数据库内部排序算法之两阶段多路归并排序算法实现
前言:
基于斯坦福大学的《数据库系统实现》,实现两阶段多路归并排序算法,通过merge-sort算法的实现,理解外存算法所基于的I/O模型与内存算法基于的RAM模型的区别;理解不同的磁盘访问优化方法是如何提高数据访问性能的。
首先生成一个具有10,000,000个记录的文本文件,其中每个记录由100个字节组成。实验只考虑记录的一个属性A,假定A为整数类型。记录在block上封装时,采用non-spanned方式,即块上小于一个记录的空间不使用。Block的大小可在自己的操作系统上查看,xp一般为4096 bytes。在内存分配50M字节的空间用于外部merge-sort。要求设计和实现程序完成下列功能:
1)生成文本文件,其中属性A的值随机产生。
2)对文本文件中的记录,按照属性A进行排序,其中在第二阶段的排序中每个子列表使用一个block大小的缓冲区缓冲数据。
3)按照教材cylinder-based buffers(1M bytes)的方法,修改第二阶段的算法。
4)比较两种方法的时间性能,如果有更大的内存空间,算法性能还能提高多少?
算法描述:
Two-Phase Multiway Merge-Sort算法的具体描述分为2个阶段,如下所示:
Phase 1
1)Fill main memory with records.
2)Sort with favorite main memory sorting algorithms.
3)Write sorted list to disk.
4)Repeat until all records have been put into one of the sorted lists.
Phase 2
1)Initially load input buffers with the first block of their respective sorted lists.
2)Repeated run a competition among the first unchosen records of each of the buffered blocks.
3)If an input block is exhausted, get the next block from the same file.
4)If the output block is full, write it to disk.
我的设计思路:
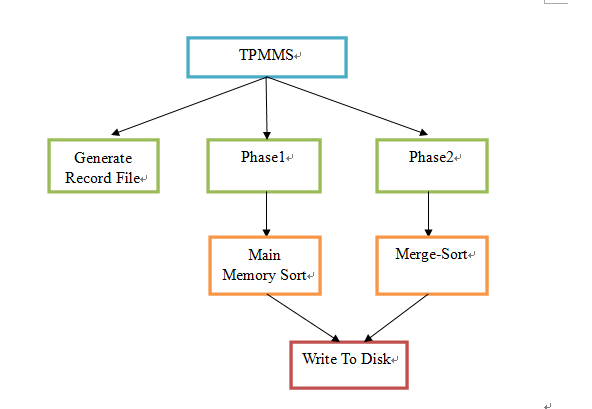
从上述的算法描述中,我们知道,系统主要由2大模块组成:Phase1和Phase2。Phase1阶段主要将生成的记录文件按内存块大小(本实验中是50MB)分成多个(本实验中是20个)相应的子记录文件,把这些文件中的记录读进内存进行排序,再写回磁盘上。Phase2阶段利用多路归并排序算法,将Phase1阶段已经排好序的子记录文件重新归并为1个有序的记录文件,写回到磁盘上。由于我们在Phase1和Phase2阶段之前必须先生成1个含有10000000个100B记录的文件,所以系统必须再加上1个生成记录文件的Generate Record File模块。终上所述,系统由3大模块组成,分别为:Generate Record File、Phase1、Phase2。Phase1模块可以细分为内存块排序模块Main Memory Sort和写回磁盘模块Write To Disk。Phase2模块可以细分为多路归并排序模块Merge-Sort和写回磁盘模块Write To Disk。
详细的系统逻辑结构图如下图所示:
TPMMS系统逻辑结构图
数据结构:
我们讨论单个记录的数据结构。由于1个记录有100个字节,其中4字节是由随机整数组成的主键属性Primary Key,另外96个字节是随意填充的数据content,而且本系统又是由C语言进行实现的,所以我们可以采取结构体来作为记录的数据结构。其中整形字段key记录4字节的主键属性,以便进行排序工作。数组字段contents用来填充剩余的96个字节,内容可以随意(本实验中均为0)。具体的数据结构如下所示:
/* the data structrue of a record */
typedef struct record
{
int key; // primary key
char contents[ROW_NUMBER + 1]; // content
}Record;
//单个记录的数据结构
具体实现:
Generate Record File阶段:
Generate Record File阶段比较简单,首先打开一个文件,然后生成随机数key并将其写入文件中,再填充96个任意内容的字节(本实验中均为0),即能生成1条完整的记录。重复10000000次,生成我们所需的记录文件。核心代码实现如下所示,其中MAX_RECORD_NUMBER大小为10000000,ROW_NUMBER大小为95。
// open file
FILE *fp = fopen( fileName.c_str(), "w" );
if ( !fp ) // open failed
{
printf("File could not be created!\n");
fprintf( stderr, "File could not be created!\n" );
exit( 1 );
}
// generate random integers and records
srand( (unsigned)time( NULL ) ); // srand seed
for ( int i = 0; i < MAX_RECORD_NUMBER; i ++ ) // generate MAX_RECORD_NUMBER records
{
if ( i > 0 )
fprintf( fp, "\n" );
int key = rand(); // primary key, random integer, 4 bytes
// write record to disk, every record has 100 bytes
fprintf( fp, "%d ", key ); // write key as the first 4 bytes
for ( int j = 0; j < ROW_NUMBER; j ++ ) // write '0' for content as the other 96 bytes
fprintf( fp, "%c", '0' );
