android sqlite数据库封装 实现crud
android常用的数据保存方式有文件、sharepreferences、数据库、网络、contentprovider集中方式。
文件存储方式,经常使用在缓存整个页面数据,比如电子书内容、html数据等。
sharepreferrences存储方式,实质也就是xml文件存储的封装,常用于存储配置参数数据。当然也可以用文件存储+Properties来存储参数数据。
网络,就是将数据存储在网络空间上。
contentprovider主要作用是统一数据存储方式,实现数据共享,以后有机会仔细分析下。
数据库的方式,常用在存储一系列的结构复杂的数据,轻量级的数据库SQlit使用起来还是比较简单,但是总想能像hibernate似的框架可以进行下封装,实现orm并且可以实现简单的rcud。这里就介绍下一个分装过程,源码下载在后面。
一、封装数据库的类结构
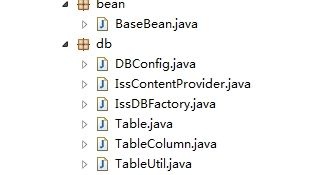
结构比较简单:BaseBean.java--实体类的基类
DBConfig.java---数据库的参数,包括数据库名、要创建的表列表、数据库版本等
IssContentProvider.java--继承了ContentProvider,定义了数据库的初始化和操作
DBFactory--数据库工厂类
Table.java----定义Table的annotation
TableColumn.java--定义表的列的annotation和属性
TableUtil.java--书库操作工具类,主要是获得表和根据标签拼装sql语句
二、封装数据库的使用过程
由于封装后的数据库使用比较简单,就跟配置好hibernate之后使用似的,所以咱们先看下咱们使用,不理解的地方,等分析了整个实现过程后就行清晰了。
1、要实现orm,肯定要定义带标签的实体类,当然是继承BaseBean类。
2、要将数据库参数传递给DBConfig,并初始化。
3、数据库操作类,通过contentprovideder实现crud。
用例子看下
1,定义实体类
- public class SmartDownloadBean extends BaseBean<SmartDownloadBean> {
- @TableColumn(type = TableColumn.Types.TEXT, isIndex = true, isNotNull = true)
- public String downpath;
- @TableColumn(type = TableColumn.Types.INTEGER)
- public int threadid;
- @TableColumn(type = TableColumn.Types.INTEGER)
- public int downlength;
- @Override
- public SmartDownloadBean parseJSON(JSONObject jsonObj) {
- return null;
- }
- @Override
- public JSONObject toJSON() {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- return null;
- }
- @Override
- public SmartDownloadBean cursorToBean(Cursor cursor) {
- this.downpath = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("downpath"));
- this.threadid = cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex("threadid"));
- this.downlength = cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex("downlength"));
- return this;
- }
- @Override
- public ContentValues beanToValues() {
- ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
- if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(downpath)) {
- values.put("downpath", downpath);
- }
- if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(threadid+"")) {
- values.put("threadid", threadid);
- }
- if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(downlength+"")) {
- values.put("downlength", downlength);
- }
- return values;
- }
- }
实体类通过标签,定义了对应表的列名、及列的属性
2、定义要创建的表、数据名等参数
- /**
- * 数据库配置
- **/
- public class SssProvider extends IssContentProvider {
- @Override
- public void init() {
- // 数据库相关参数设置
- DBConfig config = new DBConfig.Builder()
- .addTatble(SmartDownloadBean.class)
- .setName("sss.db").setVersion(2)
- .setAuthority("com.sss").build();
- IssDBFactory.init(getContext(), config);
- }
- }
要定义都个表的话,再addTatble(Bean.class)即可。
3、调用数据库的工具类
- /**
- * 操作数据库的utils
- *
- * @author dllik 2013-11-23
- */
- public class DBUtils {
- public static Uri URI_SMARTDOWNLOAD = IssContentProvider.buildUri(SmartDownloadBean.class);
- /**
- * 获取每条线程已经下载的文件长度
- *
- * @param context
- * @param downpath
- * @return
- */
- public static Map<Integer, Integer> querySmartDownData(Context context, String downpath) {
- ContentResolver mResolver = context.getContentResolver();
- Cursor cursor = mResolver.query(URI_SMARTDOWNLOAD, null, "downpath=?", new String[] {
- downpath
- }, null);
- Map<Integer, Integer> data = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
- while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
- SmartDownloadBean bean = new SmartDownloadBean();
- bean.cursorToBean(cursor);
- data.put(bean.threadid, bean.downlength);
- }
- cursor.close();
- return data;
- }
- /**
- * 保存每条线程已经下载的文件长度
- *
- * @param context
- * @param path
- * @param map
