嵌入式(Embedded System)笔记 —— Cortex-M3 Introduction and Basics(上)
随着课内的学习,我想把每节课所学记录下来,以作查阅、以饲读者。由于我所上的是英文班课程,因此我将把关键术语的英文给出,甚至有些内容直接使用英文。
本次所介绍内容是关于Cortex-M3的基础内容。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1、什么是嵌入式系统(Embedded System)
完全嵌入受控器件内部,为特定应用而设计的专用计算机系统,而平时咱们所用的个人计算机则属于通用计算机系统。
它只能实现一件或少量几件功能,同时还有很多限制,例如:电力较低,内存较小等。
2、微处理器(microprocessor,μP)和微控制器(microcontroller,μC)的区别
这个问题比较复杂,我只做简单解释,这里推荐百度知道上一个人的回答,比较详细准确地讲解了这两者的区别。
微处理器仅仅是一个单芯片CPU;而微控制器则是一块集成电路,上面集成了CPU与很多外围设备,例如:Memory、IO、Bus、Interrupt。
微处理器就是我们个人计算机中所说的CPU,而微控制器便是我们平时所说的“单片机”,所有智能设备上面都有单片机的存在。
3、嵌入式系统、通用计算机系统与微处理器、微控制器的关系
从上面的定义很容易看出,嵌入式系统必然包含微控制器,微控制器是嵌入式系统的核心;而通用计算机系统则必然包含微处理器,作为其CPU存在。
4、冯·诺依曼架构与哈佛架构
计算机的体系结构是指:其内部CPU、Memory、IO、Bus之类都是如何设计的。
而这两种架构,则是对计算机体系结构的一种分类——针对存储器所作的分类。
冯·诺依曼架构(又名普林斯顿结构):指令和数据存在一个存储器中。这种架构的中央处理器(CPU)或者微控制器有8086、ARM7、MIPS等。
哈佛架构:有两个存储器,指令存储器专门存指令, 数据存储器专门存数据。这种架构执行效率很高,非常方便流水线(Pipeline)的实现,目前使用这种架构的中央处理器或者微控制器有51单片机以及ARM9、ARM10、ARM11等。
5、什么是Cortex-M3
这是ARM公司所开发的一种计算机架构。ARM公司设计、维护这种架构,向其它公司出售版权(IPL,Intellectual Property Licensing),例如苹果。到2009年为之,ARM处理器已经占有了嵌入式32位RISC处理器大约90%的市场。而当ARM处理器开发至版本ARM7时,分为了三个方向:
| Application Cortex-A | 用于高性能计算 |
| Read-Time Cortex-R | 用于实时处理,例如数字信号处理 |
| Microcontroller Cortex-M | 用于嵌入式微处理器 |
而我这门课所学的Cortex-M3也就是ARM架构的嵌入式版本之一,不知道这样说,够不够清楚?
6、体系架构简介
图暂时还没有搞到,先仅给出文字说明。
核心是CPU,加上一个处理Interrupt的模块和一个处理Debug的模块。而外围,Interrupt使用前者处理,Debug则通过外围一个Debug模块与一个Debug接口配合核心的Debug模块协同工作。另外,CPU和Memory有两条总线(Bus),一个是Data Bus,另一个则是Inst Bus(Inst是Instruction的缩写,即指令)。Memory分为三部分:Code Memory、Memory System and Peripherals、Private Peripherals;而Bus则被一个Memory Protection Unit所监控,防止CPU访问没有权限的内存空间。
这架构听起来很乱,或许以后加上图会清晰些,但真正理解还是要在学完Cortex-M3之后才可以。
7、Cortex-M3概述
| 32-bit microprocessor | 32-bit data path, 32-bit registers, 32-bit memory interfaces |
| Harvard architecture | separate instruction bus and data bus, which allows instructions and data accesses to take place at the same time |
| 4GB Memory space | |
| Registers | Registers (R0 to R15) and special registers |
| Two operation modes | thread mode and handler mode |
| Two access levels | privileged level and user level |
| Interrupts and Exceptions | a built-in Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller, supporting 11 system exceptions plus 240 external IRQs |
| MPU(Memory Protection Unit) | an optional Memory Protection Unit allows access rules to be set up for privileged access and user program access |
| The Instruction Set | Thumb-2 instruction set allows 32-bit instructions and 16-bit instructions to be used together; no ARM instructions allowed |
| Fixed internal debugging components | provide debugging operation supports and features such as breakpoints, single step |
8、Cortex-M3优点
| Greater performance efficiency | allowing more work to be done without increasing the frequency or power requirements |
| Low power consumption | enabling longer battery life |
| Enhanced determinism | guaranteeing that critical tasks and interrupts are serviced in a known number of cycles |
| Improved code density | ensuring that code fits in even the smallest memory |
| Ease of use | providing easier programmability and debugging |
| Lower-cost solutions | reducing 32-bit-based system costs at less than US$1 for the first time |
| Wide choice of development tools | from low-cost or free compilers to full-featured development suites |
9、Cortex-M3 Processors和Cortex-M3-Based MCUs的区别
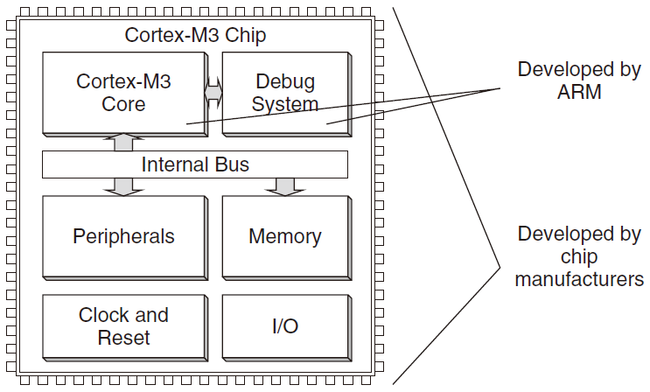
前者是ARM公司开发的,可以简单看成两个模块:Cortex-M3 Core、Debug System。
而把前者通过Internal Bus与外围设备(Peripherals、Memory、Clock and Reset、I/O)相连,就组成了一个MCU(微控制器),这个集成电路是个Cortex-M3 Chip,是别的公司使用ARM架构开发的Cortex-M3-Based MCU。
10、指令集简介
ARM架构经过多年的发展,有三个指令集,分别是ARM instructions、Thumb instructions和Thumb-2 instructions。其中ARM set用于高性能计算,都是32位的指令;Thumb set则都是16位指令,性能较差,但更密级(节省空间);而Thumb-2 set则是32位指令,具有同ARM set般的高性能。
而Cortex-M3则包含所有的Thumb指令和部分的Thumb-2指令,因此指令便有16位和32位两种。
11、操作模式——两种工作阶段(processor mode)和两种权限级别(access level)简介
这里只对几个术语做出解释。
Cortex-M3中有两种工作阶段:Thread和Handler。前者是正常运行代码的阶段,而后者则是中断。
Cortex-M3中有两种权限级别(privilege level):Privilege和User。前者是默认的,相当用root,拥有所有权限;后者则对一些特殊内存空间没有读写权。
图中Exception是异常的意思,表示各种中断(Interrupt);Control Register则是一个寄存器,专门用来修改权限级别的。