}
fclose( fp ); // close output file
//Generate Record File阶段的实现
Phase1阶段:
Phase1阶段重点在于如何进行内存排序,并写回到磁盘上。这里我们采用了STL的sort函数帮助我们进行排序。首先读入50MB记录,利用sort函数进行排序后,写到磁盘上生成1个有序的子记录文件。重复进行20次,生成20个相应的子记录文件。核心代码实现如图4-3所示,其中BLOCK_SIZE大小为50M,SUB_LIST_NUMBER大小为20。
// read all records to main memory
for ( int k = 0; k < SUB_LIST_NUMBER; k ++ )
{
// read records of a block size to main memory
for ( i = 0; i < BLOCK_SIZE; i ++ )
{
fgets( str, ROW_NUMBER + 10, infp );
sscanf( str, "%d %s", &subRecord[i].key, subRecord[i].contents );
}
// use STL algorithm sort to sort records
sort( subRecord, subRecord + BLOCK_SIZE, cmp );
temp = generateFileName( k ); // sorted list name
FILE *outfp = fopen( temp.c_str(), "w" ); // open output file
if ( !outfp ) // open failed
{
printf( "File %s could not be opened!\n", temp.c_str());
fprintf( stderr, "File %s could not be opened!\n", temp.c_str() );
exit( 1 );
}
// write the sorted records to sub list file
for ( i = 0; i < BLOCK_SIZE; i ++ )
{
if ( i > 0 )
fprintf( outfp, "\n" );
fprintf( outfp, "%d %s", subRecord[i].key, subRecord[i].contents );
}
printf( "The sorted list %s generated successfully!\n", temp.c_str() );
fclose( outfp ); // close output stream
}
//Phase1阶段的实现
Phase2阶段:
Phase2阶段是本系统实现的难点所在。主要的实现大致可以分为以下几部分进行讨论:
1)输入缓冲的实现
将Phase1阶段中得到的20个子记录文件的首字符分别读入长度为20的输入缓冲数组inputBuffer,核心代码实现如下所示:
// read all of the sublist's first record to input buffer
for ( int k = 0; k < SUB_LIST_NUMBER; k ++ )
{
temp = generateFileName( k );
infp[k] = fopen( temp.c_str(), "r" ); // open sorted list file
if ( !infp[k] ) // open failed
{
printf( "File %s could not be created!\n", temp.c_str() );
fprintf( stderr, "File %s could not be created!\n", temp.c_str() );
exit( 1 );
}
// read record to input buffer
fgets( str, ROW_NUMBER + 10, infp[k] );
sscanf( str, "%d %s", &inputBuffer[k].key, inputBuffer[k].contents );
}
//输入缓冲的实现
2)输出缓冲的实现
选取输入缓冲数组inputBuffer中主键属性key最小的那个缓冲区,输入到输出缓冲数组outputBuffer中,然后循环执行,核心代码实现如下所示:
// select the smallest record int index = selectMinRecord( SUB_LIST_NUMBER ); int newIndex = index; // write record to output buffer copyRecord( outputBuffer[count], inputBuffer[index] ); count ++; total ++; //输出缓冲的实现
3)多路归并排序的实现
如果输出缓冲数组outputBuffer已经填满,此时可知输出缓冲是有序的,且之后的主键属性key的值都不会小于该输出缓冲区,这时我们即可将其输出到最后想要得到的结果文件上,核心代码实现如下所示:
// output buffer is full, write to disk
if ( count >= BLOCK_SIZE )
{
count = 0; // reset count
writeToDisk( outfp );
}
//多路归并排序的实现
算法结果:
50MB内存TPMMS结果:
采用50MB内存块大小进行TPMMS实验的结果如下图所示:
从上图可以看出,生成1GB大小10000000条记录的文件需要152秒,phase1阶段需要136秒,phase2阶段需要150秒。所以整个排序过程需要286秒,即4分46秒的时间才能完成。
10MB内存TPMMS结果:
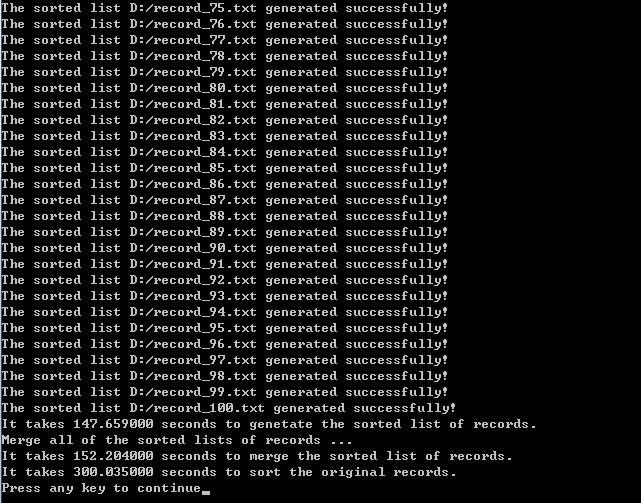
将50MB内存缩减5倍,进行10MB内存块大小的TPMMS计算。这将产生100个子记录文件。算法结果如下图所示:
生成1GB大小10000000条记录的文件所需时间不变,仍为152秒左右。我们注重于phase1阶段和phase2阶段的所需时间。从图中可以看出,phase1阶段需要147秒,phase2阶段需要152秒。整个排序过程需要300秒,即5分钟的时间才能完成。