- */
- public static void insertSmartDown(Context context, String path, Map<Integer, Integer> map) {
- ContentResolver mResolver = context.getContentResolver();
- for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
- SmartDownloadBean bean = new SmartDownloadBean();
- bean.downpath = path;
- bean.downlength = entry.getValue();
- bean.threadid = entry.getKey();
- mResolver.insert(URI_SMARTDOWNLOAD, bean.beanToValues());
- }
- }
- /**
- * 实时更新每条线程已经下载的文件长度
- *
- * @param context
- * @param path
- * @param map
- */
- public static void updateSmartDown(Context context, String path, Map<Integer, Integer> map) {
- ContentResolver mResolver = context.getContentResolver();
- for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
- SmartDownloadBean bean = new SmartDownloadBean();
- bean.downpath = path;
- bean.downlength = entry.getValue();
- bean.threadid = entry.getKey();
- mResolver.update(URI_SMARTDOWNLOAD, bean.beanToValues(), "downpath=? and threadid=?",
- new String[] {
- bean.downpath, bean.threadid + ""
- });
- }
- }
- /**
- * 当文件下载完成后,删除对应的下载记录
- *
- * @param context
- * @param path
- */
- public static void deleteSmartDown(Context context, String path) {
- ContentResolver mResolver = context.getContentResolver();
- mResolver.delete(URI_SMARTDOWNLOAD, "downpath=?", new String[] {
- path
- });
- }
- }
三、数据库的封装过程
看下实体类的基类
- public abstract class BaseBean<T> implements Serializable {
- private static final long serialVersionUID = -804757173578073135L;
- @TableColumn(type = TableColumn.Types.INTEGER, isPrimary = true)
- public static final String _ID = "_id";
- /**
- * 将json对象转化为Bean实例
- *
- * @param jsonObj
- * @return
- */
- public abstract T parseJSON(JSONObject jsonObj);
- /**
- * 将Bean实例转化为json对象
- *
- * @return
- */
- public abstract JSONObject toJSON();
- /**
- * 将数据库的cursor转化为Bean实例(如果对象涉及在数据库存取,需实现此方法)
- *
- * @param cursor
- * @return
- */
- public abstract T cursorToBean(Cursor cursor);
- /**
- * 将Bean实例转化为一个ContentValues实例,供存入数据库使用(如果对象涉及在数据库存取,需实现此方法)
- *
- * @return
- */
- public abstract ContentValues beanToValues();
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public T parseJSON(Gson gson, String json) {
- return (T) gson.fromJson(json, this.getClass());
- }
- public ContentValues toValues() {
- ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
- try {
- Class<?> c = getClass();
- Field[] fields = c.getFields();
- for (Field f : fields) {
- f.setAccessible(true);
- final TableColumn tableColumnAnnotation = f.getAnnotation(TableColumn.class);
- if (tableColumnAnnotation != null) {
- if (tableColumnAnnotation.type() == TableColumn.Types.INTEGER) {
- values.put(f.getName(), f.getInt(this));
- } else if (tableColumnAnnotation.type() == TableColumn.Types.BLOB) {
- values.put(f.getName(), (byte[]) f.get(this));
- } else if (tableColumnAnnotation.type() == TableColumn.Types.TEXT) {
- values.put(f.getName(), f.get(this).toString());
- } else {
- values.put(f.getName(), f.get(this).toString());
- }
- }
- }
- } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- } catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return values;
- }
- }
说明几点:1、用到了泛型,因为定义的数据实体类有多个
2、实现序列化,实体类数据通过Intent进行传递
3、定义了一个主键id
数据库参数类
- public class DBConfig {
- final ArrayList<Class<? extends BaseBean<?>>> tableList;
- final String dbName;
- final int dbVersion;
- final String authority;
- final ArrayList<String> tableNameList;
- private DBConfig(final Builder builder) {
- tableList = builder.tableList;
- dbName = builder.dbName;
- dbVersion = builder.dbVersion;
- authority = builder.authority;
- tableNameList = new ArrayList<String>();
