[C#.NET][VB.NET] 自訂控制項的自訂屬性編輯視窗 / User Control of Custom Properties Editor
這次我們必須要使用到基底類別: UITypeEditor
使用這個類別我們必須要覆寫以下兩個方法
1.EditValue:處理使用者介面、使用者輸入處理和值的設定。也就是在這個方法實體化你所要處理的視窗,在這裡我們有兩種視窗的彈出呈現方式可以用,IWindowsFormsEditorService 介面
1-1.DropDownControl(Control control) :下拉式清單的方式呈現。
1-2.ShowDialog(Form dialog) :彈出視窗的方式呈現。
2.GetEditStyle :以通知編輯器樣式的屬性視窗,也就是選擇編輯風格,UITypeEditorEditStyle 列舉型別
2-1 UITypeEditorEditStyle.Modal:顯示下拉選單按鈕。
2-2 UITypeEditorEditStyle.DropDown:顯示(...) 按鈕。
2-3 UITypeEditorEditStyle.None:沒有互動介面。
瞭解要做什麼之後就可以開始來寫code,首先建立一個UserControl專案名為myUITypeEditor 並繼承 UITypeEditor,覆寫EditValue、GetEditStyle方法。
public class myUITypeEditor : UITypeEditor
{
private Size DataSize;//用來存放視窗讀到的值
public override object EditValue(ITypeDescriptorContext context, IServiceProvider provider, object value)
{
IWindowsFormsEditorService EditorService = null;
if (context != null && context.Instance != null && provider != null)
{
//建立編輯服務
EditorService = (IWindowsFormsEditorService)provider.GetService(typeof(IWindowsFormsEditorService));
//讀取自訂視窗的值
PropertyListEditor ListEditorControl;
PropertyFormEditor FormEditorControl;
if (DataSize != null)
{
ListEditorControl = new PropertyListEditor(DataSize);
FormEditorControl = new PropertyFormEditor(DataSize);
}
else
{
ListEditorControl = new PropertyListEditor(new Size(0, 0));
FormEditorControl = new PropertyFormEditor(new Size(0, 0));
}
//建立編輯彈跳畫面
//法一:下拉清單
//EditorService.DropDownControl(ListEditorControl);//畫面彈跳方式
//DataSize = ListEditorControl.size;
//法二:視窗
EditorService.ShowDialog(FormEditorControl);//畫面彈跳方式
DataSize = FormEditorControl.size;
return DataSize;
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
public override UITypeEditorEditStyle GetEditStyle(ITypeDescriptorContext context)
{
if (context != null && context.Instance != null)
{
return UITypeEditorEditStyle.Modal;
//return UITypeEditorEditStyle.DropDown;
//return UITypeEditorEditStyle.None;
}
return base.GetEditStyle(context);
}
}
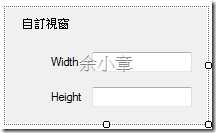
PS.ListEditorControl及FormEditorControl是兩種不同的呈現方式,擇一使用
接下來開始來刻我們所要呈現的UI,加入新的項目,分別加入一個Winform及一個UserControl項目
UserControl:PropertyListEditor
internal partial class PropertyListEditor : UserControl
{
private Size _size;
public Size size
{
get { return _size; }
set { _size = value; }
}
public PropertyListEditor()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
public PropertyListEditor(Size size)
{
InitializeComponent();
this.size = size;
}
private void PropertyListEditor_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_size != null)
{
this.txtWidth.Text = _size.Width.ToString();
this.txtHeight.Text = _size.Height.ToString();
}
}
private void PropertyListEditor_Leave(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (this.txtWidth.Text != "" && this.txtHeight.Text != "")//判斷輸入的內容,我懶的寫....
_size = new Size(Convert.ToInt16(txtWidth.Text), Convert.ToInt16(txtHeight.Text));
}
}
Winform:PropertyFormEditor
internal partial class PropertyFormEditor : Form
{
private Size _size;
public Size size
{
get { return _size; }
set { _size = value; }
}
public PropertyFormEditor()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
public PropertyFormEditor(Size size)
{
InitializeComponent();
this.size = size;
}
private void PropertyFormEditor_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_size != null)
{
this.txtWidth.Text = _size.Width.ToString();
this.txtHeight.Text = _size.Height.ToString();
}
}
private void PropertyFormEditor_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
if (this.txtWidth.Text != "" && this.txtHeight.Text != "")//判斷輸入的內容,我懶的寫....
{
_size = new Size(Convert.ToInt16(txtWidth.Text), Convert.ToInt16(txtHeight.Text));
}
}
}
我將兩種呈現方式都寫出來,不過這兩個UI的程式都一模一樣,不同的是當輸入資料完畢視窗關閉的事件觸發不一樣
UserControl是用Leave事件把視窗所輸入的值寫到欄位裡,而Winform是用FormClosing事件;以及它們所繼承的類別也不同
最後這一個公開類別裡設定我們要的屬性
public partial class UserControlType : UserControl
{
public UserControlType()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private Size _size = new Size();
[Category("A Test")]
[Editor(typeof(myUITypeEditor), typeof(UITypeEditor))]
[DesignerSerializationVisibility(DesignerSerializationVisibility.Content)]
public Size size
{
get { return _size; }
set { _size = value; }
}
}
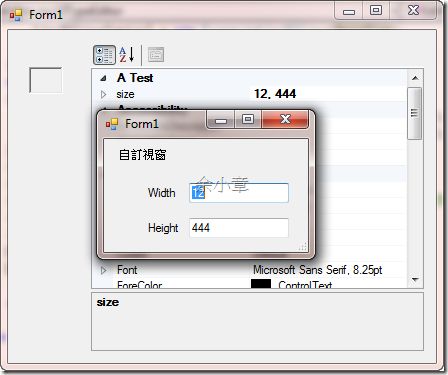
然後我們再加入一個新的Winform專案,把我們剛建立好的控制項拖曳到Form裡,並使用propertyGrid控制項來觀察我們所建立的size屬性,如下圖:
Note:用視窗跳出必需要處理一下他出現的位置,這是本範例沒有處理的。
範例下載