Render OpenCascade Geometry Surfaces in OpenSceneGraph
在OpenSceneGraph中绘制OpenCascade的曲面
Render OpenCascade Geometry Surfaces in OpenSceneGraph
摘要Abstract:本文对OpenCascade中的几何曲面数据进行简要说明,并结合OpenSceneGraph将这些曲面显示。
关键字Key Words:OpenCascade、OpenSceneGraph、Geometry Surface、NURBS
一、引言 Introduction
《BRep Format Description White Paper》中对OpenCascade的几何数据结构进行了详细说明。BRep文件中用到的曲面总共有11种:
1.Plane 平面;
2.Cylinder 圆柱面;
3.Cone 圆锥面;
4.Sphere 球面;
5.Torus 圆环面;
6.Linear Extrusion 线性拉伸面;
7.Revolution Surface 旋转曲面;
8.Bezier Surface 贝塞尔面;
9.B-Spline Surface B样条曲面;
10.Rectangle Trim Surface 矩形裁剪曲面;
11.Offset Surface 偏移曲面;
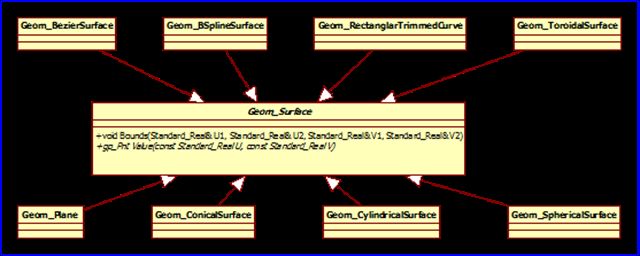
曲面的几何数据类都有一个共同的基类Geom_Surface,类图如下所示:
Figure 1.1 Geometry Surface class diagram
抽象基类Geom_Surface有几个纯虚函数Bounds()、Value()等,可用来计算曲面上的点。类图如下所示:
Figure 1.2 Geom_Surface class diagram
与另一几何内核sgCore中的几何的概念一致,几何(geometry)是用参数方程对曲线曲面精确表示的。
每种曲面都对纯虚函数进行实现,使计算曲面上点的方式统一。
曲线C(u)是单参数的矢值函数,它是由直线段到三维欧几里得空间的映射。曲面是关于两个参数u和v的矢值函数,它表示由uv平面上的二维区域R到三维欧几里得空间的映射。把曲面表示成双参数的形式为:
它的参数方程为:
u,v参数形成了一个参数平面,参数的变化区间在参数平面上构成一个矩形区域。正常情况下,参数域内的点(u,v)与曲面上的点r(u,v)是一一对应的映射关系。
给定一个具体的曲面方程,称之为给定了一个曲面的参数化。它既决定了所表示的曲面的形状,也决定了该曲面上的点与其参数域内的点的一种对应关系。同样地,曲面的参数化不是唯一的。
曲面双参数u,v的变化范围往往取为单位正方形,即u∈[0,1],v∈[0,1]。这样讨论曲面方程时,即简单、方便,又不失一般性。
二、程序示例 Code Example
使用函数Value(u, v)根据参数计算出曲面上的点,将点分u,v方向连成线,可以绘制出曲面的线框模型。程序如下所示:
/* * Copyright (c) 2013 eryar All Rights Reserved. * * File : Main.cpp * Author : [email protected] * Date : 2013-08-11 10:36 * Version : V1.0 * * Description : Draw OpenCascade Geometry Surfaces in OpenSceneGraph. * */ // OpenSceneGraph #include <osgDB/ReadFile> #include <osgViewer/Viewer> #include <osgGA/StateSetManipulator> #include <osgViewer/ViewerEventHandlers> #pragma comment(lib, "osgd.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "osgDBd.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "osgGAd.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "osgViewerd.lib") // OpenCascade #define WNT #include <TColgp_Array2OfPnt.hxx> #include <TColStd_HArray1OfInteger.hxx> #include <TColGeom_Array2OfBezierSurface.hxx> #include <GeomConvert_CompBezierSurfacesToBSplineSurface.hxx> #include <Geom_Surface.hxx> #include <Geom_BezierSurface.hxx> #include <Geom_BSplineSurface.hxx> #include <Geom_ConicalSurface.hxx> #include <Geom_CylindricalSurface.hxx> #include <Geom_Plane.hxx> #include <Geom_ToroidalSurface.hxx> #include <Geom_SphericalSurface.hxx> #pragma comment(lib, "TKernel.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "TKMath.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "TKG3d.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "TKGeomBase.lib") // Approximation Delta. const double APPROXIMATION_DELTA = 0.1; /** * @breif Build geometry surface. */ osg::Node* buildSurface(const Geom_Surface& surface) { osg::ref_ptr<osg::Geode> geode = new osg::Geode(); gp_Pnt point; Standard_Real uFirst = 0.0; Standard_Real vFirst = 0.0; Standard_Real uLast = 0.0; Standard_Real vLast = 0.0; surface.Bounds(uFirst, uLast, vFirst, vLast); Precision::IsNegativeInfinite(uFirst) ? uFirst = -1.0 : uFirst; Precision::IsInfinite(uLast) ? uLast = 1.0 : uLast; Precision::IsNegativeInfinite(vFirst) ? vFirst = -1.0 : vFirst; Precision::IsInfinite(vLast) ? vLast = 1.0 : vLast; // Approximation in v direction. for (Standard_Real u = uFirst; u <= uLast; u += APPROXIMATION_DELTA) { osg::ref_ptr<osg::Geometry> linesGeom = new osg::Geometry(); osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array> pointsVec = new osg::Vec3Array(); for (Standard_Real v = vFirst; v <= vLast; v += APPROXIMATION_DELTA) { point = surface.Value(u, v); pointsVec->push_back(osg::Vec3(point.X(), point.Y(), point.Z())); } // Set the colors. osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec4Array> colors = new osg::Vec4Array; colors->push_back(osg::Vec4(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)); linesGeom->setColorArray(colors.get()); linesGeom->setColorBinding(osg::Geometry::BIND_OVERALL); // Set the normal in the same way of color. osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array> normals = new osg::Vec3Array; normals->push_back(osg::Vec3(0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f)); linesGeom->setNormalArray(normals.get()); linesGeom->setNormalBinding(osg::Geometry::BIND_OVERALL); // Set vertex array. linesGeom->setVertexArray(pointsVec); linesGeom->addPrimitiveSet(new osg::DrawArrays(osg::PrimitiveSet::LINE_STRIP, 0, pointsVec->size())); geode->addDrawable(linesGeom.get()); } // Approximation in u direction. for (Standard_Real v = vFirst; v <= vLast; v += APPROXIMATION_DELTA) { osg::ref_ptr<osg::Geometry> linesGeom = new osg::Geometry(); osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array> pointsVec = new osg::Vec3Array(); for (Standard_Real u = vFirst; u <= uLast; u += APPROXIMATION_DELTA) { point = surface.Value(u, v); pointsVec->push_back(osg::Vec3(point.X(), point.Y(), point.Z())); } // Set the colors. osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec4Array> colors = new osg::Vec4Array; colors->push_back(osg::Vec4(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)); linesGeom->setColorArray(colors.get()); linesGeom->setColorBinding(osg::Geometry::BIND_OVERALL); // Set the normal in the same way of color. osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array> normals = new osg::Vec3Array; normals->push_back(osg::Vec3(0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f)); linesGeom->setNormalArray(normals.get()); linesGeom->setNormalBinding(osg::Geometry::BIND_OVERALL); // Set vertex array. linesGeom->setVertexArray(pointsVec); linesGeom->addPrimitiveSet(new osg::DrawArrays(osg::PrimitiveSet::LINE_STRIP, 0, pointsVec->size())); geode->addDrawable(linesGeom.get()); } return geode.release(); } /** * @breif Test geometry surfaces of OpenCascade. */ osg::Node* buildScene(void) { osg::ref_ptr<osg::Group> root = new osg::Group(); // Test Plane. Geom_Plane plane(gp::XOY()); root->addChild(buildSurface(plane)); // Test Bezier Surface and B-Spline Surface. TColgp_Array2OfPnt array1(1,3,1,3); TColgp_Array2OfPnt array2(1,3,1,3); TColgp_Array2OfPnt array3(1,3,1,3); TColgp_Array2OfPnt array4(1,3,1,3); array1.SetValue(1,1,gp_Pnt(1,1,1)); array1.SetValue(1,2,gp_Pnt(2,1,2)); array1.SetValue(1,3,gp_Pnt(3,1,1)); array1.SetValue(2,1,gp_Pnt(1,2,1)); array1.SetValue(2,2,gp_Pnt(2,2,2)); array1.SetValue(2,3,gp_Pnt(3,2,0)); array1.SetValue(3,1,gp_Pnt(1,3,2)); array1.SetValue(3,2,gp_Pnt(2,3,1)); array1.SetValue(3,3,gp_Pnt(3,3,0)); array2.SetValue(1,1,gp_Pnt(3,1,1)); array2.SetValue(1,2,gp_Pnt(4,1,1)); array2.SetValue(1,3,gp_Pnt(5,1,2)); array2.SetValue(2,1,gp_Pnt(3,2,0)); array2.SetValue(2,2,gp_Pnt(4,2,1)); array2.SetValue(2,3,gp_Pnt(5,2,2)); array2.SetValue(3,1,gp_Pnt(3,3,0)); array2.SetValue(3,2,gp_Pnt(4,3,0)); array2.SetValue(3,3,gp_Pnt(5,3,1)); array3.SetValue(1,1,gp_Pnt(1,3,2)); array3.SetValue(1,2,gp_Pnt(2,3,1)); array3.SetValue(1,3,gp_Pnt(3,3,0)); array3.SetValue(2,1,gp_Pnt(1,4,1)); array3.SetValue(2,2,gp_Pnt(2,4,0)); array3.SetValue(2,3,gp_Pnt(3,4,1)); array3.SetValue(3,1,gp_Pnt(1,5,1)); array3.SetValue(3,2,gp_Pnt(2,5,1)); array3.SetValue(3,3,gp_Pnt(3,5,2)); array4.SetValue(1,1,gp_Pnt(3,3,0)); array4.SetValue(1,2,gp_Pnt(4,3,0)); array4.SetValue(1,3,gp_Pnt(5,3,1)); array4.SetValue(2,1,gp_Pnt(3,4,1)); array4.SetValue(2,2,gp_Pnt(4,4,1)); array4.SetValue(2,3,gp_Pnt(5,4,1)); array4.SetValue(3,1,gp_Pnt(3,5,2)); array4.SetValue(3,2,gp_Pnt(4,5,2)); array4.SetValue(3,3,gp_Pnt(5,5,1)); Geom_BezierSurface BZ1(array1); Geom_BezierSurface BZ2(array2); Geom_BezierSurface BZ3(array3); Geom_BezierSurface BZ4(array4); root->addChild(buildSurface(BZ1)); root->addChild(buildSurface(BZ2)); root->addChild(buildSurface(BZ3)); root->addChild(buildSurface(BZ4)); Handle_Geom_BezierSurface BS1 = new Geom_BezierSurface(array1); Handle_Geom_BezierSurface BS2 = new Geom_BezierSurface(array2); Handle_Geom_BezierSurface BS3 = new Geom_BezierSurface(array3); Handle_Geom_BezierSurface BS4 = new Geom_BezierSurface(array4); TColGeom_Array2OfBezierSurface bezierarray(1,2,1,2); bezierarray.SetValue(1,1,BS1); bezierarray.SetValue(1,2,BS2); bezierarray.SetValue(2,1,BS3); bezierarray.SetValue(2,2,BS4); GeomConvert_CompBezierSurfacesToBSplineSurface BB (bezierarray); if (BB.IsDone()) { Geom_BSplineSurface BSPLSURF( BB.Poles()->Array2(), BB.UKnots()->Array1(), BB.VKnots()->Array1(), BB.UMultiplicities()->Array1(), BB.VMultiplicities()->Array1(), BB.UDegree(), BB.VDegree() ); BSPLSURF.Translate(gp_Vec(0,0,2)); root->addChild(buildSurface(BSPLSURF)); } // Test Spherical Surface. Geom_SphericalSurface sphericalSurface(gp::XOY(), 1.0); sphericalSurface.Translate(gp_Vec(2.5, 0.0, 0.0)); root->addChild(buildSurface(sphericalSurface)); // Test Conical Surface. Geom_ConicalSurface conicalSurface(gp::XOY(), M_PI/8, 1.0); conicalSurface.Translate(gp_Vec(5.0, 0.0, 0.0)); root->addChild(buildSurface(conicalSurface)); // Test Cylindrical Surface. Geom_CylindricalSurface cylindricalSurface(gp::XOY(), 1.0); cylindricalSurface.Translate(gp_Vec(8.0, 0.0, 0.0)); root->addChild(buildSurface(cylindricalSurface)); // Test Toroidal Surface. Geom_ToroidalSurface toroidalSurface(gp::XOY(), 1.0, 0.2); toroidalSurface.Translate(gp_Vec(11.0, 0.0, 0.0)); root->addChild(buildSurface(toroidalSurface)); return root.release(); } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { osgViewer::Viewer myViewer; myViewer.setSceneData(buildScene()); myViewer.addEventHandler(new osgGA::StateSetManipulator(myViewer.getCamera()->getOrCreateStateSet())); myViewer.addEventHandler(new osgViewer::StatsHandler); myViewer.addEventHandler(new osgViewer::WindowSizeHandler); return myViewer.run(); }
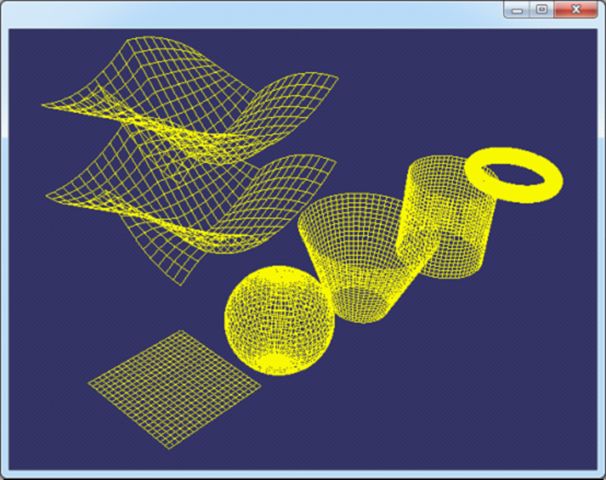
程序效果如下图所示:
Figure 2.1 OpenCascade Geometry Surfaces in OpenSceneGraph
三、结论 Conclusion
根据OpenCascade中的几何曲面的函数Value(u, v)可以计算出曲面上的点。分u方向和v方向分别绘制曲面上的点,并将之连接成线,即可以表示出曲面的线框模型。因为这样的模型没有面的信息,所以不能有光照效果、材质效果等。要有光照、材质的信息,必须将曲面进行三角剖分。相关的剖分算法有Delaunay三角剖分等。
PDF Version: Draw OpenCascade Geometry Surfaces in OpenSceneGraph