java红黑树实现
java红黑树实现:
- 定义
红黑树是一种自平衡二叉树,红黑树和AVL树一样都对插入时间、删除时间和查找时间提供了最好可能的最坏情况担保。这不只是使它们在时间敏感的应用如实时应用(real time application)中有价值,而且使它们有在提供最坏情况担保的其他数据结构中作为建造板块的价值;例如,在计算几何中使用的很多数据结构都可以基于红黑树。
- 性质
1. 节点是红色或黑色。
2. 根是黑色。
3. 所有叶子都是黑色(这里需要将null看作叶子节点,且认为时黑色)。
4. 每个红色节点的两个子节点都是黑色。(从每个叶子到根的所有路径上不能有两个连续的红色节点)
5. 从任一节点到其每个叶子的所有简单路径都包含相同数目的黑色节点。
本文红黑树结构图会类似:
NIL: 为公用的叶子节点,为了满足性质3,和后面的操作方便,后面的图不将再画出来。
实现过程:
- 基本的数据结构抽象:
/**
* 红黑树实现:
* 性质:
* 1.节点要么红,要么黑;
* 2.根是黑色;
* 3.所有叶子都是黑色;(叶子为null节点)
* 4.每个红色节点的两个子节点都是黑色(从每个叶子到根的所有路径上不能有两个连续的红色节点)
* 5.从任一节点到其每个叶子的所有简单路径都包含相同数目的黑色节点
*/
public class RedBlackTree<T extends Comparable<T>> {
private Node<T> root; // tree root
private int size; // tree elements' count
private Node<T> NIL =
new Node<T>(null, null, null, null, Color.BLACK); //标志叶子节点
/**
* 节点类
*/
private static class Node<E>{
E value;
Node<E> parent;
Node<E> left;
Node<E> right;
Color color;
public Node(E value, Node<E> parent, Node<E> left, Node<E> right, Color color) {
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.color = color;
}
}
/**
* 节点颜色
*/
private static enum Color{
RED,
BLACK
}
}
- 通用函数:
/**
* 获取叔叔节点
* @param n 当前节点
* @return 其叔节点
*/
private Node<T> uncle(Node<T> n){
Node<T> gp = grandParent(n);
if (gp == null) return null;
if (n.parent == gp.left){ //若其父节点在其祖父节点左边
return gp.right;
} else {
return gp.left;
}
}
/**
* 获取祖父节点
* @param n 当前节点
* @return 其祖父节点
*/
private Node<T> grandParent(Node<T> n){
if (n.parent == null) return null;
return n.parent.parent;
}
- 最大,最小元素:
/**
* 返回最小元素
* @return 获取某节点为根的树的最小元素
*/
public T min(Node<T> n) {
Node<T> min = minN(n);
return min == NIL ? null : min.value;
}
/**
* 返回最小节点
* @param n 树根节点
* @return 最小节点
*/
private Node<T> minN(Node<T> n) {
Node<T> min = n;
while (min.left != NIL) {
min = min.left;
}
return min == NIL ? null : min;
}
/**
* 获取某节点为根的树的最大元素
* @return 最大元素, 没有返回null
*/
public T max(Node<T> n) {
Node<T> max = maxN(n);
return max == NIL ? null : max.value;
}
/**
* 获取某节点为根的树的最大节点
* @return 最大节点, 没有返回null
*/
public Node<T> maxN(Node<T> n) {
Node<T> max = n;
while (max.right != NIL) {
max = max.right;
}
return max == NIL ? null : max;
}
- 左,右旋函数实现:
/**
* 左旋以n节点为根的子树:
* 1.将rightChild的左子树作为n的右子树
* 2.将rightChild作为根
* 3.将n节点作为rightChild的左孩子
*/
private void leftRotate(Node<T> n){
Node<T> rightChild = n.right;
//1.
