Step by Step:Linux C多线程编程入门(基本API及多线程的同步与互斥)
介绍:什么是线程,线程的优点是什么
线程在Unix系统下,通常被称为轻量级的进程,线程虽然不是进程,但却可以看作是Unix进程的表亲,同一进程中的多条线程将共享该进程中的全部系统资源,如虚拟地址空间,文件描述符和信号处理等等。但同一进程中的多个线程有各自的调用栈(call stack),自己的寄存器环境(register context),自己的线程本地存储(thread-local storage)。 一个进程可以有很多线程,每条线程并行执行不同的任务。
线程可以提高应用程序在多核环境下处理诸如文件I/O或者socket I/O等会产生堵塞的情况的表现性能。在Unix系统中,一个进程包含很多东西,包括可执行程序以及一大堆的诸如文件描述符地址空间等资源。在很多情况下,完成相关任务的不同代码间需要交换数据。如果采用多进程的方式,那么通信就需要在用户空间和内核空间进行频繁的切换,开销很大。但是如果使用多线程的方式,因为可以使用共享的全局变量,所以线程间的通信(数据交换)变得非常高效。
Hello World(线程创建、结束、等待)
创建线程 pthread_create
线程创建函数包含四个变量,分别为: 1. 一个线程变量名,被创建线程的标识 2. 线程的属性指针,缺省为NULL即可 3. 被创建线程的程序代码 4. 程序代码的参数 For example: - pthread_t thrd1; - pthread_attr_t attr; - void thread_function(void argument); - char *some_argument;
pthread_create(&thrd1, NULL, (void *)&thread_function, (void *) &some_argument);
结束线程 pthread_exit
线程结束调用实例:pthread_exit(void *retval); //retval用于存放线程结束的退出状态
线程等待 pthread_join
pthread_create调用成功以后,新线程和老线程谁先执行,谁后执行用户是不知道的,这一块取决与操作系统对线程的调度,如果我们需要等待指定线程结束,需要使用pthread_join函数,这个函数实际上类似与多进程编程中的waitpid。 举个例子,以下假设 A 线程调用 pthread_join 试图去操作B线程,该函数将A线程阻塞,直到B线程退出,当B线程退出以后,A线程会收集B线程的返回码。 该函数包含两个参数:
- pthread_t th //th是要等待结束的线程的标识
- void **thread_return //指针thread_return指向的位置存放的是终止线程的返回状态。
调用实例:pthread_join(thrd1, NULL);
example1:
1 /************************************************************************* 2 > File Name: thread_hello_world.c 3 > Author: couldtt(fyby) 4 > Mail: [email protected] 5 > Created Time: 2013年12月14日 星期六 11时48分50秒 6 ************************************************************************/ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #include <stdlib.h> 10 #include <pthread.h> 11 12 void print_message_function (void *ptr); 13 14 int main() 15 { 16 int tmp1, tmp2; 17 void *retval; 18 pthread_t thread1, thread2; 19 char *message1 = "thread1"; 20 char *message2 = "thread2"; 21 22 int ret_thrd1, ret_thrd2; 23 24 ret_thrd1 = pthread_create(&thread1, NULL, (void *)&print_message_function, (void *) message1); 25 ret_thrd2 = pthread_create(&thread2, NULL, (void *)&print_message_function, (void *) message2); 26 27 // 线程创建成功,返回0,失败返回失败号 28 if (ret_thrd1 != 0) { 29 printf("线程1创建失败\n"); 30 } else { 31 printf("线程1创建成功\n"); 32 } 33 34 if (ret_thrd2 != 0) { 35 printf("线程2创建失败\n"); 36 } else { 37 printf("线程2创建成功\n"); 38 } 39 40 //同样,pthread_join的返回值成功为0 41 tmp1 = pthread_join(thread1, &retval); 42 printf("thread1 return value(retval) is %d\n", (int)retval); 43 printf("thread1 return value(tmp) is %d\n", tmp1); 44 if (tmp1 != 0) { 45 printf("cannot join with thread1\n"); 46 } 47 printf("thread1 end\n"); 48 49 tmp2 = pthread_join(thread1, &retval); 50 printf("thread2 return value(retval) is %d\n", (int)retval); 51 printf("thread2 return value(tmp) is %d\n", tmp1); 52 if (tmp2 != 0) { 53 printf("cannot join with thread2\n"); 54 } 55 printf("thread2 end\n"); 56 57 } 58 59 void print_message_function( void *ptr ) { 60 int i = 0; 61 for (i; i<5; i++) { 62 printf("%s:%d\n", (char *)ptr, i); 63 } 64 }
编译
gcc thread_hello_world.c -otest -lpthread 一定要加上-lpthread,要不然会报错,因为源代码里引用了pthread.h里的东西,所以在gcc进行链接的时候,必须要找到这些库的二进制实现代码。
运行结果