100MB内存TPMMS算法结果:
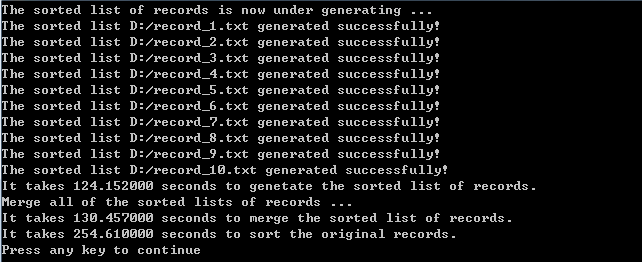
将50MB内存增加2倍,进行100MB内存块大小的TPMMS计算。这将产生10个子记录文件。运行结果如下图所示:
生成1GB大小10000000条记录的文件所需时间不变,仍为152秒左右。我们注重于phase1阶段和phase2阶段的所需时间。从图中可以看出,phase1阶段需要124秒,phase2阶段需要130秒。整个排序过程需要254秒,即4分14秒的时间才能完成。
三者的比较:
从上面的实验结果,我们可以很明显地看出,内存块大小越大,算法所需时间越少。这是因为内存块越小,生成的子记录文件个数就越多,这样phase1阶段生成子记录文件的时间就增加了。并且这还使得phase2阶段的输出缓冲区变小,导致多路归并时程序读写磁盘的次数增多,所以phase2阶段时间也增加了。这样整个排序过程时间当然增加。
终上所述,当在理想条件下,我们应使用内存块大小较大的方法来进行TPMMS算法的实现。在本章中TPMMS算法的性能为:100MB优于50MB优于10MB。所以在可能的情况下,应该考虑采纳100MB的TPMMS算法。
算法问题及解决:
Phase2阶段遇到的问题和解决方法:
前文已经详细描述了Phase2阶段的3个主要的实现阶段,但是仅仅依靠这3个阶段还不能完全实现Phase2阶段,必须解决以下几个关键问题才能完成Phase2阶段的所有任务。
读完某个子记录文件后,输入缓冲的填充方法:
当某个输入缓冲数组inputBuffer[i]相对应的子记录文件infp[i]已经读完时,我们就必须重新查找其余可用的子记录文件,按数组下标i搜索到第一个可用的文件infp[k]后,将它的第一个字节继续填充到输入缓冲数组inputBuffer[i]中。
特别的,当数组下标i超过子记录文件总数SUB_LIST_NUMBER(本实验中为20)时,我们就认为所有子记录文件已经读取完毕,这时可以设置一个bool型变量flag = true,进行标识。核心代码实现如下所示:
if ( feof( infp[index] ) ) // the whole sub file hase been resd
{
// select a file that has more record to be read
for ( i = 0; i < SUB_LIST_NUMBER; i ++ )
{
if ( !feof( infp[i] ) )
{
newIndex = i;
break;
}
}
// all sorted file have been read
if ( i >= SUB_LIST_NUMBER )
flag = true;
}
//读完某个子记录文件后,输入缓冲的填充方法
读完所有子记录文件后,处理最后一组输入缓冲数据的方法:
利用在上一步中设置的bool型变量flag,当flag=true时,我们知道子记录文件已经全部读取完毕。这时在输入缓冲数组inputBuffer中只剩下最后一组数据,并且根据Phase2阶段的定义,它们肯定比之前输入缓冲中的数据要大。所以我们只需利用STL提供的sort函数对它们进行排序后,直接输出到最终结果文件即可。核心代码实现如下所示:
// handle the last number of size records
sort( inputBuffer, inputBuffer + SUB_LIST_NUMBER, cmp );
for ( i = 1; i < SUB_LIST_NUMBER; i ++ )
{
// copy to output buffer
copyRecord( outputBuffer[BLOCK_SIZE - SUB_LIST_NUMBER + i], inputBuffer[i] );
count ++;
total ++;
}
writeToDisk( outfp ); // write to disk
//读完所有子记录文件后,处理最后一组输入缓冲数据的方法
生成子记录文件名的方法:
当我们生成子记录文件时,想要赋予文件类似于record_k.txt (k = i+1, 0 <= i <= 19) 的文件名。由于在C语言中,不支持字符串和整数的直接连接。在这里我们需要一个generateFileName函数,采用itoa函数将整数k = i+1转换成字符串,再连接到“record_”后面,从而得到想要的文件名。核心代码实现如下所示:
/* give an integer, to generate a file name */
string generateFileName( int i )
{
char str[20]; // temporary charater array
string temp = ""; // temporary string
itoa( i+1, str, 10 ); // store integer k+1 to array str
temp = str; // convert array str to temporary string
temp = "D:/record_" + temp + ".txt"; // form the file name
return temp; // return the temporary string of file name
}
//生成子记录文件名的方法
完整代码实现:
#include <algorithm> // for sort function
#include <string> // for strcpy
#include <cstdio> // for fscanf, fprintf, fopen
#include <ctime> // for clock
using namespace std;
/* define the constants used in this program */
const int MAX_RECORD_NUMBER = 10000000; // max record number
const int BLOCK_SIZE = 500000; // main memory block size
const int ROW_NUMBER = 95; // for record to fill the other 96 bytes
const int SUB_LIST_NUMBER = ( MAX_RECORD_NUMBER / BLOCK_SIZE ); // sub list number