//将rightChild的左子树接到n的右边
n.right = rightChild.left;
if(rightChild.left != NIL) rightChild.left.parent = n;
//2.
rightChild.parent = n.parent;
if (n.parent == null){ //若n为树根
root = rightChild;
} else if (n.parent.left == n){ //若n为父亲的左孩子
n.parent.left = rightChild;
} else { //若n为父亲的右孩子
n.parent.right = rightChild;
}
//3.
rightChild.left = n;
n.parent = rightChild;
}
/**
* 右旋以n节点为根的子树:
* 1.将leftChild的右子树作为n的左子树
* 2.将leftChild作为根
* 3.将n节点作为leftChild的右孩子
*/
private void rightRotate(Node<T> n){
Node<T> leftChild = n.left;
//1.
n.left = leftChild.right;
if (leftChild.right != NIL) leftChild.right.parent = n;
//2.
leftChild.parent = n.parent;
if (n.parent == null){ //n为树根
root = leftChild;
} else if (n == n.parent.left){ //n为父节点点左孩子
n.parent.left = leftChild;
} else{ //n为父节点右孩子
n.parent.right = leftChild;
}
//3.
leftChild.right = n;
n.parent = leftChild;
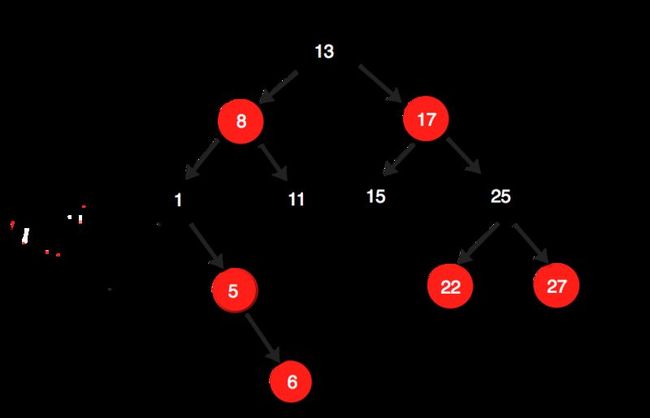
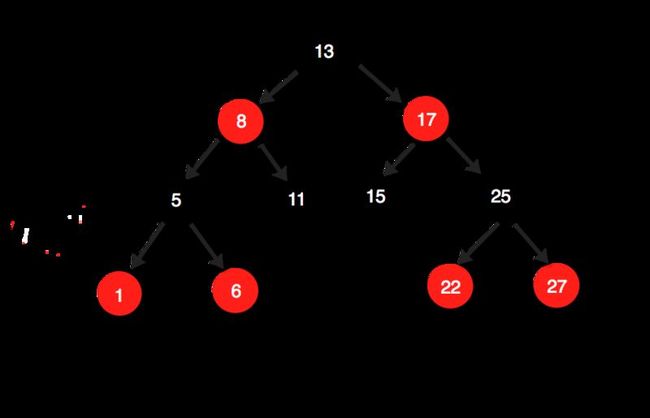
} 左,右旋如图所示:
接下来讲比较核心操作insert, remove等。
- 插入实现,其实现与查询二叉树基本一致,但插入之后需要做树调整:
/**
* 插入元素
*/
public boolean insert(T t){
//插入新节点时,以红色着色
Node<T> n = new Node<T>(t, null, NIL, NIL, Color.RED);
Node<T> pointer = root;
boolean inserted = false;
//遍历插入
while(!inserted){
if (root == null){ //空树
root = n;
inserted = true;
} else if (n.value.compareTo(pointer.value) > 0){ //向右子树找
if (pointer.right == NIL){ //插入右边
n.parent = pointer;
pointer.right = n;
inserted = true;
} else{
pointer = pointer.right;
}
} else if (n.value.compareTo(pointer.value) < 0){ //向左子树找
if (pointer.left == NIL){ //插入左边
n.parent = pointer;
pointer.left = n;
inserted = true;
} else{
pointer = pointer.left;
}
} else { //相等了
return false;
}
}
size++;
insertFixup(n); //调整树
return inserted;
} 插入后的调整操作就比较重要了,要分几种情况,分别说说吧:
- 树为空,我们没必要调整,直接讲新添加的节点作为根,并将颜色置为黑色:
- 如果添加节点的父节点为黑色,这样并不会违反红黑树的性质,所以不必调整:
- 当新节点的父节点为红色时,也分两种情况:
1.叔节点存在且为红色,这时只需要将父,叔节点置为黑色,将祖父节点(祖父节点必定存在)置为红色,然后以祖父节点递归上面的调整过程 insertFixup(grandParent), 你可以想像成祖父节点为新插入的节点即可;
2.叔节点为黑色或不存在,就需要进行旋转调整,这里讲述一种情况,其他类同:
假如我们对上面的初始图添加一个节点5,添加后:
明显现在树不满足性质4,所以需要进行旋转,而且通过一次旋转是不够的,我们需要进行两次旋转:
第一次旋转:以新添加的节点5的父节点6为根进行右旋转后:
第二次旋转,先调整颜色,将5置为黑色,1,6置为红色,以节点1进行左旋转:
这样红黑树的性质又得以满足,树调整的代码实现:
/**
* 调整树以满足红黑树性质
