mybatis源码分析(3)——SqlSessionManager类
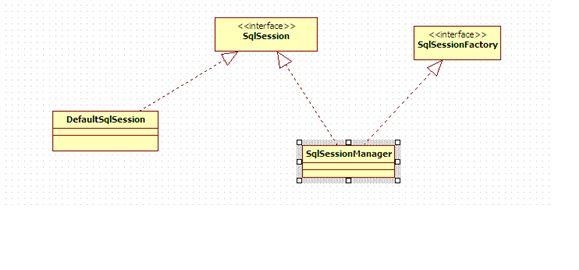
从上图可能看出,在 mybatis中,SqlSession的实现类有两个,其中SqlSessionManager类不但实现了SqlSession接口,同时也实现了SqlSessionFactory接口。那么SqlSessionManager类究竟有何作用 ? 由于源码中缺少注释,所以从mybatis目前的提供官方文档来看,似乎该类已被弃用,其功能被DefaultSqlSession类和DefaultSqlSessionFactory类所代替。只是该类的部分代码对我们理解mybatis的一些底层机制还具有一定的参考价值,例如:
SqlSessionManager的下面的构造方法,会产生一个SqlSession的一个代理对象:
private SqlSessionManager(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) { this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory; this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) Proxy.newProxyInstance( SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{SqlSession.class}, new SqlSessionInterceptor()); }
SqlSessionInterceptor类实现了InvocationHandler接口
privaprivate class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler { public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { final SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionManager.this.localSqlSession.get(); if (sqlSession != null) { try { return method.invoke(sqlSession, args); } catch (Throwable t) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } } else { final SqlSession autoSqlSession = openSession(); try { final Object result = method.invoke(autoSqlSession, args); autoSqlSession.commit(); return result; } catch (Throwable t) { autoSqlSession.rollback(); throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } finally { autoSqlSession.close(); } } } } private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler { public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { final SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionManager.this.localSqlSession.get(); if (sqlSession != null) { try { return method.invoke(sqlSession, args); } catch (Throwable t) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } } else { final SqlSession autoSqlSession = openSession(); try { final Object result = method.invoke(autoSqlSession, args); autoSqlSession.commit(); return result; } catch (Throwable t) { autoSqlSession.rollback(); throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } finally { autoSqlSession.close(); } } } }
下面对这一段使用JAVA动态代理技术产生SqlSession代理对象的代码进行分析:
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{SqlSession.class},
new SqlSessionInterceptor()) 这句是关键,JDK的Proxy类的newProxyInstance方法的方法原型如下:
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
throws IllegalArgumentException
在调这个方法中需要传入三个参数:
Ø 一个interfaces的数组参数
Ø 一个InvocationHanler 接口的实例对象
Ø 一个类加载器,
则Proxy.newProxyInstance方法执行后会返回interfaces中任一接口的实例对象(假设该对象为proxyObject),那么当我们在调用这个对象proxyObject的相应方法时,就会进入到InvocationHandler 这个参数对象的invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)方法中,或者换句话说,就会被h这个对象的invoke方法拦截, 对象proxyObject会作为
Invoke中的proxy参数,proxyObject调用的方法的方法对象会作为method参数,方法的参数会作为args参数,这样在InvocationHandler 对象的invoke方法中,就会通过Method.invoke方法来执行具体的目标对象的相应方法,在mybatis的这个应用场景上,这个目标对象其实就是一个SqlSession的实例,通过SqlSessionManager类的成员变量sqlSessionFactory的openSession()获得或者从当前线程中获取。
以上的实现技术主要就是使用了java的动态代理技术,看到网上不少人在问这个InvocationHandler 接口中的invoke方法的第一个参数proxy究竟有何作用,这个proxy其实就是一个代理对象实例(通过Proxy.newProxyInstance方法产生),下面就举例说明一下它的作用:
可参照 java.rmi.server.RemoteObjectInvocationHandler类中的相应方法invoke方法,一个用法就是判断invoke的method参数,看是否有必要调用proxy对象的其他方法,另一个用处就是作为参数把该对象提供给远程调用的方法使用。