const int MAX = 99999999; // for function selectMinRecord to initialize the variable "min"
/* the data structrue of a record */
typedef struct record
{
int key; // primary key
char contents[ROW_NUMBER + 1]; // content
}Record;
Record subRecord[BLOCK_SIZE]; // main memory buffer
Record inputBuffer[BLOCK_SIZE + 1]; // input buffer
Record outputBuffer[BLOCK_SIZE + 1]; // output buffer
/* generate a file of MAX_RECORD_NUMBER (= 10000000) records,
every record is 100 bytes */
void generateFile( string fileName )
{
// calculate time
printf("The records is now under generating ...\n");
clock_t start, finish;
double duration;
start = clock(); // start time
// open file
FILE *fp = fopen( fileName.c_str(), "w" );
if ( !fp ) // open failed
{
printf("File could not be created!\n");
fprintf( stderr, "File could not be created!\n" );
exit( 1 );
}
// generate random integers and records
srand( (unsigned)time( NULL ) ); // srand seed
for ( int i = 0; i < MAX_RECORD_NUMBER; i ++ ) // generate MAX_RECORD_NUMBER records
{
if ( i > 0 )
fprintf( fp, "\n" );
int key = rand(); // primary key, random integer, 4 bytes
// write record to disk, every record has 100 bytes
fprintf( fp, "%d ", key ); // write key as the first 4 bytes
for ( int j = 0; j < ROW_NUMBER; j ++ ) // write '0' for content as the other 96 bytes
fprintf( fp, "%c", '0' );
}
fclose( fp ); // close output file
// calculate time
finish = clock(); // finish time
duration = (double)( finish - start ) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; // run time
printf ( "It takes %f seconds to genetate the whole records.\n", duration );
}
/* use for phase 1 of two phase multiway merge sort
compare two record by primary key, with ascending order */
bool cmp( const Record &r1, const Record &r2 )
{
return r1.key < r2.key;
}
/* give an integer, to generate a file name */
string generateFileName( int i )
{
char str[20]; // temporary charater array
string temp = ""; // temporary string
itoa( i+1, str, 10 ); // store integer k+1 to array str
temp = str; // convert array str to temporary string
temp = "D:/record_" + temp + ".txt"; // form the file name
return temp; // return the temporary string of file name
}
/* phase 1 of two phase multiway merge sort
read record with maximum block size to main memory
and sort them by primary key */
void phase1( string fileName )
{
// open file
FILE *infp = fopen( fileName.c_str(), "r" );
if ( !infp ) // open failed
{
printf( "File %s could not be opened!\n", fileName.c_str() );
fprintf( stderr, "File %s could not be opened!\n", fileName.c_str() );
exit( 1 );
}
string temp = ""; // temporary string
int i = 0, j = 0;
// calculate time
printf( "The sorted list of records is now under generating ...\n" );
clock_t start, finish;
double duration;
start = clock(); // start time