* @param n 新添加的节点
*/
private void insertFixup(Node<T> n) {
//若是树根
if (n.parent == null){
n.color = Color.BLACK;
return;
}
//父节点为黑色,无须调整
if (n.parent.color == Color.BLACK){
return;
}
Node<T> u = uncle(n);
Node<T> g = grandParent(n);
// 1.父节点及叔节点都为红色
if (u != null && u.color == Color.RED){
//将parent和uncle颜色置BLACK
n.parent.color = Color.BLACK;
u.color = Color.BLACK;
//将grand parent置RED
g.color = Color.RED;
//递归调整 grand parent, 这时可想像grand parent为新添加的红色节点
insertFixup(g);
} else { //父节点P是红色而叔节点是黑色或缺少
if (n == n.parent.right && n.parent == g.left){ //n为父节点右孩子,且父节点为祖父节点的左孩子
//以父左旋
leftRotate(n.parent);
n = n.left;
} else if(n == n.parent.left && n.parent == g.right){ //n为父节点左孩子,且父节点为祖父节点右孩子
//以父右旋
rightRotate(n.parent);
n = n.right;
}
n.parent.color = Color.BLACK; //parent颜色置为黑色
g.color = Color.RED;
if (n == n.parent.left && n.parent == g.left){ //n节点为父节点的左孩子,且父节点为祖父节点的左孩子
//以祖父右旋
rightRotate(g);
} else{ //n节点为父节点的右孩子,且父节点为祖父节点的右孩子
//以祖父左旋
leftRotate(g);
}
}
} 以上就是红黑树插入实现,下面说说红黑树删除实现。
- 删除实现
对于删除操作,我们需要考虑几种情况(来自维基百科):
- 如果我们删除一个红色节点(此时该节点的儿子将都为叶子节点),它的父亲和儿子一定是黑色的。所以我们可以简单的用它的黑色儿子替换它,并不会破坏属性3和4。通过被删除节点的所有路径只是少了一个红色节点,这样可以继续保证属性5。
- 另一种简单情况是在被删除节点是黑色而它的儿子是红色的时候。如果只是去除这个黑色节点,用它的红色儿子顶替上来的话,会破坏属性5,但是如果我们重绘它的儿子为黑色,则曾经通过它的所有路径将通过它的黑色儿子,这样可以继续保持属性5。
- 需要进一步讨论的是在要删除的节点和它的儿子二者都是黑色的时候,这是一种复杂的情况。我们首先把要删除的节点替换为它的儿子,后面代码中讨论。
看基本实现代码(算法导论13.4):
/**
* 删除元素
* 类似二叉查找树的删除
* @param t 待删除节点
* @return 删除成功返回true, 反之返回false
*/
public boolean remove(T t) {
boolean removed = false;
Node<T> n = getN(t); // 获取要删除的节点
Node<T> replace = null; // 用于替换节点n
Node<T> child = null; // 后继节点next的孩子节点
if (n != null) {
if (n.left == NIL || n.right == NIL) { // 若有最多一个非空孩子
replace = n;
} else { // 若有2个非空孩子, 则找其后继节点
replace = locateNextN(n);
}
// 获取替换节点replace的孩子, 有可能为NIL
child = replace.left != NIL ? replace.left : replace.right;
// 删除节点replace, 连接replace父节点-->child节点
child.parent = replace.parent;
if (replace.parent == null) { // 根节点
root = child;
} else if (replace == replace.parent.left) { // replace为其父节点左孩子
replace.parent.left = child;
} else { // replace为其父节点右孩子
replace.parent.right = child;
}
// 替换n节点的值为replace节点
if (replace != n) {
n.value = replace.value;
}
