Maven项目环境搭建(Maven + Spring + IBatis)步骤
准备步骤
1. 安装Maven,下载解压即可。官网下载
2. 修改maven_home/conf/settings.xml中的<localRepository>D:/MavenRepo</localRepository>指定本地仓库位置,这个位置是本地计算机上用来存放所有jar包的地方。
3. 修改settings.xml中的<mirrors></mirrors>标签,添加常用的maven远程仓库地址。这些仓库地址就是用来下载jar包的时候用的。由于中央仓库的访问速度较慢(或者因为某些原因导致你根本不能访问),因此一般需要设置其他的仓库地址以提高访问速度。比如:
<mirror> <id>oschina</id> <mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf> <url>http://maven.oschina.net/content/groups/public/</url> </mirror> <mirror> <id>repo2</id> <mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf> <url>http://repo2.maven.org/maven2/</url> </mirror> <mirror> <id>net-cn</id> <mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf> <url>http://maven.net.cn/content/groups/public/</url> </mirror>
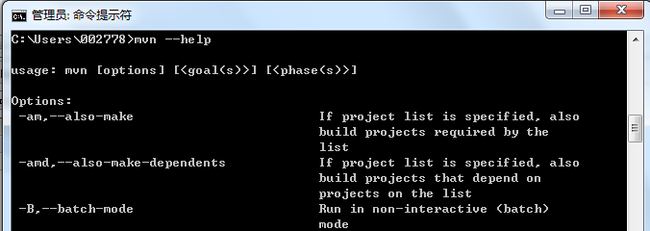
如果使用mvn命令行来创建、构建和运行maven项目,则需要配置环境变量,路径指向maven_home/bin即可。配置好后,可以查看mvn命令:
由于使用命令太麻烦而且难记,我直接使用Eclipse的maven插件来创建和运行maven项目。
4. 在Eclipse中集成Maven。
先安装Eclipse的maven插件(具体过程网上一大堆,比如:安装Eclipse Maven插件的几种方法)
在Eclipse中通过Windows->Preferences->Maven菜单下指定安装的maven:
并指定自己的配置文件settings.xml:
创建Maven项目
5. New->Maven Project->Next,选择webapp类型的项目结构。由于不同类型的项目有不同的项目结构,因此Maven自带了很多套项目骨架(archetype),这里我们选择webapp类型的骨架即可:
6. 输入Group ID, Artifact ID, Version和Package, Finish.
7. 创建好后如图,默认情况下已经将junit3.8导入到项目中:
8. 先把默认使用的JRE环境替换成当前Eclipse中使用的JRE环境。
9. 每个Maven项目都有一个pom.xml文件,这个文件描述了这个项目的依赖关系,以及自身的一些属性,包括properties的定义,以及Maven Modules的版本声明,父模块以及子模块的名字等。同时这个文件还包括了该项目在构建过程中做的事情的定义。现在打开这个pom.xml文件,先在<dependencies>标签上方添加该项目用到的属性定义(为了集中管理spring的版本,因此将其定义为属性,在依赖spring的jar包时直接使用这个属性即可):
<properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <spring.version>4.0.0.RELEASE</spring.version> </properties>
并在<dependencies></dependencies>标签中添加如下依赖关系,其他的内容无需修改:
<dependencies>
<!-- MyBatis相关 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL相关 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.36</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>c3p0</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>0.9.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring相关,这里的spring.version就是上方声明的版本号,这样引用更方便修改和维护 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ibatis</artifactId>
<version>2.0.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 测试相关 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.10</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Servlet相关 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>tomcat</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>5.5.23</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Log相关 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
10. 在Maven的世界中,每一个jar包都可以通过Group ID, Artifact ID, Version这三个字段(一般简写为GAV)来唯一定位,因此如果需要使用哪个jar包,只需要提供这三个字段即可。
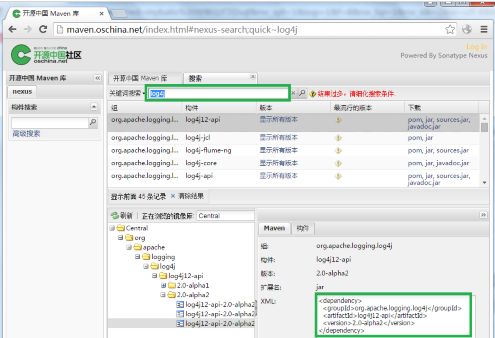
如果不知道版本号或者GroupID,可以去公共的Maven仓库搜索关键字。比如搜索:log4j,即可出现仓库中已经收录的关于log4j的jar包:
如图,我在oschina提供的maven库中搜索log4j,出现了一些可用的jar包列表(这里需要注意:有些jar包名称看上去很相近,因此需要注意区别,选择正确的jar包)。选择某一个,右下方会有该包的GAV属性。直接将这一段拷贝到maven项目pom.xml文件中即可。
还有一个很好用的maven仓库地址,推荐给大家:http://mvnrepository.com/
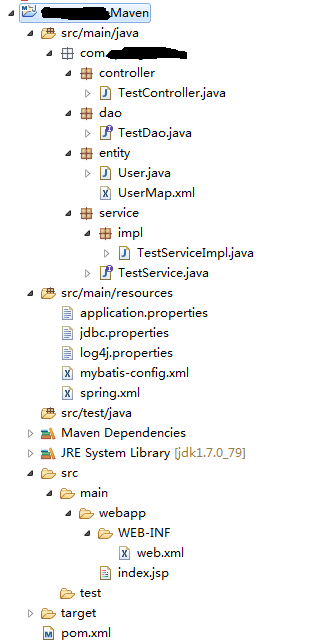
11. Jar包准备完毕后,开始项目接口的定义了。修改后的结构如图:
12. web.xml仅仅定义了基本的DispatchServlet,用于转发请求:
<servlet> <servlet-name>spring</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:spring.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>spring</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
13. spring.xml(xml头有点冗余,如果觉得用不到,可以删除相应的xmlns和schemaLocation声明)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.abc" />
<!-- 属性注入器,用于读取项目配置文件中的属性 -->
<bean id="PropertiesConfigurer"
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>classpath:log4j.properties</value>
<value>classpath:jdbc.properties</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 数据源,不需要解释 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>