结果分析: 1.这段程序我运行了两次,可以看到,两次的运行结果是不一样的,从而说明,新线程和老线程谁先执行,谁后执行用户是不知道的,这一块取决与操作系统对线程的调度。 2.另外,我们看到,在thread2的join结果出现了错误,打印出cannot join with thread2其实这个是个小错误,因为,我pthread_join传进去的th是thread1,在上面的结果中,thread1早已经结束了,所以我们再次等待thread1结束肯定会出现无法取到状态的错误的。 3.pthread_join(thread1, &retval)确实等待了thread1的结束,我们看到,在print_message_function函数循环了5遍结束以后,才打印出thread1 end
这是一个非常简单的例子,hello world级别的,只是用来演示Linux下C多线程的使用,在实际应用中,由于多个线程往往会访问共享的资源(典型的是访问同一个全局变量),因此多个县城间存在着竞争的关系,这就需要对多个线程进行同步,对其访问的数据予以保护。
多线程的同步与互斥
方式一:锁
- 在主线程中初始化锁为解锁状态
- pthread_mutex_t mutex;
- pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
- 在编译时初始化锁为解锁状态
- 锁初始化 pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
- 访问对象时的加锁操作与解锁操作
- 加锁 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex)
- 释放锁 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex)
不加锁,数据不同步
我们先来看一个不加锁,多个线程访问同一段数据的程序。
1 /************************************************************************* 2 > File Name: no_mutex.c 3 > Author: couldtt(fyby) 4 > Mail: [email protected] 5 > Created Time: 2013年12月15日 星期日 17时52分24秒 6 ************************************************************************/ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #include <stdlib.h> 10 #include <pthread.h> 11 12 int sharedi = 0; 13 void increse_num(void); 14 15 int main(){ 16 int ret; 17 pthread_t thrd1, thrd2, thrd3; 18 19 ret = pthread_create(&thrd1, NULL, (void *)increse_num, NULL); 20 ret = pthread_create(&thrd2, NULL, (void *)increse_num, NULL); 21 ret = pthread_create(&thrd3, NULL, (void *)increse_num, NULL); 22 23 pthread_join(thrd1, NULL); 24 pthread_join(thrd2, NULL); 25 pthread_join(thrd3, NULL); 26 27 printf("sharedi = %d\n", sharedi); 28 29 return 0; 30 31 } 32 33 void increse_num(void) { 34 long i,tmp; 35 for(i=0; i<=100000; i++) { 36 tmp = sharedi; 37 tmp = tmp + 1; 38 sharedi = tmp; 39 } 40 }
编译
gcc no_mutex.c -onomutex -lpthread
运行分析
从上图可知,我们no_mutex每次的运行结果都不一致,而且,运行结果也不符合我们的预期,出现了错误的结果。 原因就是三个线程竞争访问全局变量sharedi,并且都没有进行相应的同步。
举个例子,当线程thrd1访问到sharedi的时候,sharedi的值是1000,然后线程thrd1将sharedi的值累加到了1001,可是线程thrd2取到sharedi的时候,sharedi的值是1000,这时候线程thrd2对sharedi的值进行加1操作,使其变成了1001,可是这个时候,sharedi的值已经被线程thrd1加到1001了,然而,thrd2并不知道,所以又将sharedi的值赋为了1001,从而导致了结果的错误。
这样,我们就需要一个线程互斥的机制,来保护sharedi这个变量,让同一时刻,只有一个线程能够访问到这个变量,从而使它的值能够保证正确的变化。
加锁,数据同步
通过加锁,保证sharedi变量在进行变更的时候,只有一个线程能够取到,并在在该线程对其进行操作的时候,其它线程无法对其进行访问。
1 /************************************************************************* 2 > File Name: mutex.c 3 > Author: couldtt(fyby) 4 > Mail: [email protected] 5 > Created Time: 2013年12月15日 星期日 17时52分24秒 6 ************************************************************************/ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #include <stdlib.h> 10 #include <pthread.h> 11 12 int sharedi = 0; 13 void increse_num(void); 14 15 pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; 16 17 int main(){ 18 int ret; 19 pthread_t thrd1, thrd2, thrd3; 20 21 ret = pthread_create(&thrd1, NULL, (void *)increse_num, NULL); 22 ret = pthread_create(&thrd2, NULL, (void *)increse_num, NULL); 23 ret = pthread_create(&thrd3, NULL, (void *)increse_num, NULL); 24 25 pthread_join(thrd1, NULL); 26 