BP神经网络的Java实现
课程作业要求实现一个BPNN。此前只用Matlab实现过,这次尝试使用Java实现了一个。现共享之。版权属于大家。关于BPNN的原理,就不赘述了。
下面是BPNN的实现代码。类名为BP。
package ml;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* BPNN.
*
* @author RenaQiu
*
*/
public class BP {
/**
* input vector.
*/
private final double[] input;
/**
* hidden layer.
*/
private final double[] hidden;
/**
* output layer.
*/
private final double[] output;
/**
* target.
*/
private final double[] target;
/**
* delta vector of the hidden layer .
*/
private final double[] hidDelta;
/**
* output layer of the output layer.
*/
private final double[] optDelta;
/**
* learning rate.
*/
private final double eta;
/**
* momentum.
*/
private final double momentum;
/**
* weight matrix from input layer to hidden layer.
*/
private final double[][] iptHidWeights;
/**
* weight matrix from hidden layer to output layer.
*/
private final double[][] hidOptWeights;
/**
* previous weight update.
*/
private final double[][] iptHidPrevUptWeights;
/**
* previous weight update.
*/
private final double[][] hidOptPrevUptWeights;
public double optErrSum = 0d;
public double hidErrSum = 0d;
private final Random random;
/**
* Constructor.
* <p>
* <strong>Note:</strong> The capacity of each layer will be the parameter
* plus 1. The additional unit is used for smoothness.
* </p>
*
* @param inputSize
* @param hiddenSize
* @param outputSize
* @param eta
* @param momentum
* @param epoch
*/
public BP(int inputSize, int hiddenSize, int outputSize, double eta,
double momentum) {
input = new double[inputSize + 1];
hidden = new double[hiddenSize + 1];
output = new double[outputSize + 1];
target = new double[outputSize + 1];
hidDelta = new double[hiddenSize + 1];
optDelta = new double[outputSize + 1];
iptHidWeights = new double[inputSize + 1][hiddenSize + 1];
hidOptWeights = new double[hiddenSize + 1][outputSize + 1];
random = new Random(19881211);
randomizeWeights(iptHidWeights);
randomizeWeights(hidOptWeights);
iptHidPrevUptWeights = new double[inputSize + 1][hiddenSize + 1];
hidOptPrevUptWeights = new double[hiddenSize + 1][outputSize + 1];
this.eta = eta;
this.momentum = momentum;
}
private void randomizeWeights(double[][] matrix) {
for (int i = 0, len = matrix.length; i != len; i++)
for (int j = 0, len2 = matrix[i].length; j != len2; j++) {
double real = random.nextDouble();
matrix[i][j] = random.nextDouble() > 0.5 ? real : -real;
}
}
/**
* Constructor with default eta = 0.25 and momentum = 0.3.
*
* @param inputSize
* @param hiddenSize
* @param outputSize
* @param epoch
*/
public BP(int inputSize, int hiddenSize, int outputSize) {
this(inputSize, hiddenSize, outputSize, 0.25, 0.9);
}
/**
* Entry method. The train data should be a one-dim vector.
*
* @param trainData
* @param target
*/
public void train(double[] trainData, double[] target) {
loadInput(trainData);
loadTarget(target);
forward();
calculateDelta();
adjustWeight();
}
/**
* Test the BPNN.
*
* @param inData
* @return
*/
public double[] test(double[] inData) {
if (inData.length != input.length - 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Size Do Not Match.");
}
System.arraycopy(inData, 0, input, 1, inData.length);
forward();
return getNetworkOutput();
}
/**
* Return the output layer.
*
* @return
*/
private double[] getNetworkOutput() {
int len = output.length;
double[] temp = new double[len - 1];
for (int i = 1; i != len; i++)
temp[i - 1] = output[i];
return temp;
}
/**
* Load the target data.
*
* @param arg
*/
private void loadTarget(double[] arg) {
if (arg.length != target.length - 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Size Do Not Match.");
}
System.arraycopy(arg, 0, target, 1, arg.length);
}
/**
* Load the training data.
*
* @param inData
*/
private void loadInput(double[] inData) {
if (inData.length != input.length - 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Size Do Not Match.");
}
System.arraycopy(inData, 0, input, 1, inData.length);
}
/**
* Forward.
*
* @param layer0
* @param layer1
* @param weight
*/
private void forward(double[] layer0, double[] layer1, double[][] weight) {
// threshold unit.
layer0[0] = 1.0;
for (int j = 1, len = layer1.length; j != len; ++j) {
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0, len2 = layer0.length; i != len2; ++i)
sum += weight[i][j] * layer0[i];
layer1[j] = sigmoid(sum);
}
}
/**
* Forward.