<!-- SqlSessionFactory -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<!-- <property name="mapperLocations"
value="classpath*:com/abc/dao/*.xml" /> -->
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml" />
</bean>
<!-- Mybatis sql session -->
<bean id="sqlSession" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="sqlSessionFactory" />
</bean>
<!-- Mybatis mapper scanner, scans for java mapper -->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.abc.dao" />
<property name="sqlSessionTemplateBeanName" value="sqlSession" />
</bean>
</beans>
14. log4j.properties,用于定义Log4j的日志输出内容及格式,我这里就不凑字数了。
jdbc.properties,上方的配置中引用到的关于数据库的配置,请在这个文件中配置。
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc\:mysql\://192.168.12.1\:3306/abc?useUnicode\=true&characterEncoding\=UTF-8 jdbc.username=abc jdbc.password=abc123_
15. mybatis-config.xml文件,这里面指定了哪些xml文件可以作为DAO接口的映射文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <mappers> <mapper resource="com/abc/entity/UserMap.xml"/> </mappers> </configuration>
16. UserMap.xml文件定义了对于User对象的操作的sql语句:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" " <mapper namespace="com.abc.dao.TestDao"> <resultMap id="UserResultMap" type="com.abc.entity.User"> <id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id" /> <result column="userName" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name" /> <result column="userAge" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age" /> <result column="userAddress" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="address" /> </resultMap> <select id="testQuery" resultMap="UserResultMap"> SELECT * FROM user </select> </mapper>
17. Controller, Service和DAO的声明,都是很标准很简单的Controller调用Service,Service再调用DAO接口的过程。
TestDao(完成数据读写):
package com.abc.dao;
import java.util.List;
import com.abc.entity.User;
public interface TestDao {
public List<User> testQuery() throws Exception;
}
TestService(接口编程,在面向多实现的时候非常有用):
package com.abc.service;
public interface TestService {
public String testQuery() throws Exception;
}
TestServiceImpl(完成主要的业务逻辑):
package com.abc.service.impl;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.abc.dao.TestDao;
import com.abc.entity.User;
import com.abc.service.TestService;
@Service
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService {
@Autowired
private TestDao dao;
public String testQuery() throws Exception {
List<User> users = dao.testQuery();
String res = "";
if (users != null && users.size() > 0) {
for (User user : users) {
res += user.toString() + "|";
}
} else {
res = "Not found.";
}
return res;
}
}
TestController(完成请求转发,响应封装):
package com.abc.controller;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import com.abc.service.TestService;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/testController")
public class TestController {
public static final Logger LOGGER = Logger.getLogger(TestController.class);
@Autowired
private TestService testService;
@RequestMapping("/test")
public void test(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
try {
String result = testService.testQuery();
response.getWriter().print(result);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
代码部分到此就结束了。
构建和运行
18. 编写好以后,在项目上右键->Run As->Maven Build…准备构建这个maven项目。
19. 在BaseDirectory中指定需要构建的项目(点击图中的Brose Workspace或Browse File System按钮可以选择),并在Goals框中指定构建的目标(Maven有自己的构建的阶段,有的地方又叫生命周期,如果不清楚的同学,可以参看Maven生命周期详解)。并可以选择一些附加的属性(绿色框中),如图:
20. 如果构建成功,则会出现类似于下面的输出:
21. 当构建成功后,可以像普通的Web Project一样来运行这个项目。这里将其添加到Tomcat中,并启动之。
22. 先看看数据库的内容:
23. 在浏览器中访问指定的接口,查看结果(在我的实现类TestServiceImpl中,仅仅是打印了查询到的结果):
附:例子下载:AbcDemo.zip
链接: http://pan.baidu.com/s/1pJ3pSBT 密码: 3gpt