值设置。
- nn.GLU——应用门控线性单元功能。
3、torch.nn中非线性激活的使用实例
3.1 nn.ReLU使用实例
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import ReLU
input = torch.tensor([[3, -2],
[1, -1.5]])
print(input.shape)
class My_module(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(My_module, self).__init__()
self.relu1 = ReLU()
def forward(self, input):
output = self.relu1(input)
return output
mymodule = My_module()
output = mymodule(input)
print(output)
输出:
torch.Size([2, 2])
tensor([[3., 0.],
[1., 0.]])
可以看到,原始输入中小于0的元素都被整流为0了,大于等于0的元素保持不变。
3.2 nn.Sigmoid使用实例
- 测试nn.Sigmoid
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Sigmoid
input = torch.tensor([1, 0])
print(input.shape)
class My_module(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(My_module, self).__init__()
self.sigmoid1 = Sigmoid()
def forward(self, input):
output = self.sigmoid1(input)
return output
mymodule = My_module()
output = mymodule(input)
print(output)
torch.Size([2])
tensor([0.7311, 0.5000])
可以代入数据验证一下: σ ( x ) = 1 1 + e − x \sigma(x) = \frac{1}{1 + e^{-x}} σ(x)=1+e−x1
σ ( 1 ) = 0.7310585786... \sigma(1)=0.7310585786... σ(1)=0.7310585786... σ ( 0 ) = 0.5000 \sigma(0)=0.5000 σ(0)=0.5000
- 使用真实图像数据
使用torchvision.datasets内置数据集并使用torchvision.transforms预处理数据集,使用DataLoader加载数据。
torchvision.datasets内置数据集、transforms、DataLoader及Tensorboard的使用见:
torchvision中数据集的使用
Pytorch中的Transforms学习
Pytorch中DataLoader的介绍
Pytorch中Tensorboard的学习
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Sigmoid
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("dataset", train=False, download=False,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor())
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=32)
class My_module(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(My_module, self).__init__()
self.sigmoid1 = Sigmoid()
def forward(self, input):
output = self.sigmoid1(input)
return output
mymodule = My_module()
writer = SummaryWriter("runs")
step = 0
for data in dataloader:
imgs, targets = data
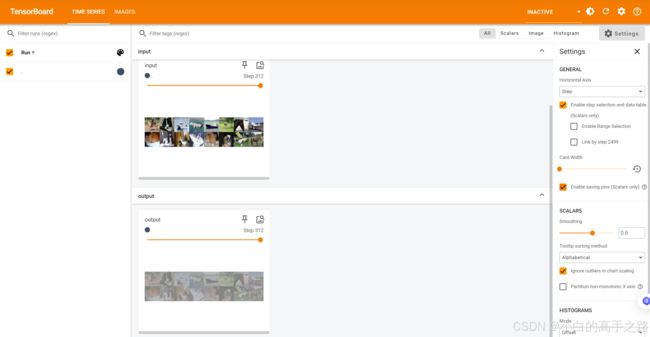
writer.add_images("input", imgs, global_step=step)
output = mymodule(imgs)
writer.add_images("output", output, step)
step += 1
writer.close()
运行完在终端执行命令:
tensorboard --logdir=runs
TensorFlow installation not found - running with reduced feature set.
Serving TensorBoard on localhost; to expose to the network, use a proxy or pass --bind_all
TensorBoard 2.19.0 at http://localhost:6006/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)