- for(Class<? extends BaseBean<?>> c:tableList){
- String name = TableUtil.getTableName(c);
- tableNameList.add(name);
- }
- }
- public static class Builder {
- private ArrayList<Class<? extends BaseBean<?>>> tableList;
- private String dbName;
- private int dbVersion;
- private String authority = "com.iss.mobile";
- public Builder() {
- tableList = new ArrayList<Class<? extends BaseBean<?>>>();
- }
- public Builder setName(String name) {
- dbName = name;
- return this;
- }
- public Builder setVersion(int version) {
- dbVersion = version;
- return this;
- }
- public Builder addTatble(Class<? extends BaseBean<?>> table) {
- tableList.add(table);
- return this;
- }
- public Builder setAuthority(String authority){
- this.authority = authority;
- return this;
- }
- public DBConfig build(){
- return new DBConfig(this);
- }
- }
- }
通过该类,来设置数据库的参数,在初始化数据库的时候用到。
内容提供者类,初始化和操作数据库
- public abstract class IssContentProvider extends ContentProvider {
- public static String CONTENT_TYPE = "vnd.android.cursor.dir/iss.db";
- protected SQLiteDatabase mDB;
- public static String AUTHORITY = "com.iss.mobile";
- @Override
- public boolean onCreate() {
- init();
- IssDBFactory issDBFactory = IssDBFactory.getInstance();
- DBConfig config = IssDBFactory.getInstance().getDBConfig();
- if (config == null) {
- throw new RuntimeException("db factory not init");
- }
- AUTHORITY = config.authority;
- CONTENT_TYPE = "vnd.android.cursor.dir/" + config.dbName;
- mDB = issDBFactory.open();
- return true;
- }
- public abstract void init();
- public static final String SCHEME = "content";
- @Override
- public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values) {
- String tableName = getTableName(uri);
- long result = mDB.insert(tableName, null, values);
- if (result != -1) {
- getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(uri, null);
- }
- return buildResultUri(tableName, result);
- }
- @Override
- public int bulkInsert(Uri uri, ContentValues[] values) {
- mDB.beginTransaction();
- String tableName = getTableName(uri);
- for(ContentValues value:values){
- mDB.insert(tableName, null, value);
- }
- mDB.setTransactionSuccessful();
- mDB.endTransaction();
- return values.length;
- }
- @Override
- public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection, String[] selectionArgs,
- String sortOrder) {
- String tableName = getTableName(uri);
- return mDB.query(tableName, projection, selection, selectionArgs, null, null, sortOrder);
- }
- @Override
- public String getType(Uri uri) {
- return CONTENT_TYPE;
- }
- @Override
- public int delete(Uri uri, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
- String tableName = getTableName(uri);
- int result = mDB.delete(tableName, selection, selectionArgs);
- if (result != 0) {
- getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(uri, null);
- }
- return result;
- }
- @Override
- public int update(Uri uri, ContentValues values, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
- String tableName = getTableName(uri);
- int result = mDB.update(tableName, values, selection, selectionArgs);
- if (result != 0) {
- getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(uri, null);
- }
- return result;
- }
- private Uri buildResultUri(String tableName, long result) {
- final Uri.Builder builder = new Uri.Builder();
- DBConfig config = IssDBFactory.getInstance().getDBConfig();
- if (config == null) {
- throw new RuntimeException("db factory not init");
- }
- builder.scheme(SCHEME);
- builder.authority(config.authority);
- builder.path(tableName);
- builder.appendPath(String.valueOf(result));
- return builder.build();
