oracle 分析函数
分析函数是用于计算一组中多行的聚合值,与聚合函数的区别在于聚合函数只返回一个值,而分析函数能返回多个值
分析函数是一个查询语句中除了排序之外的最后操作,先通过连接,过滤,分组等操作之后再进行的操作
analytic_function::=

Description of the illustration analytic_function.gif
analytic_clause::=
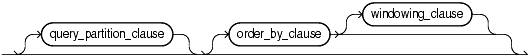
Description of the illustration analytic_clause.gif
query_partition_clause::=
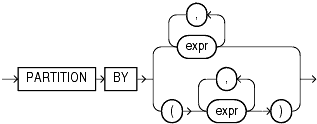
Description of the illustration query_partition_clause.gif
order_by_clause::=
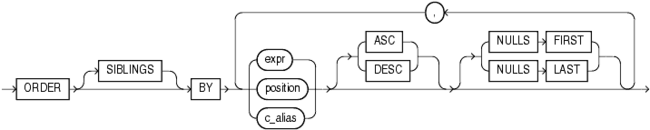
Description of the illustration order_by_clause.gif
windowing_clause ::=
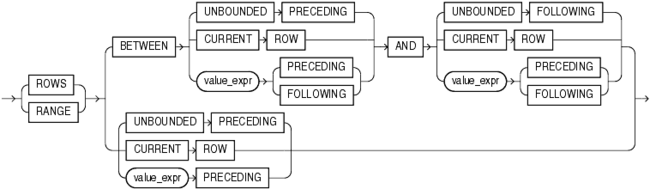
Description of the illustration windowing_clause.gif
The semantics of this syntax are discussed in the sections that follow.
analytic_function
Specify the name of an analytic function (see the listing of analytic functions following this discussion of semantics).
arguments
Analytic functions take 0 to 3 arguments. The arguments can be any numeric datatype or any nonnumeric datatype that can be implicitly converted to a numeric datatype. Oracle determines the argument with the highest numeric precedence and implicitly converts the remaining arguments to that datatype. The return type is also that datatype, unless otherwise noted for an individual function.
See Also:
"Numeric Precedence " for information on numeric precedence and Table 2-11, "Implicit Type Conversion Matrix" for more information on implicit conversion
analytic_clause
Use OVER analytic_clause to indicate that the function operates on a query result set. That is, it is computed after the FROM, WHERE, GROUP BY, and HAVING clauses. You can specify analytic functions with this clause in the select list or ORDER BY clause. To filter the results of a query based on an analytic function, nest these functions within the parent query, and then filter the results of the nested subquery.
Notes on the analytic_clause:
You cannot specify any analytic function in any part of the analytic_clause. That is, you cannot nest analytic functions. However, you can specify an analytic function in a subquery and compute another analytic function over it.
You can specify OVER analytic_clause with user-defined analytic functions as well as built-in analytic functions. See CREATE FUNCTION .
query_partition_clause
Use the PARTITION BY clause to partition the query result set into groups based on one or more value_expr. If you omit this clause, then the function treats all rows of the query result set as a single group.
To use the query_partition_clause in an analytic function, use the upper branch of the syntax (without parentheses). To use this clause in a model query (in the model_column_clauses) or a partitioned outer join (in the outer_join_clause), use the lower branch of the syntax (with parentheses).
You can specify multiple analytic functions in the same query, each with the same or different PARTITION BY keys.
If the objects being queried have the parallel attribute, and if you specify an analytic function with the query_partition_clause, then the function computations are parallelized as well.
Valid values of value_expr are constants, columns, nonanalytic functions, function expressions, or expressions involving any of these.
order_by_clause
Use the order_by_clause to specify how data is ordered within a partition. For all analytic functions except PERCENTILE_CONT and PERCENTILE_DISC (which take only a single key), you can order the values in a partition on multiple keys, each defined by a value_expr and each qualified by an ordering sequence.
Within each function, you can specify multiple ordering expressions. Doing so is especially useful when using functions that rank values, because the second expression can resolve ties between identical values for the first expression.
Whenever the order_by_clause results in identical values for multiple rows, the function returns the same result for each of those rows. Please refer to the analytic example for SUM for an illustration of this behavior.
Restriction on the ORDER BY Clause
When used in an analytic function, the order_by_clause must take an expression (expr). The SIBLINGS keyword is not valid (it is relevant only in hierarchical queries). Position (position) and column aliases (c_alias) are also invalid. Otherwise this order_by_clause is the same as that used to order the overall query or subquery.
ASC | DESC
Specify the ordering sequence (ascending or descending). ASC is the default.
NULLS FIRST | NULLS LAST
Specify whether returned rows containing nulls should appear first or last in the ordering sequence.
NULLS LAST is the default for ascending order, and NULLS FIRST is the default for descending order.
Analytic functions always operate on rows in the order specified in the order_by_clause of the function. However, the order_by_clause of the function does not guarantee the order of the result. Use the order_by_clause of the query to guarantee the final result ordering.
See Also:
order_by_clause of SELECT for more information on this clause
windowing_clause
Some analytic functions allow the windowing_clause. In the listing of analytic functions at the end of this section, the functions that allow the windowing_clause are followed by an asterisk (*).
ROWS | RANGE
These keywords define for each row a window (a physical or logical set of rows) used for calculating the function result. The function is then applied to all the rows in the window. The window moves through the query result set or partition from top to bottom.
ROWS specifies the window in physical units (rows).
RANGE specifies the window as a logical offset.
You cannot specify this clause unless you have specified the order_by_clause.
The value returned by an analytic function with a logical offset is always deterministic. However, the value returned by an analytic function with a physical offset may produce nondeterministic results unless the ordering expression results in a unique ordering. You may have to specify multiple columns in the order_by_clause to achieve this unique ordering.
BETWEEN ... AND
Use the BETWEEN ... AND clause to specify a start point and end point for the window. The first expression (before AND) defines the start point and the second expression (after AND) defines the end point.
If you omit BETWEEN and specify only one end point, then Oracle considers it the start point, and the end point defaults to the current row.
UNBOUNDED PRECEDING
Specify UNBOUNDED PRECEDING to indicate that the window starts at the first row of the partition. This is the start point specification and cannot be used as an end point specification.
UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING
Specify UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING to indicate that the window ends at the last row of the partition. This is the end point specification and cannot be used as a start point specification.
CURRENT ROW
As a start point, CURRENT ROW specifies that the window begins at the current row or value (depending on whether you have specified ROW or RANGE, respectively). In this case the end point cannot be value_expr PRECEDING.
As an end point, CURRENT ROW specifies that the window ends at the current row or value (depending on whether you have specified ROW or RANGE, respectively). In this case the start point cannot be value_expr FOLLOWING.
value_expr PRECEDING or value_expr FOLLOWING
For RANGE or ROW:
If value_expr FOLLOWING is the start point, then the end point must be value_expr FOLLOWING.
If value_expr PRECEDING is the end point, then the start point must be value_expr PRECEDING.
If you are defining a logical window defined by an interval of time in numeric format, then you may need to use conversion functions.
See Also:
NUMTOYMINTERVAL and NUMTODSINTERVAL for information on converting numeric times into intervals
If you specified ROWS:
value_expr is a physical offset. It must be a constant or expression and must evaluate to a positive numeric value.
If value_expr is part of the start point, then it must evaluate to a row before the end point.
If you specified RANGE:
value_expr is a logical offset. It must be a constant or expression that evaluates to a positive numeric value or an interval literal. Please refer to "Literals " for information on interval literals.
You can specify only one expression in the order_by_clause
If value_expr evaluates to a numeric value, then the ORDER BY expr must be a numeric or DATE datatype.
If value_expr evaluates to an interval value, then the ORDER BY expr must be a DATE datatype.
If you omit the windowing_clause entirely, then the default is RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW.
Analytic functions are commonly used in data warehousing environments. In the list of analytic functions that follows, functions followed by an asterisk (*) allow the full syntax, including the windowing_clause.
