散列表
摘要
散列表的实现常常叫做散列(hashing).散列是一种用于以常数平均时间执行插入、删除和查找的技术。但是,那些需要元素间任何排序信息的操作将不会得到有效的支持。
直接寻址表
当关键字的全域U比较小时,直接寻址是一种简单而有效的技术。一般可以采用数组实现直接寻址表,数组下标对应的就是关键字的值,即具有关键字k的元素被放在直接寻址表的槽k中。直接寻址表的字典操作实现比较简单,直接操作数组即可,只需O(1)的时间
散列表
直接寻址表的不足之处在于当关键字的范围U很大时,在计算机内存容量的限制下,构造一个存储|U|大小的数组不太实际。当存储在字典中的关键字集合K比所有可能的关键字域U要小的多时,散列表需要的存储空间要比直接寻址表少的很多。散列表通过散列函数h计算出关键字k在槽的位置。散列函数h将关键字域U映射到散列表T[0...m-1]的槽位上:
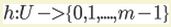
采用散列函数的目的在于缩小需要处理的小标范围,从而降低空间的开销
散列函数
一个好的散列函数应(近似地)满足简单一致散列的假设:每个关键字都等可能地散列到m个槽位的任何一个之中去,并与其他的关键字已被散列到哪一个槽位中无关。多数散列函数都假定关键字域为自然数集 N = {0, 1, 2,...}.如果所给关键字不是自然数,则必须有一种方法来将它们解释为自然数
除法散列法
通过取k除以m的余数,来将关键字k映射到m个槽的某一个中去,散列函数为:
h(k) = k mod m;
乘法散列法
用关键字k先乘上A,然后取出k * A 的小数部分,然后用m乘以这个值,再取结果的底(floor),散列函数为:
h(k) = floor(m * (k * A % 1));
根据研究,knuth认为A取(sqrt(5) - 1) / 2是一个比较理想的值(ps:我是没搞懂这个方法)
全域散列
全域散列用的方式是:随机地选择散列函数,使之独立于要存储的关键字,这样就很难出现最坏情况,平均性能很好,最后设计的散列函数为:
h(a, b) = ((ak + b) % p) % m;
这几个散列函数可以参考算法导论,我就是看了点皮毛,不多说了
碰撞处理
散列表的缺点就是容易出现冲突(也叫碰撞),两个关键字可能映射到同一个槽中,然后就产生了冲突,解决冲突的方法有很多种,这里只讨论其中最简单的两种:
链接法
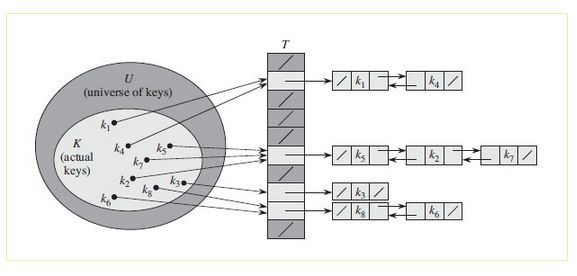
就是把散列到同一个槽中的所有元素都放在一个链表中,如果,槽j中有一个指针,它指向所有散列到j的元素构成的链表的头;如果不存在这样的元素,则j为null,如图所示:
参考代码(c语言)
参考链接:
http://mindlee.net/2011/08/06/solve-hash-conflict-links-method-and-separation-open-addressing-method/, 我改善了原文中的链接法解决hash冲突的代码,并且增加了冲突测试用例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXN 400000 // MAXN : size
int prime[MAXN]; // true : prime number
/**
* 每行链表上的一个的节点
*/
typedef struct lnode {
int element;
struct lnode *next;
} *position;
/**
* 一个点代表槽中的一个链表上的一个点
*/
typedef struct hashtb {
int tablesize;
position *dlist; // 指针的指针,指向由于冲突形成的链表
} *hashtable;
/**
* 素数筛选法
*/
void sievePrime()
{
int i, j;
memset(prime, 1, sizeof(prime));
prime[0] = prime[1] = 0;
for (i = 2; i < MAXN; i ++) {
if (prime[i]) {
for (j = 2 * i; j < MAXN; j += i)
prime[j] = 0;
}
}
}
/**
* 散列函数,除法散列法
*/
int hashFunction(int key, int tablesize)
{
return key % tablesize;
}
/**
* 找到第一个>=x的素数
*/
int nextPrime(int x)
{
while (prime[x] == 0)
x = x + 1;
return x;
}
/**
* 初始化hash表,返回指向hash表的指针
*/
hashtable initializeTable(int tablesize)
{
if (tablesize <= 1) {
printf("Table size is too small!\n");
return NULL;
}
hashtable ht = (hashtable)malloc(sizeof(struct hashtb));
if (ht == NULL) {
printf("Malloc is failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
