学习凸包(三):凸包练习 POJ 1113
接上文:学习凸包(二):分治法求解
http://128kj.iteye.com/blog/1748622
通过前面两文学习,基本上明白了凸包,先做个练习POJ 1113.
POJ 1113题意:
从前有一个吝啬的国王要求他的总设计师在他的城堡周围建一道围墙。这国王非常吝啬,以至于他没有听总设计师的建一个拥有外形漂亮又高大的砖头塔楼的围墙的建议,而是要求用最少的石头和劳工围着整个城堡建围墙,但是要求围墙必须远离城堡一定的距离。要是国王发现发现设计师用了超过建造围墙所需要的材料,那么这个设计师的脑袋将保不住了。而且,国王要求设计师马上拿出一个建墙的计划,列出建造围墙所需要的最少的材料。你的任务是去帮助这个可怜的设计师保住他的性命,请写一个程序算出建造满足国王要求的围墙的最小的长度。这个任务事实上稍微有点简单,因为国王的城堡是一个多边形的,除开顶点处,其他的地方不会相交,并且位于平坦的地面上,设计师早已画好了一个笛卡尔坐标系,而且精确地计算出了城堡中每一个点的坐标。
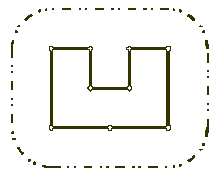
Input
第一行包括两个整数,N,L,第一个整数是点的个数,第二个整数是围墙必须远离城堡的距离。接下来n行,每行两个数{中间一个空格}表示每一个点的坐标。所有的点各不相同。
Output
输出一个整数,即围墙的长度。答案四舍五入
样例:
Sample Input
9 100
200 400
300 400
300 300
400 300
400 400
500 400
500 200
350 200
200 200
Sample Output
1628
从图可以看出,所求围墙(虚线部分)长度 = 凸包边长 + 一个圆周长
下面是AC代码(分治法求凸包):
源码:
通过前面两文学习,基本上明白了凸包,先做个练习POJ 1113.
POJ 1113题意:
从前有一个吝啬的国王要求他的总设计师在他的城堡周围建一道围墙。这国王非常吝啬,以至于他没有听总设计师的建一个拥有外形漂亮又高大的砖头塔楼的围墙的建议,而是要求用最少的石头和劳工围着整个城堡建围墙,但是要求围墙必须远离城堡一定的距离。要是国王发现发现设计师用了超过建造围墙所需要的材料,那么这个设计师的脑袋将保不住了。而且,国王要求设计师马上拿出一个建墙的计划,列出建造围墙所需要的最少的材料。你的任务是去帮助这个可怜的设计师保住他的性命,请写一个程序算出建造满足国王要求的围墙的最小的长度。这个任务事实上稍微有点简单,因为国王的城堡是一个多边形的,除开顶点处,其他的地方不会相交,并且位于平坦的地面上,设计师早已画好了一个笛卡尔坐标系,而且精确地计算出了城堡中每一个点的坐标。

Input
第一行包括两个整数,N,L,第一个整数是点的个数,第二个整数是围墙必须远离城堡的距离。接下来n行,每行两个数{中间一个空格}表示每一个点的坐标。所有的点各不相同。
Output
输出一个整数,即围墙的长度。答案四舍五入
样例:
Sample Input
9 100
200 400
300 400
300 300
400 300
400 400
500 400
500 200
350 200
200 200
Sample Output
1628
从图可以看出,所求围墙(虚线部分)长度 = 凸包边长 + 一个圆周长
下面是AC代码(分治法求凸包):
import java.util.*;
class Line {//线
Point p1, p2;
Line(Point p1, Point p2) {
this.p1 = p1;
this.p2 = p2;
}
public double getLength() {
double dx = Math.abs(p1.x - p2.x);
double dy = Math.abs(p1.y - p2.y);
return Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
}
class Point{//点
double x;
double y;
public Point(double x,double y){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
}
/*
* 分治法求凸包
*/
class QuickTuBao {
List<Point> pts = null;//点集
List<Line> lines = new ArrayList<Line>();//点集pts的凸包
public void setPointList(List<Point> pts) {
this.pts = pts;
}
public QuickTuBao(List<Point> pts){
this.pts=pts;
}
//求凸包,结果存入lines中
public List<Line> eval() {
lines.clear();
if (pts == null || pts.isEmpty()) { return lines; }
List<Point> ptsLeft = new ArrayList<Point>();//左凸包中的点
List<Point> ptsRight = new ArrayList<Point>();//右凸包中的点
//按x坐标对pts排序
Collections.sort(pts, new Comparator<Point>() {
public int compare(Point p1, Point p2) {
if(p1.x-p2.x>0) return 1;
if(p1.x-p2.x<0) return -1;
return 0;
}
});
Point p1 = pts.get(0);//最左边的点
Point p2 = pts.get(pts.size()-1);//最右边的点,用直线p1p2将原凸包分成两个小凸包
Point p3 = null;
double area = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < pts.size(); i++) {
p3 = pts.get(i);
area = getArea(p1, p2, p3);//求此三点所成三角形的有向面积
if (area > 0) {
ptsLeft.add(p3);
} else if (area < 0) {
ptsRight.add(p3);
}
}
d(p1, p2, ptsLeft);//分别求解
d(p2, p1, ptsRight);
return lines;
}
private void d(Point p1, Point p2, List<Point> s) {
//s集合为空
if (s.isEmpty()) {
lines.add(new Line(p1, p2));
return;
}
//s集合不为空,寻找Pmax
double area = 0;
double maxArea = 0;
Point pMax = null;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
area = getArea(p1, p2, s.get(i));//最大面积对应的点就是Pmax
if (area > maxArea) {
pMax = s.get(i);
maxArea = area;
}
}
//找出位于(p1, pMax)直线左边的点集s1
//找出位于(pMax, p2)直线左边的点集s2
List<Point> s1 = new ArrayList<Point>();
List<Point> s2 = new ArrayList<Point>();
Point p3 = null;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
p3 = s.get(i);
if (getArea(p1, pMax, p3) > 0) {
s1.add(p3);
} else if (getArea(pMax, p2, p3) > 0) {
s2.add(p3);
}
}
//递归
d(p1, pMax, s1);
d(pMax, p2, s2);
}
// 三角形的面积等于返回值绝对值的二分之一
// 当且仅当点p3位于直线(p1, p2)左侧时,表达式的符号为正
private double getArea(Point p1, Point p2, Point p3) {
return p1.x * p2.y + p3.x * p1.y + p2.x * p3.y -
p3.x * p2.y - p2.x * p1.y - p1.x * p3.y;
}
}
public class Main {
//计算凸包周长+圆周长
private static int getLength(List<Line> ls, int d) {
double length = 0.0;
Line l1 = null;
for (int i = 0; i < ls.size(); i++) {
l1 = ls.get(i);
length += l1.getLength();
}
length += 2 * d * Math.PI;
return (int)(length + 0.5);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = cin.nextInt();
int d = cin.nextInt();
List<Point> pts = new ArrayList<Point>(n);
int x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
x = cin.nextInt();
y = cin.nextInt();
pts.add(new Point(x, y));
}
QuickTuBao qt = new QuickTuBao(pts);
List<Line> ls = qt.eval();
int length = getLength(ls, d);
System.out.println(length);
}
}
源码: