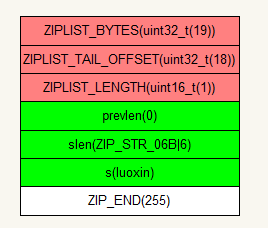
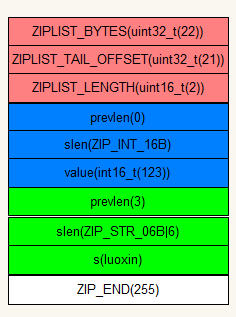
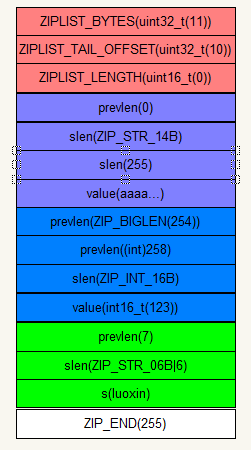
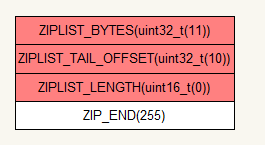
ziplist相比之前分析的zipmap要相对复杂一些,但也有一些相似的地方。
首先通过注释来了解一下它的基本结构
<zlbytes><zltail><zllen><entry><entry><zlend>
* <zlbytes>是一个无符号整数,用来存储 ziplist占用的字节数。
* <zltail>是list中到最后一个 entry的平移量。这样就允许直接操作尾部而不用去遍历。
* <zllen>是list中entry的个数,当它的值大于2的16次方-2时,需要遍历整个list得出。
* <zllen>是list的特殊值,代表list的尾部,值为255.
* <entry>就是要存的数据,第一个是数据的长度,第二个是数据的值
我们先来看看list的初始化
/* Utility macros */
#define ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl) (*((uint32_t*)(zl)))
#define ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) (*((uint32_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t))))
#define ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) (*((uint16_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t)*2)))
#define ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE (sizeof(uint32_t)*2+sizeof(uint16_t)) //10
#define ZIPLIST_ENTRY_HEAD(zl) ((zl)+ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE)
#define ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl) ((zl)+intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl)))
#define ZIPLIST_ENTRY_END(zl) ((zl)+intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl))-1)
/* Create a new empty ziplist. */
unsigned char *ziplistNew(void) {
unsigned int bytes = ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE+1;
unsigned char *zl = zmalloc(bytes);
ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl) = intrev32ifbe(bytes);
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE);
ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) = 0;
zl[bytes-1] = ZIP_END;
return zl;
} 图解:
相比zipmap,有相似之处,如它的结尾都是255,有存储其数据的个数,但在list中其所用字节为2。
而且list多了统计所有字节的ZIPLIST_BYTES,和偏移量的ZIPLIST_LENGTH,也就意味着一个list的字节长度是不能大于unit32_t的取值范围的
/* Decode the number of bytes required to store the length of the previous
* element, from the perspective of the entry pointed to by 'ptr'. */
#define ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(ptr, prevlensize) do { \
if ((ptr)[0] < ZIP_BIGLEN) {//zip_BIGLEN=254,解码,获取prevlensize占用的字节 \
(prevlensize) = 1; \
} else { \
(prevlensize) = 5; \
} \
} while(0);
/* Decode the length of the previous element, from the perspective of the entry
* pointed to by 'ptr'. */
//通过解码出prevlensize占用的字节数,解码出prevlen的值
#define ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(ptr, prevlensize, prevlen) do { \
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(ptr, prevlensize); \
if ((prevlensize) == 1) { \
(prevlen) = (ptr)[0]; \
} else if ((prevlensize) == 5) { \
assert(sizeof((prevlensize)) == 4); \
memcpy(&(prevlen), ((char*)(ptr)) + 1, 4); \
memrev32ifbe(&prevlen); \
} \
} while(0); 这两个预处理是不是有点类似zipmap的解码呢?
//下面是比较头晕的部分,entry的加码与解码
/* Check if string pointed to by 'entry' can be encoded as an integer.