- }
- private String getTableName(Uri uri) {
- DBConfig config = IssDBFactory.getInstance().getDBConfig();
- if (config == null) {
- throw new RuntimeException("db factory not init");
- }
- String path = uri.getLastPathSegment();
- if (!config.tableNameList.contains(path)) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown URI " + uri);
- }
- return path;
- }
- public static Uri buildUri(String path, String id) {
- final Uri.Builder builder = new Uri.Builder();
- DBConfig config = IssDBFactory.getInstance().getDBConfig();
- if (config == null) {
- throw new RuntimeException("db factory not init");
- }
- builder.scheme(SCHEME);
- builder.authority(config.authority);
- builder.path(path);
- builder.appendPath(id);
- return builder.build();
- }
- public static Uri buildUri(String path) {
- final Uri.Builder builder = new Uri.Builder();
- DBConfig config = IssDBFactory.getInstance().getDBConfig();
- if (config == null) {
- throw new RuntimeException("db factory not init");
- }
- builder.scheme(SCHEME);
- builder.authority(config.authority);
- builder.path(path);
- return builder.build();
- }
- public static Uri buildUri(Class<? extends BaseBean<?>> c) {
- final String tableName = TableUtil.getTableName(c);
- return buildUri(tableName);
- }
- }
该内容提供者在创建的时候,先执行init()(将要数据库的参数设置好,再将参数传递给工厂类),工厂类根据参数创建数据库mDB = issDBFactory.open();
数据库工厂类:
- public class IssDBFactory {
- private static final String TAG = IssDBFactory.class.getSimpleName();
- private DBConfig mConfig;
- private SQLiteDatabase mSQLiteDB;
- private IssDBOpenHelper mDBOpenHelper;
- private final Context mContext;
- private static IssDBFactory instance ;
- private IssDBFactory(Context context) {
- mContext = context;
- }
- public static void init(Context context,DBConfig dbConfig){
- if(instance==null){
- instance = new IssDBFactory(context.getApplicationContext());
- instance.setDBConfig(dbConfig);
- }
- }
- public static IssDBFactory getInstance(){
- return instance;
- }
- public void setDBConfig(DBConfig dbConfig){
- mConfig = dbConfig;
- }
- public DBConfig getDBConfig(){
- return mConfig;
- }
- public SQLiteDatabase open() {
- if(mSQLiteDB==null){
- mDBOpenHelper = new IssDBOpenHelper(mContext, mConfig.dbName, null, mConfig.dbVersion);
- mSQLiteDB = mDBOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
- }
- return mSQLiteDB;
- }
- public void close() {
- if(mDBOpenHelper!=null){
- mDBOpenHelper.close();
- }
- }
- public void beginTransaction() {
- if(mSQLiteDB==null){
- mSQLiteDB.beginTransaction();
- }
- }
- public void endTransaction() {
- if (mSQLiteDB==null&&mSQLiteDB.inTransaction()) {
- mSQLiteDB.endTransaction();
- }
- }
- public void setTransactionSuccessful() {
- if (mSQLiteDB==null){
- mSQLiteDB.setTransactionSuccessful();
- }
- }
- private final class IssDBOpenHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
- public IssDBOpenHelper(Context context, String name, CursorFactory factory, int version) {
- super(context, name, factory, version);
- }
- @Override
- public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
- for (Class<? extends BaseBean<?>> table : mConfig.tableList) {
- try {
- for (String statment : TableUtil.getCreateStatments(table)) {
- Log.d(TAG, statment);
- db.execSQL(statment);
- }
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- Log.e(TAG, "Can't create table " + table.getSimpleName());
- }
- }
- /**
- * 初始化数据
- */
- // initData();
- }
- @Override
- public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
- Log.d(TAG, "onUpgrade: " + oldVersion + " >> " + newVersion);
- for (Class<? extends BaseBean<?>> table : mConfig.tableList) {
