使用Aspose.Cell控件实现Excel高难度报表的生成(一)
本文章主要介绍报表的生成,基于Aspose.Cell控件的报表生成。谈到报表,估计大家都有所领悟以及个人的理解,总的来说,一般的报表生成,基本上是基于以下几种方式:一种是基于微软Excel内置的引擎来实现;一种是构造HTML格式的Excle报表;一种是基于控件的方式来处理,基于控件有很多种方式,个人认为比较有名的是Aspose.Cell(收费破解)和NPOI(开源)。
而报表的表现方式大致可以分为两种:
一种是通用的二维表导出的Excel格式,这种方式通过封装一个操作类,传递一个DataTable参数,把数据导出就可以了。这种报表特点是操作方便,通用,能应付一般常用的数据报表,如下所示;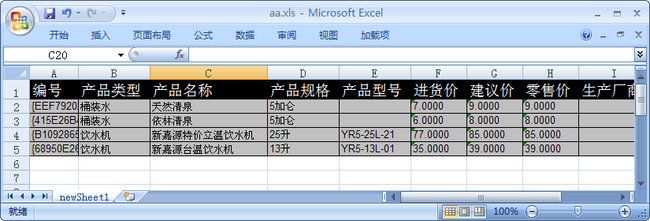
由于这种报表,一般是在一个数据表格中显示,通常的做法是把这个东西做成控件,一个可以解决分页问题,一个可以解决导出、打印问题等,
当然,也可以把导入导出Excel的操作封装成一个公用的辅助来调用,如我封装的Aspose.Cell的导入导出处理函数如下所示:
代码 public class AsposeExcelTools { public static bool DataTableToExcel(DataTable datatable, string filepath, out string error) { error = ""; try { if (datatable == null) { error = "DataTableToExcel:datatable 为空"; return false; } Aspose.Cells.Workbook workbook = new Aspose.Cells.Workbook(); Aspose.Cells.Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]; Aspose.Cells.Cells cells = sheet.Cells; int nRow = 0; foreach (DataRow row in datatable.Rows) { nRow++; try { for (int i = 0; i < datatable.Columns.Count; i++) { if (row[i].GetType().ToString() == "System.Drawing.Bitmap") { //------插入图片数据------- System.Drawing.Image image = (System.Drawing.Image)row[i]; MemoryStream mstream = new MemoryStream(); image.Save(mstream, System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageFormat.Jpeg); sheet.Pictures.Add(nRow, i, mstream); } else { cells[nRow, i].PutValue(row[i]); } } } catch (System.Exception e) { error = error + " DataTableToExcel: " + e.Message; } } workbook.Save(filepath); return true; } catch (System.Exception e) { error = error + " DataTableToExcel: " + e.Message; return false; } } public static bool DataTableToExcel2(DataTable datatable, string filepath, out string error) { error = ""; Aspose.Cells.Workbook wb = new Aspose.Cells.Workbook(); try { if (datatable == null) { error = "DataTableToExcel:datatable 为空"; return false; } //为单元格添加样式 Aspose.Cells.Style style = wb.Styles[wb.Styles.Add()]; //设置居中 style.HorizontalAlignment = Aspose.Cells.TextAlignmentType.Center; //设置背景颜色 style.ForegroundColor = System.Drawing.Color.FromArgb(153, 204, 0); style.Pattern = BackgroundType.Solid; style.Font.IsBold = true; int rowIndex = 0; for (int i = 0; i < datatable.Columns.Count; i++) { DataColumn col = datatable.Columns[i]; string columnName = col.Caption ?? col.ColumnName; wb.Worksheets[0].Cells[rowIndex, i].PutValue(columnName); wb.Worksheets[0].Cells[rowIndex, i].Style = style; } rowIndex++; foreach (DataRow row in datatable.Rows) { for (int i = 0; i < datatable.Columns.Count; i++) { wb.Worksheets[0].Cells[rowIndex, i].PutValue(row[i].ToString()); } rowIndex++; } for (int k = 0; k < datatable.Columns.Count; k++) { wb.Worksheets[0].AutoFitColumn(k, 0, 150); } wb.Worksheets[0].FreezePanes(1, 0, 1, datatable.Columns.Count); wb.Save(filepath); return true; } catch (Exception e) { error = error + " DataTableToExcel: " + e.Message; return false; } } /// <summary> /// Excel文件转换为DataTable. /// </summary> /// <param name="filepath">Excel文件的全路径</param> /// <param name="datatable">DataTable:返回值</param> /// <param name="error">错误信息:返回错误信息,没有错误返回""</param> /// <returns>true:函数正确执行 false:函数执行错误</returns> public static bool ExcelFileToDataTable(string filepath, out DataTable datatable, out string error) { error = ""; datatable = null; try { if (File.Exists(filepath) == false) { error = "文件不存在"; datatable = null; return false; } Aspose.Cells.Workbook workbook = new Aspose.Cells.Workbook(); workbook.Open(filepath); Aspose.Cells.Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]; datatable = worksheet.Cells.ExportDataTable(0, 0, worksheet.Cells.MaxRow + 1, worksheet.Cells.MaxColumn + 1); //-------------图片处理------------- Aspose.Cells.Pictures pictures = worksheet.Pictures; if (pictures.Count > 0) { string error2 = ""; if (InsertPicturesIntoDataTable(pictures, datatable, out datatable, out error2) == false) { error = error + error2; } } return true; } catch (System.Exception e) { error = e.Message; return false; } } public static bool ExcelFileToLists(string filepath, out IList[] lists, out string error) { error = ""; lists = null; DataTable datatable = new DataTable(); IList list = new ArrayList(); Pictures[] pictures; if (ExcelFileToDataTable(filepath, out datatable, out error) && GetPicturesFromExcelFile(filepath, out pictures, out error)) { lists = new ArrayList[datatable.Rows.Count]; //------------DataTable转换成IList[]-------------- //数据 int nRow = 0; foreach (DataRow row in datatable.Rows) { lists[nRow] = new ArrayList(datatable.Columns.Count); for (int i = 0; i <= datatable.Columns.Count - 1; i++) { lists[nRow].Add(row[i]); } nRow++; } //图片 for (int i = 0; i < pictures.Length; i++) { foreach (Picture picture in pictures[i]) { try { //----把图片转换成System.Drawing.Image---- //MemoryStream mstream = new MemoryStream(); //mstream.Write(picture.Data, 0, picture.Data.Length); //System.Drawing.Image image = System.Drawing.Image.FromStream(mstream); //----Image放入IList------ //图片有可能越界 if (picture.UpperLeftRow <= datatable.Rows.Count && picture.UpperLeftColumn <= datatable.Columns.Count) { lists[picture.UpperLeftRow][picture.UpperLeftColumn] = picture.Data; } } catch (System.Exception e) { error = error + e.Message; } } } } else { return false; } return true; } public static bool ListsToExcelFile(string filepath, IList[] lists, out string error) { error = ""; //----------Aspose变量初始化---------------- Aspose.Cells.Workbook workbook = new Aspose.Cells.Workbook(); Aspose.Cells.Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]; Aspose.Cells.Cells cells = sheet.Cells; //-------------输入数据------------- int nRow = 0; sheet.Pictures.Clear(); cells.Clear(); foreach (IList list in lists) { for (int i = 0; i <= list.Count - 1; i++) { try { System.Console.WriteLine(i.ToString() + " " + list[i].GetType()); if (list[i].GetType().ToString() == "System.Drawing.Bitmap") { //插入图片数据 System.Drawing.Image image = (System.Drawing.Image)list[i]; MemoryStream mstream = new MemoryStream(); image.Save(mstream, System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageFormat.Jpeg); sheet.Pictures.Add(nRow, i, mstream); } else { cells[nRow, i].PutValue(list[i]); } } catch (System.Exception e) { error = error + e.Message; } } nRow++; } //-------------保存------------- workbook.Save(filepath); return true; }
