关于Graphics/Graphics2D以及简单的几何图像制作(一个简单钟表的实现)
题外话:正好赶上OperatingSystem的作业要做一个模拟线程/进程调度的问题,决定用JAVA实现才发现这些内容和之前学过的GUI制作是两码事儿- -b
通过学习java.swing库的ActionListener接口我们初步了解了一些关于java框体程序的各个部件JFrame,JPanel,JComponent和控件之间是如何联系通讯的,然而这次我们要从另一个视角来看java程序框体。
从一个框体实现“表”的代码我们来初步看一下java是如何在JFrame平台上制作出自己想要的图案的吧!
(实现效果图)
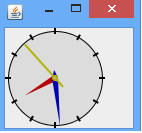
有几个可能会比较陌生的类先筛选出来:
(1)GeneralPath:是java.awt.geom.Path2D的一个子类,path的设定过程主要用两个函数moveTo(double x,double y)和linkTo(double x,double y),当然如果需要实现path的动态绘制的话需要的方法远不止这两个,可以自行去javadoc查阅。
(2)Ellipse2D:是java.awt.geom下的一个类,可以用来绘制理论上的椭圆构造参数为(double x,double y,double width,double height)意义不多赘述。
(3)AffineTransform:这个是整个代码中最有分量的一个类,这个类的引用的获取方法是用静态方法AffineTransform.getInstance(double theta,double x,double y)这里的x和y指的是锚点也就是整个旋转过程参照的旋转中心,theta是要用弧度制表示的旋转角度。具体使用方法下文中会详细总结。
(4)Timer类是在我接触到的新的控件,和JButton或者JLabel等等不同的是这个空间不要手动加上ActionListener的接口来进行事件驱动。使用方法在代码中有详述。

1 import java.awt.*; 2 import java.awt.event.*; 3 import java.awt.geom.*; 4 import java.util.Calendar; 5 import javax.swing.*; 6 7 public class Main extends JPanel implements ActionListener 8 { 9 // Create a shape for the face of the clock 10 protected static Ellipse2D face = new Ellipse2D.Float(3, 3, 94, 94); 11 12 // Create a path that represents a tick mark 13 protected static GeneralPath tick = new GeneralPath(); 14 static 15 { 16 tick.moveTo(100, 100); 17 tick.moveTo(49, 0); 18 tick.lineTo(51, 0); 19 tick.lineTo(51, 6); 20 tick.lineTo(49, 6); 21 tick.lineTo(49, 0); 22 23 } 24 25 // Create a cool hour hand 26 protected static GeneralPath hourHand = new GeneralPath(); 27 static 28 { 29 hourHand.moveTo(50, 15); 30 hourHand.lineTo(53, 50); 31 hourHand.lineTo(50, 53); 32 hourHand.lineTo(47, 50); 33 hourHand.lineTo(50, 15); 34 } 35 36 // Create a cool minute hand 37 protected static GeneralPath minuteHand = new GeneralPath(); 38 static 39 { 40 minuteHand.moveTo(50, 2); 41 minuteHand.lineTo(53, 50); 42 minuteHand.lineTo(50, 58); 43 minuteHand.lineTo(47, 50); 44 minuteHand.lineTo(50, 2); 45 } 46 47 // And a cool second hand 48 protected static GeneralPath secondHand = new GeneralPath(); 49 static 50 { 51 secondHand.moveTo(49, 5); 52 secondHand.lineTo(51, 5); 53 secondHand.lineTo(51, 62); 54 secondHand.lineTo(49, 62); 55 secondHand.lineTo(49, 5); 56 } 57 58 // Create some colors for the pieces of the clock 59 protected static Color faceColor = new Color(220, 220, 220); 60 protected static Color hourColor = Color.red.darker(); 61 protected static Color minuteColor = Color.blue.darker(); 62 protected static Color secondColor = new Color(180, 180, 0); 63 protected static Color pinColor = Color.gray.brighter(); 64 65 // Create circles for the pivot and center pin 66 protected Ellipse2D pivot = new Ellipse2D.Float(47, 47, 6, 6); 67 protected Ellipse2D centerPin = new Ellipse2D.Float(49, 49, 2, 2); 68 69 70 // Create three transforms that center around the pivot point 71 protected AffineTransform hourTransform = 72 AffineTransform.getRotateInstance(0, 50, 50); 73 protected AffineTransform minuteTransform = 74 AffineTransform.getRotateInstance(0, 50, 50); 75 protected AffineTransform secondTransform = 76 AffineTransform.getRotateInstance(0,50,50); 77 78 // Create a timer that fires once a second and a Calendar 79 // instance for getting the time values 80 protected Timer timer = new Timer(1000, this); 81 protected Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); 82 83 // Constructor - hardcode a preferred size of 100x100 84 public Main() 85 { 86 setPreferredSize(new Dimension(100, 100)); 87 } 88 89 // Invoked when panel is added to a container 90 public void addNotify() 91 { 92 // Call the superclass and start the timer 93 super.addNotify(); 94 timer.start(); 95 } 96 97 // Invoked when panel is removed from a container 98 public void removeNotify() 99 { 100 // Call the superclass and stop the timer 101 timer.stop(); 102 super.removeNotify(); 103 } 104 105 // 106 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) 107 { 108 // Update the calendar's time 109 this.calendar.setTime(new