- try {
- db.execSQL("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS " + TableUtil.getTableName(table));
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- Log.e(TAG, "Can't create table " + table.getSimpleName());
- }
- }
- onCreate(db);
- }
- }
- public void cleanTable(String tableName, int maxSize, int batchSize) {
- Cursor cursor = mSQLiteDB.rawQuery("select count(_id) from " + tableName, null);
- if (cursor.getCount() != 0 && cursor.moveToFirst() && !cursor.isAfterLast()) {
- if (cursor.getInt(0) >= maxSize) {
- int deleteSize = maxSize - batchSize;
- mSQLiteDB.execSQL("delete from " + tableName + " where _id in (" + "select _id from " + tableName
- + " order by _id " + " limit " + deleteSize + " )");
- }
- }
- cursor.close();
- }
看到这用过数据库的就比较清晰了,用到了SQLiteOpenHelper是以内部类的形式实现的,在oncreat里创建了表,在onupgrade里实现了更新表。
其中用到TableUtil.getCreateStatments(table),
数据库工具类:
- public class TableUtil {
- public static String getTableName(Class<? extends BaseBean<?>> c) {
- String name = null;
- Table tableNameAnnotation = c.getAnnotation(Table.class);
- if (tableNameAnnotation != null) {
- name = tableNameAnnotation.name();
- }
- if (TextUtils.isEmpty(name)) {
- name = c.getSimpleName();
- }
- return name;
- }
- /**
- * 拼装sql用的建表语句以及索引语句
- *
- * @param c
- * @return
- */
- public final static List<String> getCreateStatments(Class<? extends BaseBean<?>> c) {
- final List<String> createStatments = new ArrayList<String>();
- final List<String> indexStatments = new ArrayList<String>();
- final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
- final String tableName = getTableName(c);
- builder.append("CREATE TABLE ");
- builder.append(tableName);
- builder.append(" (");
- int columnNum = 0;
- for (final Field f : c.getFields()) {
- f.setAccessible(true);
- final TableColumn tableColumnAnnotation = f.getAnnotation(TableColumn.class);
- if (tableColumnAnnotation != null) {
- columnNum++;
- String columnName = f.getName();
- builder.append(columnName);
- builder.append(" ");
- if (tableColumnAnnotation.type() == TableColumn.Types.INTEGER) {
- builder.append(" INTEGER");
- } else if (tableColumnAnnotation.type() == TableColumn.Types.BLOB) {
- builder.append(" BLOB");
- } else if (tableColumnAnnotation.type() == TableColumn.Types.TEXT) {
- builder.append(" TEXT");
- } else {
- builder.append(" DATETIME");
- }
- if (tableColumnAnnotation.isPrimary()) {
- builder.append(" PRIMARY KEY");
- } else {
- if (tableColumnAnnotation.isNotNull()) {
- builder.append(" NOT NULL");
- }
- if (tableColumnAnnotation.isUnique()) {
- builder.append(" UNIQUE");
- }
- }
- if (tableColumnAnnotation.isIndex()) {
- indexStatments.add("CREATE INDEX idx_" + columnName + "_" + tableName + " ON "
- + tableName + "(" + columnName + ");");
- }
- builder.append(", ");
- }
- }
- builder.setLength(builder.length() - 2); // remove last ','
- builder.append(");");
- if (columnNum > 0) {
- createStatments.add(builder.toString());
- createStatments.addAll(indexStatments);
- }
- return createStatments;
- }
- }
就两个方法,获取表名,在更新表的时候用到,拼装sql在创建表时候用到。
最后两个标签类:
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
- public @interface Table {
- String name();
- }
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
- public @interface TableColumn {
- public enum Types {
- INTEGER, TEXT, BLOB, DATETIME
- }
- Types type() default Types.TEXT;
- boolean isPrimary() default false;
- boolean isIndex() default false;
- boolean isNotNull() default false;
- boolean isUnique() default false;
- }
思路比较简单,就是注意先标签、过滤器、内容提供者的使用就行了。
最后是封装包代码,使用过程没有加,自己加入吧:http://download.csdn.net/detail/xiangxue336/7001299