AVG *
CORR *
COVAR_POP *
COVAR_SAMP *
COUNT *
CUME_DIST
DENSE_RANK
FIRST
FIRST_VALUE *
LAG
LAST
LAST_VALUE *
LEAD
MAX *
MIN *
NTILE
PERCENT_RANK
PERCENTILE_CONT
PERCENTILE_DISC
RANK
RATIO_TO_REPORT
REGR_ (Linear Regression) Functions *
ROW_NUMBER
STDDEV *
STDDEV_POP *
STDDEV_SAMP *
SUM *
VAR_POP *
VAR_SAMP *
VARIANCE *
See Also:
Oracle Data Warehousing Guide for more information on these functions and for scenarios illustrating their use
Object Reference Functions
Object reference functions manipulate REFs, which are references to objects of specified object types. The object reference functions are:
DEREF
MAKE_REF
REF
REFTOHEX
VALUE
分析函数是一个查询语句中除了排序之外的最后操作,先通过连接,过滤,分组等操作之后再进行的操作
analytic_function::=
Description of the illustration analytic_function.gif
analytic_clause::=

Description of the illustration analytic_clause.gif
query_partition_clause::=

Description of the illustration query_partition_clause.gif
order_by_clause::=

Description of the illustration order_by_clause.gif
windowing_clause ::=

Description of the illustration windowing_clause.gif
The semantics of this syntax are discussed in the sections that follow.
analytic_function
Specify the name of an analytic function (see the listing of analytic functions following this discussion of semantics).
arguments
Analytic functions take 0 to 3 arguments. The arguments can be any numeric datatype or any nonnumeric datatype that can be implicitly converted to a numeric datatype. Oracle determines the argument with the highest numeric precedence and implicitly converts the remaining arguments to that datatype. The return type is also that datatype, unless otherwise noted for an individual function.
See Also:
"Numeric Precedence " for information on numeric precedence and Table 2-11, "Implicit Type Conversion Matrix" for more information on implicit conversion
analytic_clause
Use OVER analytic_clause to indicate that the function operates on a query result set. That is, it is computed after the FROM, WHERE, GROUP BY, and HAVING clauses. You can specify analytic functions with this clause in the select list or ORDER BY clause. To filter the results of a query based on an analytic function, nest these functions within the parent query, and then filter the results of the nested subquery.
Notes on the analytic_clause:
You cannot specify any analytic function in any part of the analytic_clause. That is, you cannot nest analytic functions. However, you can specify an analytic function in a subquery and compute another analytic function over it.
You can specify OVER analytic_clause with user-defined analytic functions as well as built-in analytic functions. See CREATE FUNCTION .
query_partition_clause
Use the PARTITION BY clause to partition the query result set into groups based on one or more value_expr. If you omit this clause, then the function treats all rows of the query result set as a single group.
To use the query_partition_clause in an analytic function, use the upper branch of the syntax (without parentheses). To use this clause in a model query (in the model_column_clauses) or a partitioned outer join (in the outer_join_clause), use the lower branch of the syntax (with parentheses).
You can specify multiple analytic functions in the same query, each with the same or different PARTITION BY keys.
If the objects being queried have the parallel attribute, and if you specify an analytic function with the query_partition_clause, then the function computations are parallelized as well.
Valid values of value_expr are constants, columns, nonanalytic functions, function expressions, or expressions involving any of these.
order_by_clause
Use the order_by_clause to specify how data is ordered within a partition. For all analytic functions except PERCENTILE_CONT and PERCENTILE_DISC (which take only a single key), you can order the values in a partition on multiple keys, each defined by a value_expr and each qualified by an ordering sequence.
Within each function, you can specify multiple ordering expressions. Doing so is especially useful when using functions that rank values, because the second expression can resolve ties between identical values for the first expression.
Whenever the order_by_clause results in identical values for multiple rows, the function returns the same result for each of those rows. Please refer to the analytic example for SUM for an illustration of this behavior.
Restriction on the ORDER BY Clause
When used in an analytic function, the order_by_clause must take an expression (expr). The SIBLINGS keyword is not valid (it is relevant only in hierarchical queries). Position (position) and column aliases (c_alias) are also invalid. Otherwise this order_by_clause is the same as that used to order the overall query or subquery.
ASC | DESC
Specify the ordering sequence (ascending or descending). ASC is the default.
NULLS FIRST | NULLS LAST
Specify whether returned rows containing nulls should appear first or last in the ordering sequence.
NULLS LAST is the default for ascending order, and NULLS FIRST is the default for descending order.