// 若后继节点为黑色, 则需做调整, 因为删除红色replace节点对红黑树性质无影响
if (replace.color == Color.BLACK) {
removeFixup(child);
}
removed = true;
}
return removed;
}
/**
* 由于删除节点而做调整
* @param n 删除节点的后继节点的孩子
*/
private void removeFixup(Node<T> n) {
while (n != root && n.color == Color.BLACK) {
if (n == n.parent.left) { // n为其父节点的左孩子
Node<T> rightBrother = rightBrother(n);
if (rightBrother.color == Color.RED) { // 兄弟颜色为红
rightBrother.color = Color.BLACK;
n.parent.color = Color.RED;
leftRotate(n.parent); // 以父左旋
rightBrother = n.parent.right;
}
// 右兄弟的两个孩子都为黑色
if (rightBrother.left.color == Color.BLACK
&& rightBrother.right.color == Color.BLACK) {
rightBrother.color = Color.RED;
n = n.parent;
} else if (rightBrother.right.color == Color.BLACK) { // 右兄弟右孩子为黑色
rightBrother.left.color = Color.BLACK;
rightBrother.color = Color.RED;
rightRotate(rightBrother);
rightBrother = n.parent.right;
} else { // 右兄弟右孩子为红色或其他情况,比如为空叶子节点NIL
rightBrother.color = n.parent.color;
n.parent.color = Color.BLACK;
rightBrother.right.color = Color.BLACK;
leftRotate(n.parent);
n = root;
}
} else { // n为其父节点的右孩子
Node<T> leftBrother = leftBrother(n);
if (leftBrother.color == Color.RED) { // 左兄弟为红色
leftBrother.color = Color.BLACK;
n.parent.color = Color.RED;
rightRotate(n.parent);
leftBrother = n.parent.left;
}
if (leftBrother.left.color == Color.BLACK
&& leftBrother.right.color == Color.BLACK) { // 左兄弟左孩子和右孩子都为黑色
leftBrother.color = Color.RED;
n = n.parent;
} else if (leftBrother.left.color == Color.BLACK) { // 仅左兄弟左孩子为黑色
leftBrother.color = Color.RED;
leftBrother.right.color = Color.BLACK;
leftRotate(leftBrother);
leftBrother = n.parent.left;
} else { // 左兄弟左孩子为红色
leftBrother.color = n.parent.color;
n.parent.color = Color.BLACK;
leftBrother.left.color = Color.BLACK;
rightRotate(n.parent);
n = root;
}
}
}
n.color = Color.BLACK;
}
左兄弟,右兄弟实现:
/**
* 获取节点的右兄弟
* @param n 当前节点
* @return 节点的右兄弟
*/
private Node<T> rightBrother(Node<T> n) {
return n == null ? null : (n.parent == null ? null : n.parent.right);
}
/**
* 获取节点的左兄弟
* @param n 当前节点
* @return 节点的右兄弟
*/
private Node<T> leftBrother(Node<T> n) {
return n == null ? null : (n.parent == null ? null : n.parent.left);
}
大家可以自己带一些实例,去体会其中对树的调整的各种情况。
不吝指正。