// 构建hash表的dlist指针数组
ht->tablesize = nextPrime(tablesize);
ht->dlist = (position *)malloc(sizeof(position) * ht->tablesize);
if (ht->dlist == NULL) {
printf("Malloc is failed\n");
exit(-1);
}
// TODO: 这里作用没搞清楚,学习完redis的源码后回来更新
// 初始化dlist数组
ht->dlist[0] = (position)malloc(ht->tablesize * sizeof(struct lnode));
if (ht->dlist[0] == NULL) {
printf("Malloc is failed\n");
}
int i;
for (i = 0; i < ht->tablesize; i ++) {
ht->dlist[i] = ht->dlist[0] + i;
ht->dlist[i]->next = NULL;
}
return ht;
}
/**
* 查找key所在的单元
*/
position findElement(int key, hashtable ht)
{
position p, l;
// 先找到所在的行
int loc = hashFunction(key, ht->tablesize);
l = ht->dlist[loc];
p = l->next;
while (p != NULL && p->element != key) {
p = p->next;
}
if (p == NULL)
return l;
else
return p;
}
/**
* 向hash表中插入元素key
*/
void insertElement(int key, hashtable ht)
{
position pos, new;
pos = findElement(key, ht);
if (pos->element != key) { // key没找到,执行插入操作
new = (position)malloc(sizeof(struct lnode));
if (new == NULL) {
printf("Malloc is failed!\n");
exit(-1);
} else {
new->element = key;
new->next = pos->next;
pos->next = new;
}
printf("%d 插入表中!\n", key);
} else {
printf("%d 已经存在,无需重复插入!\n", key);
}
}
/**
* 在hash表中删除元素
*/
void deleteElement(int key, hashtable ht)
{
position pos, new;
pos = findElement(key, ht);
if (pos->element == key) {
new = ht->dlist[hashFunction(key, ht->tablesize)];
while (new->next != pos) {
new = new->next;
}
new->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
printf("%d删除成功!\n", key);
} else {
printf("%d不存在,无法删除!\n", key);
}
}
/**
* 查找描述
*/
inline void findDescription(position p, int key)
{
if (p->element == key) {
printf("%d查找成功\n", key);
} else {
printf("%d不在hash表中\n", key);
}
}
int main(void)
{
sievePrime();
hashtable table = initializeTable(20);
printf("hash表的大小是:%d\n", table->tablesize); // tsize = 23
position pos = NULL;
// 先插入6个元素
insertElement(20, table); // --> 20
insertElement(89, table); // --> 20
insertElement(18, table); // --> 18
insertElement(49, table); // --> 3
insertElement(58, table); // --> 12
insertElement(69, table); // --> 0
// 测试可以查找的元素
pos = findElement(89, table);
findDescription(pos, 89);
pos = findElement(20, table);
findDescription(pos, 20);
// 测试找不到的
pos = findElement(25, table);
findDescription(pos, 25);
// 测试删除
deleteElement(69, table);
return 0;
}
运行结果

开放寻址法
未完待续!!