java.util.Date()); 110 111 // Extract the hours minutes and seconds 112 int hours = this.calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR); 113 int minutes = this.calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE); 114 int seconds = this.calendar.get(Calendar.SECOND); 115 116 // Using a little trigonometry, set the transforms to rotate 117 // each hand into the proper position. Center the rotation 118 // around the pivot point (50, 50) instead of the origin 119 hourTransform.setToRotation(((double) hours) * 120 (Math.PI / 6.0), 50, 50); 121 minuteTransform.setToRotation(((double) minutes) * 122 (Math.PI / 30.0), 50, 50); 123 secondTransform.setToRotation(((double) seconds) * 124 (Math.PI / 30.0), 50, 50); 125 126 // Force the component to repaint ASAP 127 repaint(); 128 } 129 130 // This is an alternative to creating a UI delegate. Since JPanel's 131 // paint() method only paints the border and backgound, we can just 132 // override the paint method of the component to do the graphics. 133 public void paint(Graphics g) 134 { 135 // Call the superclass first to paint the border (if one is assigned) 136 super.paint(g); 137 138 // Get the graphics context and turn on anti-aliasing 139 Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g; 140 g2.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING, 141 RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON); 142 143 // Set the paint for the clock face and fill it in 144 g2.setPaint(faceColor); 145 g2.fill(face); 146 147 // Set the paint to black and draw the clock's outline 148 g2.setPaint(Color.black); 149 g2.draw(face); 150 151 // Fill in the 12 ticks around the face of the clock 152 for (double p = 0.0; p < 12.0; p += 1.0) 153 { 154 // This is probably terribly inefficient and should be 155 // done statically or in the constructor - draw the 156 // tick as a transformed shape that is rotated. 157 g2.fill(tick.createTransformedShape( 158 AffineTransform.getRotateInstance((Math.PI / 6.0) * p, 159 50, 50))); 160 } 161 162 // Set the paint and draw the hour hand. It is lowest in the 163 // 'z-order' so will appear underneath the other hands. Notice 164 // how each hand is transformed by a different <AffineTransform>. 165 g2.setPaint(hourColor); 166 g2.fill(hourHand.createTransformedShape(hourTransform)); 167 168 // Set the paint and draw the minute hand, the second hand, 169 // the pivot and the center pin 170 g2.setPaint(minuteColor); 171 g2.fill(minuteHand.createTransformedShape(minuteTransform)); 172 g2.setPaint(secondColor); 173 g2.fill(secondHand.createTransformedShape(secondTransform)); 174 g2.fill(pivot); 175 g2.setPaint(pinColor); 176 g2.fill(centerPin); 177 } 178 179 // A little test frame to show off our fancy clock 180 public static void main(String[] args) 181 { 182 JFrame frame = new JFrame(); 183 frame.setLocation(700, 400); 184 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 185 frame.getContentPane().add(new Main()); 186 frame.pack(); 187 frame.show(); 188 } 189 }
Okay,Here are the points :-P
下面进阶深入探究一下这段代码:
#1#关于每次图形变换之后,变化前图形的擦除?
Ans:是这样的,一般来讲有两种办法实现所谓的擦除效果以完成动画:
1.手动擦除,直接对这个paint出来的geom下的类调用clear**方法,或者直接使用新的颜色/画布将需要擦除的形状删除/覆盖。
2.super.paint(g)这个方法有点神奇,以后需要进一步探讨一下,直接在子类的paint方法之中调用父类的paint的方法来实现“擦除”。
代码中方法其实是第一种,在每次repaint过程中,都会有一次将整个表盘“覆盖”重画的过程,但是不得不说,这么实现的话每秒钟都需要对整个表盘全部的空间进行重画,是很浪费时间/空间的。
#2#怎么递推实现的表盘圆周上的12个标记的绘制?
Ans:这里用了一个新的类叫做AffineTransform。使用这个类的方法是在geom下的几何类中直接调用createTransformedShape(AffineTransform at)返回一个Shape类型,这时匿名调用这个类进行draw(勾勒轮廓)/fill(填充颜色)方法可以完成对转换完成之后的几何体的绘制。关于AffineTransform类的更多用法和数学解释:
http://www.apihome.cn/api/java/AffineTransform.html
#3#怎么实现消除斜线的锯齿状?
Ans:这个我真的不懂,但是我知道是下面这段神奇的代码起到的作用,至于这个“渲染提示”具体的用法还得慢慢学..
g2.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING,RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON);
#4#阿西巴,addNotify方法到底有没有用?
Ans:addNotify方法是在JPanel添加到JComponent上的时候用的,本例中是在添加pane的直接启动计时器(Timer),关于代码最后那个若有若无的getContentPane()为什么会出现,其实还要从JFrame的四层结构开始说起(传送门见下):
http://tieba.baidu.com/p/2004216123