这样封装了Aspose.Cell的操作,每次生成Excel文件或者导入Excel内容,就非常方便,只需要如下调用方式即可完成:
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { DataTable dt = CreateTable("测试1,测试2,Test1,Test2", "testTable"); for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { DataRow dr = dt.NewRow(); for (int j = 0; j < dt.Columns.Count; j++) { dr[j] = i.ToString(); } dt.Rows.Add(dr); } string outError = ""; string fileName = @"C:\test.xls"; AsposeExcelTools.DataTableToExcel2(dt, fileName, out outError); if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(outError)) { MessageBox.Show(outError); } else { Process.Start(fileName); } } public DataTable CreateTable(string nameString, string tableName) { string[] nameArray = nameString.Split(new char[] { ',', ';' }); List<string> nameList = new List<string>(); foreach (string item in nameArray) { if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(item)) { nameList.Add(item); } } return CreateTable(nameList, tableName); }
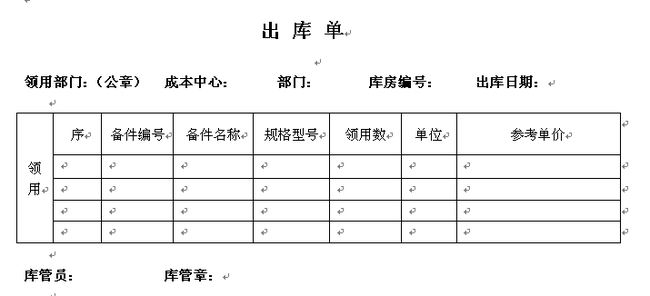
另外一种是以Excel文件作为模板,然后填入必要的内容,形成比较综合性,复杂性较高的报表,这种报表一般比较专业、比较规范好看,在一些特殊的场合,必须使用这些固定格式的报表,如下所示:
或者这样的报表格式
这些报表,基本上就是用到了变量、函数等的概念才能处理好这些数据,如上面的出库单,里面的成本中心、部门、库房编号等,这些通过变量绑定应该就可以了,而里面的列表,则可以通过集合绑定实现,Aspose.Cell控件功能非常强大,很好支持这些操作,下面一步步介绍该控件制作这类报表的实现代码。
Aspose.Cell控件支持多种参数变量的绑定操作,如支持DataSet、Datatable、IList集合,实体类集合、类对象等。
DataSet ds = LoadDataSet();//使用DataSet对象 List<Customers> entity = GetCustomers();//使用实体类对象 DataTable dt = GetCustomersTable();//使用DataTable对象 //创建一个workbookdesigner对象 WorkbookDesigner designer = new WorkbookDesigner(); //制定报表模板 string path = System.IO.Path.Combine(Application.StartupPath,"SmartMarkerDesigner.xls"); designer.Open(path); //设置DataSet对象 //designer.SetDataSource(ds); //设置实体类对象 //designer.SetDataSource("Customers", entity); //设置Datatable对象 designer.SetDataSource(dt); designer.SetDataSource(ds.Tables["Order Details"]); //设置变量对象 designer.SetDataSource("Variable", "Single Variable"); //设置集合变量 designer.SetDataSource("MultiVariable", new string[] { "Variable 1", "Variable 2", "Variable 3" }); //设置集合变量 designer.SetDataSource("MultiVariable2", new string[] { "Skip 1", "Skip 2", "Skip 3" }); //根据数据源处理生成报表内容 designer.Process(); //保存Excel文件 string fileToSave = System.IO.Path.Combine(Application.StartupPath, "SmartMarker.xls"); if (File.Exists(fileToSave)) { File.Delete(fileToSave); } designer.Save(fileToSave, FileFormatType.Excel2003); //打开Excel文件 Process.Start(fileToSave);
以上的代码说明了改控件支持的各种参数变量,我们先看看报表的模板,然后看看报表的生成内容,对比一下就更直观了。
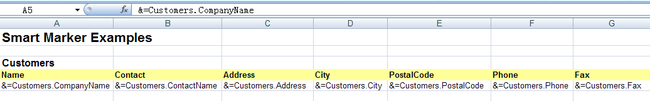
报表1模板如下所示(其中通过引用集合的对象是通过&=来引用,对象的属性或者列名,通过如&=Customer.City方式引用,非常直观方便:
报表1生成的效果如下所示(Customers可以使DataTable对象,也可以List<Customer>实体对象集合。
报表2的模板如下所示,对象也可以通过&=[Order Detail]方式引用,另外模板支持一些参数,其中{r}为当行的变量,翻译到实际的报表可能就是C4*D4这样的格式了,其中两个&=表示动态公式引用,区别于普通的变量和字符,如&=&=C{r}*D{r}后者汇总函数&=&=Sum(C{r}:D{r})等等。