*/
private void forward() {
forward(input, hidden, iptHidWeights);
forward(hidden, output, hidOptWeights);
}
/**
* Calculate output error.
*/
private void outputErr() {
double errSum = 0;
for (int idx = 1, len = optDelta.length; idx != len; ++idx) {
double o = output[idx];
optDelta[idx] = o * (1d - o) * (target[idx] - o);
errSum += Math.abs(optDelta[idx]);
}
optErrSum = errSum;
}
/**
* Calculate hidden errors.
*/
private void hiddenErr() {
double errSum = 0;
for (int j = 1, len = hidDelta.length; j != len; ++j) {
double o = hidden[j];
double sum = 0;
for (int k = 1, len2 = optDelta.length; k != len2; ++k)
sum += hidOptWeights[j][k] * optDelta[k];
hidDelta[j] = o * (1d - o) * sum;
errSum += Math.abs(hidDelta[j]);
}
hidErrSum = errSum;
}
/**
* Calculate errors of all layers.
*/
private void calculateDelta() {
outputErr();
hiddenErr();
}
/**
* Adjust the weight matrix.
*
* @param delta
* @param layer
* @param weight
* @param prevWeight
*/
private void adjustWeight(double[] delta, double[] layer,
double[][] weight, double[][] prevWeight) {
layer[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1, len = delta.length; i != len; ++i) {
for (int j = 0, len2 = layer.length; j != len2; ++j) {
double newVal = momentum * prevWeight[j][i] + eta * delta[i]
* layer[j];
weight[j][i] += newVal;
prevWeight[j][i] = newVal;
}
}
}
/**
* Adjust all weight matrices.
*/
private void adjustWeight() {
adjustWeight(optDelta, hidden, hidOptWeights, hidOptPrevUptWeights);
adjustWeight(hidDelta, input, iptHidWeights, iptHidPrevUptWeights);
}
/**
* Sigmoid.
*
* @param val
* @return
*/
private double sigmoid(double val) {
return 1d / (1d + Math.exp(-val));
}
}
为了验证正确性,我写了一个测试用例,目的是对于任意的整数(int型),BPNN在经过训练之后,能够准确地判断出它是奇数还是偶数,正数还是负数。
package ml;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BP bp = new BP(32, 15, 4);
Random random = new Random();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i != 1000; i++) {
int value = random.nextInt();
list.add(value);
}
for (int i = 0; i != 200; i++) {
for (int value : list) {
double[] real = new double[4];
if (value >= 0)
if ((value & 1) == 1)
real[0] = 1;
else
real[1] = 1;
else if ((value & 1) == 1)
real[2] = 1;
else
real[3] = 1;
double[] binary = new double[32];
int index = 31;
do {
binary[index--] = (value & 1);
value >>>= 1;
} while (value != 0);
bp.train(binary, real);
}
}
System.out.println("训练完毕,下面请输入一个任意数字,神经网络将自动判断它是正数还是复数,奇数还是偶数。");
while (true) {
byte[] input = new byte[10];
System.in.read(input);
Integer value = Integer.parseInt(new String(input).trim());
int rawVal = value;
double[] binary = new double[32];
int index = 31;
do {
binary[index--] = (value & 1);
value >>>= 1;
} while (value != 0);
double[] result = bp.test(binary);
double max = -Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int idx = -1;
for (int i = 0; i != result.length; i++) {
if (result[i] > max) {
max = result[i];
idx = i;
}
}
switch (idx) {
case 0:
System.out.format("%d是一个正奇数\n", rawVal);
break;
case 1:
System.out.format("%d是一个正偶数\n", rawVal);
break;
case 2:
System.out.format("%d是一个负奇数\n", rawVal);
break;
case 3:
System.out.format("%d是一个负偶数\n", rawVal);
break;
}
}
}
}
运行结果截图如下:
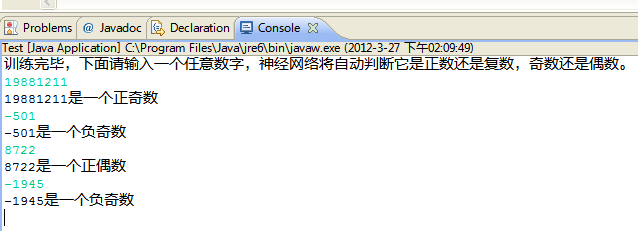
这个测试的例子非常简单。大家可以根据自己的需要去使用BP这个类。
已有 0 人发表留言,猛击->> 这里<<-参与讨论
ITeye推荐
- —软件人才免语言低担保 赴美带薪读研!—