pthread_join(thrd2, NULL); 27 pthread_join(thrd3, NULL); 28 29 printf("sharedi = %d\n", sharedi); 30 31 return 0; 32 33 } 34 35 void increse_num(void) { 36 long i,tmp; 37 for(i=0; i<=100000; i++) { 38 /*加锁*/ 39 if (pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex) != 0) { 40 perror("pthread_mutex_lock"); 41 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 42 } 43 tmp = sharedi; 44 tmp = tmp + 1; 45 sharedi = tmp; 46 /*解锁锁*/ 47 if (pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex) != 0) { 48 perror("pthread_mutex_unlock"); 49 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 50 } 51 } 52 }
结果分析
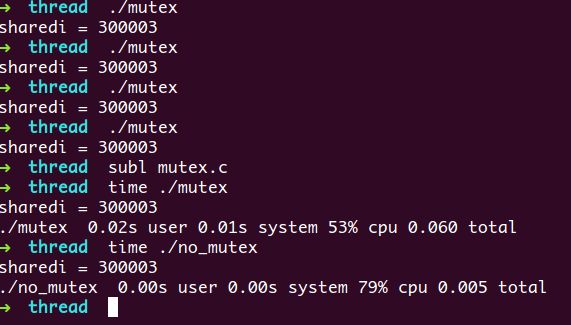
这一次,我们的结果是正确的,锁有效得保护了我们的数据安全。然而:
-
锁保护的并不是我们的共享变量(或者说是共享内存),对于共享的内存而言,用户是无法直接对其保护的,因为那是物理内存,无法阻止其他程序的代码访问。事实上,锁之所以对关键区域进行了保护,在本例中,是因为所有线程都遵循了一个规则,那就是在进入关键区域钱加
同一把锁,在退出关键区域钱释放同一把锁 -
我们从上述运行结果中可以看到,加锁是会带来额外的开销的,加锁的代码其运行速度,明显比不加锁的要慢一些,所以,在使用锁的时候,要合理,在不需要对关键区域进行保护的场景下,我们便不要画蛇添足,为其加锁了
方式二:信号量
锁有一个很明显的缺点,那就是它只有两种状态:锁定与不锁定。
信号量本质上是一个非负数的整数计数器,它也被用来控制对公共资源的访问。当公共资源增加的时候,调用信号量增加函数sem_post()对其进行增加,当公共资源减少的时候,调用函数sem_wait()来减少信号量。其实,我们是可以把锁当作一个0-1信号量的。
它们是在/usr/include/semaphore.h中进行定义的,信号量的数据结构为sem_t, 本质上,它是一个long型整数
相关函数
在使用semaphore之前,我们需要先引入头文件#include <semaphore.h>
- 初始化信号量:
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);- 成功返回0,失败返回-1
- 参数
- sem:指向信号量结构的一个指针
- pshared: 不是0的时候,该信号量在进程间共享,否则只能为当前进程的所有线程们共享
- value:信号量的初始值
- 信号量减1操作,当sem=0的时候该函数会堵塞
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem);- 成功返回0,失败返回-1
- 参数
- sem:指向信号量的一个指针
- 信号量加1操作
int sem_post(sem_t *sem);- 参数与返回同上
- 销毁信号量
int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);- 参数与返回同上
代码示例
1 /************************************************************************* 2 > File Name: sem.c 3 > Author: couldtt(fyby) 4 > Mail: [email protected] 5 > Created Time: 2013年12月15日 星期日 19时25分08秒 6 ************************************************************************/ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #include <unistd.h> 10 #include <pthread.h> 11 #include <semaphore.h> 12 13 #define MAXSIZE 10 14 15 int stack[MAXSIZE]; 16 int size = 0; 17 sem_t sem; 18 19 // 生产者 20 void provide_data(void) { 21 int i; 22 for (i=0; i< MAXSIZE; i++) { 23 stack[i] = i; 24 sem_post(&sem); //为信号量加1 25 } 26 } 27 28 // 消费者 29 void handle_data(void) { 30 int i; 31 while((i = size++) < MAXSIZE) { 32 sem_wait(&sem); 33 printf("乘法: %d X %d = %d\n", stack[i], stack[i], stack[i]*stack[i]); 34 sleep(1); 35 } 36 } 37 38 int main(void) { 39 40 pthread_t provider, handler; 41 42 sem_init(&sem, 0, 0); //信号量初始化 43 pthread_create(&provider, NULL, (void *)handle_data, NULL); 44 pthread_create(&handler, NULL, (void *)provide_data, NULL); 45 pthread_join(provider, NULL); 46 pthread_join(handler, NULL); 47 sem_destroy(&sem); //销毁信号量 48 49 return 0; 50 }
运行结果:
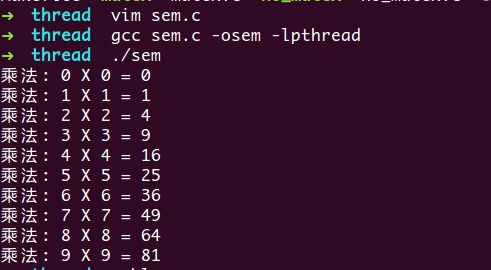
因为信号量机制的存在,所以代码在handle_data的时候,如果sem_wait(&sem)时,sem为0,那么代码会堵塞在sem_wait上面,从而避免了在stack中访问错误的index而使整个程序崩溃。
参考资料
- [1] http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2013/04/processes_and_threads.html
- [2] 《Linux下C语言应用编程》(北京航空航天大学出版社)
- [3] getting started with posix thread