大数据的概念
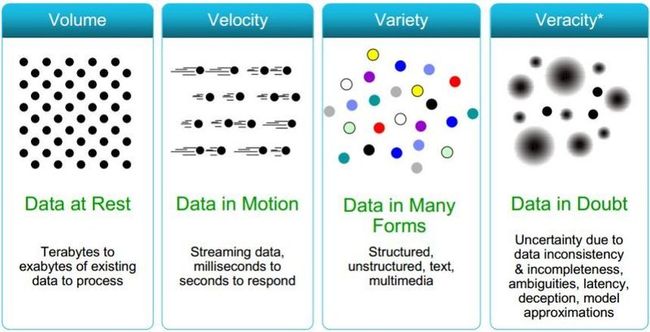
What is big data? 4V or 3V?
维基百科对大数据的定义:大数据是指利用常用软件工具捕获、管理和处理数据所耗时间超过可容忍时间的数据集
http://www.nature.com/news/specials/bigdata/index.html
http://www.sciencemag.org/site/special/data/
数据库与大数据的区别与联系
看似只是一个简单的技术演进,但细细考究不难发现两者有着本质上的差别.大数据的出现必将颠覆传统的数据管理方式.在数据来源、数据处理方式和数据思维等方面都会对其带来革命性的变化.如果要用简单的方式来比较传统的数据库和大数据的区别,我们认为“池塘捕鱼”和“大海捕鱼”是个很好的类比.“池塘捕鱼”代表着传统数据库时代的数据管理方式,而“大海捕鱼”则对应着大数据时代的数据管理方式,“鱼”是待处理的数据.“捕鱼”环境条件的变化导致了“捕鱼”方式的根本性差异.这些差异主要体现在如下几个方面:
1)数据规模.“池塘”和“大海”最容易发现的区别就是规模.“池塘”规模相对较小,即便是先前认为比较大的“池塘”,譬如VLDB(very large database),和“大海”XLDB(extremely large database)相比仍旧偏小.“池塘”的处理对象通常以MB为基本单位,而“大海”则常常以GB,甚至是TB,PB为基本处理单位.
2)数据类型.过去的“池塘”中,数据的种类单一,往往仅仅有一种或少数几种,这些数据又以结构化数据为主.而在“大海”中数据的种类繁多,数以千计,而这些数据又包含着结构化、半结构化以及非结构化的数据,并且半结构化和非结构化数据所占份额越来越大
3)模式(schema)和数据的关系.传统的数据库都是先有模式,然后才会产生数据.这就好比是先选好合适的“池塘”,然后才会向其中投放适合在该“池塘”环境生长的“鱼”.而大数据时代很多情况下难以预先确定模式,模式只有在数据出现之后才能确定,且模式随着数据量的增长处于不断的演变之中.这就好比先有少量的鱼类,随着时间推移,鱼的种类和数量都在不断地增长.鱼的变化会使大海的成分和环境处于不断的变化之中.
4)处理对象.在“池塘”中捕鱼,“鱼”仅仅是其捕捞对象.而在“大海”中,“鱼”除了是捕捞对象之外,还可以通过某些“鱼”的存在来判断其他种类的“鱼”是否存在.也就是说传统数据库中数据仅作为处理对象.而在大数据时代,要将数据作为一种资源来辅助解决其他诸多领域的问题
5)处理工具.捕捞“池塘”中的“鱼”,一种渔网或少数几种基本就可以应对,也就是所谓的one size fits all.但是在“大海”中,不可能存在一种渔网能够捕获所有的鱼类,也就是说No size fit all
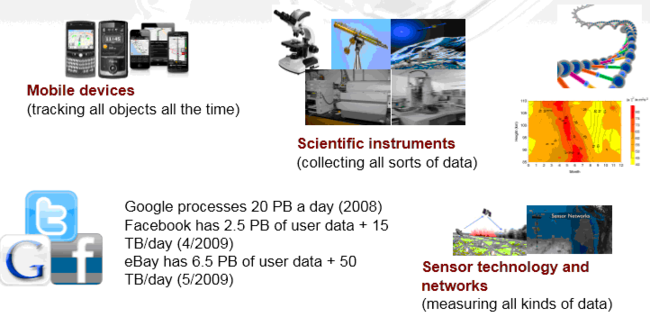
大数据的来源
信息技术的发展创造了数据产生和处理条件:云计算\网络、存储设施、数据库等技术的发展\物联网\RFID 技术\视频监控
互联网运用的广泛普及:社交网络、博客、微信、基于位置服务、搜索服务
结构化的数据与非结构化的数据
Structured data will continue to be analyzed in an enterprise using structured access methods like Structured Query Language (SQL). However, the big data systems provide tools and structures for analyzing unstructured data.
New sources of data that contribute to the unstructured data are sensors, web logs, human-generated interaction data like click streams, tweets, Facebook chats, mobile text messages, e-mails, and so forth. The presence of this hybrid mix of data makes big data analysis complex, as decisions need to be made regarding whether all this data should be first merged and then analyzed or whether only an aggregated view from different sources has to be compared.
大数据的分析方法
Unstructured data is analyzed using methods like natural language processing (NLP), data mining, master data management (MDM), and statistics.
Text analytics use NoSQL databases to standardize the structure of the data so that it can be analyzed using query languages like PIG, Hive, and others.
The analysis and extraction processes take advantageof techniques that originated in linguistics, statistics, and numerical analysis.
Bloom Filter
hashing
triel
index
parallel computing
大数据面临的挑战
Understand and prioritize the data from the garbage that is coming into the enterprise. Ninety percent of all the data is noise, and it is a daunting task to classify and filter the knowledge from the noise.
In the search for inexpensive methods of analysis, organizations have to compromise and balance against the confidentiality requirements of the data.(安全性)
Organizations struggle to determine how long this data has to be retained. This is a tricky question, as some data is useful for making long-term decisions, while other data is not relevant even a few hours after it has been generated and analyzed and insight has been obtained.
Availability of skills is a big challenge for CIOs. A higher level of proficiency in the data sciences is required to implement big data solutions today because the tools are not user-friendly yet. They still require computer science graduates to configure and operationalize a big data system.
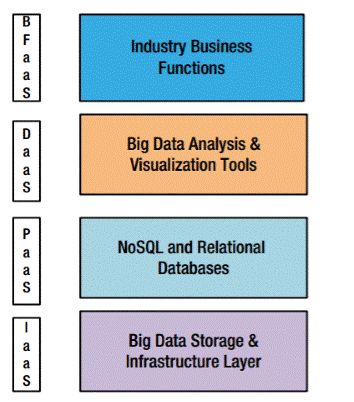
大数据的研究结构
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
This includes the storage, servers, and networkas the base, inexpensive commodities of the big data stack. This stack can be bare metal or virtual (cloud). The distributed file systems are part of this layer.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
The NoSQL data stores and distributed caches that can be logically queried using query languages form the platform layer of big data. This layer provides the logical model for the raw, unstructured data stored in the files.
Data as a Service (DaaS)
The entire array of tools available for integrating with the PaaS layer using search engines, integration adapters, batch programs, and so on is housed in this layer. The APIs available at this layer can be consumed by all endpoint systems in an elastic-computing mode.
Big Data Business Functions as a Service (BFaaS)
Specific industries—like health, retail, ecommerce, energy, and banking—can build packaged applications that serve a specific business need and leverage the DaaS layer for cross-cutting data functions.