Analytic functions always operate on rows in the order specified in the order_by_clause of the function. However, the order_by_clause of the function does not guarantee the order of the result. Use the order_by_clause of the query to guarantee the final result ordering.
See Also:
order_by_clause of SELECT for more information on this clause
windowing_clause
Some analytic functions allow the windowing_clause. In the listing of analytic functions at the end of this section, the functions that allow the windowing_clause are followed by an asterisk (*).
ROWS | RANGE
These keywords define for each row a window (a physical or logical set of rows) used for calculating the function result. The function is then applied to all the rows in the window. The window moves through the query result set or partition from top to bottom.
ROWS specifies the window in physical units (rows).
RANGE specifies the window as a logical offset.
You cannot specify this clause unless you have specified the order_by_clause.
The value returned by an analytic function with a logical offset is always deterministic. However, the value returned by an analytic function with a physical offset may produce nondeterministic results unless the ordering expression results in a unique ordering. You may have to specify multiple columns in the order_by_clause to achieve this unique ordering.
BETWEEN ... AND
Use the BETWEEN ... AND clause to specify a start point and end point for the window. The first expression (before AND) defines the start point and the second expression (after AND) defines the end point.
If you omit BETWEEN and specify only one end point, then Oracle considers it the start point, and the end point defaults to the current row.
UNBOUNDED PRECEDING
Specify UNBOUNDED PRECEDING to indicate that the window starts at the first row of the partition. This is the start point specification and cannot be used as an end point specification.
UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING
Specify UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING to indicate that the window ends at the last row of the partition. This is the end point specification and cannot be used as a start point specification.
CURRENT ROW
As a start point, CURRENT ROW specifies that the window begins at the current row or value (depending on whether you have specified ROW or RANGE, respectively). In this case the end point cannot be value_expr PRECEDING.
As an end point, CURRENT ROW specifies that the window ends at the current row or value (depending on whether you have specified ROW or RANGE, respectively). In this case the start point cannot be value_expr FOLLOWING.
value_expr PRECEDING or value_expr FOLLOWING
For RANGE or ROW:
If value_expr FOLLOWING is the start point, then the end point must be value_expr FOLLOWING.
If value_expr PRECEDING is the end point, then the start point must be value_expr PRECEDING.
If you are defining a logical window defined by an interval of time in numeric format, then you may need to use conversion functions.
See Also:
NUMTOYMINTERVAL and NUMTODSINTERVAL for information on converting numeric times into intervals
If you specified ROWS:
value_expr is a physical offset. It must be a constant or expression and must evaluate to a positive numeric value.
If value_expr is part of the start point, then it must evaluate to a row before the end point.
If you specified RANGE:
value_expr is a logical offset. It must be a constant or expression that evaluates to a positive numeric value or an interval literal. Please refer to "Literals " for information on interval literals.
You can specify only one expression in the order_by_clause
If value_expr evaluates to a numeric value, then the ORDER BY expr must be a numeric or DATE datatype.
If value_expr evaluates to an interval value, then the ORDER BY expr must be a DATE datatype.
If you omit the windowing_clause entirely, then the default is RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW.
Analytic functions are commonly used in data warehousing environments. In the list of analytic functions that follows, functions followed by an asterisk (*) allow the full syntax, including the windowing_clause.
AVG *
CORR *
COVAR_POP *
COVAR_SAMP *
COUNT *
CUME_DIST
DENSE_RANK
FIRST
FIRST_VALUE *
LAG
LAST
LAST_VALUE *
LEAD
MAX *
MIN *
NTILE
PERCENT_RANK
PERCENTILE_CONT
PERCENTILE_DISC
RANK
RATIO_TO_REPORT
REGR_ (Linear Regression) Functions *
ROW_NUMBER
STDDEV *
STDDEV_POP *
STDDEV_SAMP *
SUM *
VAR_POP *
VAR_SAMP *
VARIANCE *
See Also:
Oracle Data Warehousing Guide for more information on these functions and for scenarios illustrating their use
Object Reference Functions
Object reference functions manipulate REFs, which are references to objects of specified object types. The object reference functions are:
DEREF
MAKE_REF
REF
REFTOHEX
VALUE