char str[ROW_NUMBER + 10];
// read all records to main memory
for ( int k = 0; k < SUB_LIST_NUMBER; k ++ )
{
// read records of a block size to main memory
for ( i = 0; i < BLOCK_SIZE; i ++ )
{
fgets( str, ROW_NUMBER + 10, infp );
sscanf( str, "%d %s", &subRecord[i].key, subRecord[i].contents );
}
// use STL algorithm sort to sort records
sort( subRecord, subRecord + BLOCK_SIZE, cmp );
temp = generateFileName( k ); // sorted list name
FILE *outfp = fopen( temp.c_str(), "w" ); // open output file
if ( !outfp ) // open failed
{
printf( "File %s could not be opened!\n", temp.c_str());
fprintf( stderr, "File %s could not be opened!\n", temp.c_str() );
exit( 1 );
}
// write the sorted records to sub list file
for ( i = 0; i < BLOCK_SIZE; i ++ )
{
if ( i > 0 )
fprintf( outfp, "\n" );
fprintf( outfp, "%d %s", subRecord[i].key, subRecord[i].contents );
}
printf( "The sorted list %s generated successfully!\n", temp.c_str() );
fclose( outfp ); // close output stream
}
fclose( infp ); // close input file
// calculate time
finish = clock(); // finish time
duration = (double)( finish - start ) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; // run time
printf( "It takes %f seconds to genetate the sorted list of records.\n", duration );
}
/* copy record r2 to record r1 */
void copyRecord( Record &r1, Record &r2 )
{
r1.key = r2.key;
strcpy( r1.contents, r2.contents );
}
/* copy a record to input buffer */
void copyToInputBuffer( FILE *fp, int index )
{
char str[ROW_NUMBER + 10];
fgets( str, ROW_NUMBER + 10, fp );
sscanf( str, "%d %s", &inputBuffer[index].key, inputBuffer[index].contents );
}
/* write the records in output buffer to disk
when the output buffer is full */
void writeToDisk( FILE *fp )
{
// flush output buffer to disk
for ( int j = 0; j < BLOCK_SIZE; j ++ )
{
fprintf( fp, "%d %s\n", outputBuffer[j].key, outputBuffer[j].contents );
}
}
/* select the minimum record in input buffer
by primary key */
int selectMinRecord( int size )
{
int min = MAX;
int index = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < size; i ++ )
{
if ( inputBuffer[i].key < min )
{
min = inputBuffer[i].key;
index = i;
}
}
return index;
}
/* phase 2 of two phase multiway merge sort
merge the sorted sub list to a sorted result file
of ascending order */
void phase2()
{
// open output file to store the sorted records
FILE *outfp = fopen( "D:/result.txt", "w" );
if ( !outfp ) // open failed
{
printf( "Output file could not be created!\n" );
fprintf( stderr, "Output file could not be created!\n" );
exit( 1 );
}
string temp = ""; // temporary string
int count = 0; // the used output buffer size
int total = 0; // the record number written to disk
int i = 0, j = 0;
// array of input stream object, to open sub list of sorted records
FILE * *infp = new FILE*[ SUB_LIST_NUMBER ];
// calculate time
printf( "Merge all of the sorted lists of records ...\n" );
clock_t start, finish;
double duration;
start = clock(); // start time
char str[ROW_NUMBER + 10];
// read all of the sublist's first record to input buffer
for ( int k = 0; k < SUB_LIST_NUMBER; k ++ )
{
temp = generateFileName( k );
infp[k] = fopen( temp.c_str(), "r" ); // open sorted list file
if ( !infp[k] ) // open failed
{
printf( "File %s could not be created!\n", temp.c_str() );
fprintf( stderr, "File %s could not be created!\n", temp.c_str() );
exit( 1 );
}
// read record to input buffer
fgets( str, ROW_NUMBER + 10, infp[k] );
sscanf( str, "%d %s", &inputBuffer[k].key, inputBuffer[k].contents );
}
// mark whether all the sored list have been read
bool flag = false;
// merge the sorted list
while ( total < MAX_RECORD_NUMBER )
{
// select the smallest record
int index = selectMinRecord( SUB_LIST_NUMBER );
int newIndex = index;
// write record to output buffer
copyRecord( outputBuffer[count], inputBuffer[index] );
count ++;
total ++;
// output buffer is full, write to disk
if ( count >= BLOCK_SIZE )
{
count = 0; // reset count
writeToDisk( outfp );
}
if ( feof( infp[index] ) ) // the whole sub file hase been resd
{
// select a file that has more record to be read
for ( i = 0; i < SUB_LIST_NUMBER; i ++ )
{
if ( !feof( infp[i] ) )
{
newIndex = i;
break;
}
}
// all sorted file have been read
if ( i >= SUB_LIST_NUMBER )
flag = true;
}
if ( !flag ) // not all sublist have been read
copyToInputBuffer( infp[newIndex], index );
else // all sublist have been read
{
// handle the last number of size records
sort( inputBuffer, inputBuffer + SUB_LIST_NUMBER, cmp );
for ( i = 1; i < SUB_LIST_NUMBER; i ++ )
{
// copy to output buffer
copyRecord( outputBuffer[BLOCK_SIZE - SUB_LIST_NUMBER + i], inputBuffer[i] );
count ++;
total ++;
}
writeToDisk( outfp ); // write to disk
break;
}
}
// close all input file
for ( i = 0; i < SUB_LIST_NUMBER; i ++ )
fclose( infp[i] );
fclose( outfp ); // close output file
// calculate time
finish = clock(); // finish time
duration = (double)( finish - start ) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; // run time
printf( "It takes %f seconds to merge the sorted list of records.\n", duration );
}
/* the entrance of the program */
int main()
{
// generate record file
string fileName = "D:/record.txt";
generateFile( fileName );
// calculate time
clock_t start, finish;
double duration;
start = clock();
// phase1 and phase2
phase1( fileName );
phase2();
// calculate time
finish = clock(); // finish time
duration = (double)( finish - start ) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; // run time
printf( "It takes %f seconds to sort the original records.\n", duration );
return 0;
}
该算法的优点是磁盘中的数据只被读入主存两次,就完成了海量数据的排序。减少了IO时间。基于以上的实现,就完成了数据库的海量数据的排序!