* Stores the integer value in 'v' and its encoding in 'encoding'. */
//这个方法是尝试将value转为long long类型,并根据其值生成encoding
static int zipTryEncoding(unsigned char *entry, unsigned int entrylen, long long *v, unsigned char *encoding) {
long long value;
if (entrylen >= 32 || entrylen == 0) return 0;//value的长度不能超过32
if (string2ll((char*)entry,entrylen,&value)) {//转int方法,此处不深入
/* Great, the string can be encoded. Check what's the smallest
* of our encoding types that can hold this value. */
if (value >= 0 && value <= 12) {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN+value;
} else if (value >= INT8_MIN && value <= INT8_MAX) {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_8B;
} else if (value >= INT16_MIN && value <= INT16_MAX) {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_16B;
} else if (value >= INT24_MIN && value <= INT24_MAX) {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_24B;
} else if (value >= INT32_MIN && value <= INT32_MAX) {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_32B;
} else {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_64B;
}
//ZIP_INT_8|16|32|64B都是大于ZIP_STR_MASK的
*v = value;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
/* Extract the encoding from the byte pointed by 'ptr' and set it into
* 'encoding'. */
//解码entry,如果encoding<ZIP_STR_MASK,说明string,否则是int
#define ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING(ptr, encoding) do { \
(encoding) = (ptr[0]); \
if ((encoding) < ZIP_STR_MASK) (encoding) &= ZIP_STR_MASK; \
} while(0)
/* Decode the length encoded in 'ptr'. The 'encoding' variable will hold the
* entries encoding, the 'lensize' variable will hold the number of bytes
* required to encode the entries length, and the 'len' variable will hold the
* entries length. */
#define ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(ptr, encoding, lensize, len) do { \
ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING((ptr), (encoding));
//如上,小于则为int,将len转回 \
if ((encoding) < ZIP_STR_MASK) { \
if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_06B) { \
(lensize) = 1; \
(len) = (ptr)[0] & 0x3f; \
} else if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_14B) { \
(lensize) = 2; \
(len) = (((ptr)[0] & 0x3f) << 8) | (ptr)[1]; \
} else if (encoding == ZIP_STR_32B) { \
(lensize) = 5; \
(len) = ((ptr)[1] << 24) | \
((ptr)[2] << 16) | \
((ptr)[3] << 8) | \
((ptr)[4]); \
} else { \
assert(NULL); \
} \
} else { \
(lensize) = 1; \
(len) = zipIntSize(encoding); \
} \
} while(0);
/* Return bytes needed to store integer encoded by 'encoding' */
static unsigned int zipIntSize(unsigned char encoding) {
switch(encoding) {
case ZIP_INT_8B: return 1;
case ZIP_INT_16B: return 2;
case ZIP_INT_24B: return 3;
case ZIP_INT_32B: return 4;
case ZIP_INT_64B: return 8;
default: return 0; /* 4 bit immediate */
}
assert(NULL);
return 0;
}
现在我们住这刚初始化的list中lpush('luoxin',6)
/* Insert item at "p". */
static unsigned char *__ziplistInsert(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen) {
size_t curlen = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl)), reqlen, prevlen = 0;
size_t offset;
int nextdiff = 0;
unsigned char encoding = 0;//这个参数用于编码解码
long long value = 123456789; /* initialized to avoid warning. Using a value
that is easy to see if for some reason
we use it uninitialized. */
zlentry entry, tail;
/* Find out prevlen for the entry that is inserted. */
if (p[0] != ZIP_END) {//我们是第一次插入,所以p[0]==ZIP_END
entry = zipEntry(p);
prevlen = entry.prevrawlen;
} else {
unsigned char *ptail = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl);//通过偏移量直接到list的尾部
if (ptail[0] != ZIP_END) {
prevlen = zipRawEntryLength(ptail);
}
}
/* See if the entry can be encoded */
if (zipTryEncoding(s,slen,&value,&encoding)) {//这里尝试将value转成为int
/* 'encoding' is set to the appropriate integer encoding */
reqlen = zipIntSize(encoding);
} else {
/* 'encoding' is untouched, however zipEncodeLength will use the
* string length to figure out how to encode it. */
reqlen = slen;
}
/* We need space for both the length of the previous entry and
* the length of the payload. */
//计算出整个entry将要占用的字节数
reqlen += zipPrevEncodeLength(NULL,prevlen);
reqlen += zipEncodeLength(NULL,encoding,slen);
/* When the insert position is not equal to the tail, we need to
* make sure that the next entry can hold this entry's length in
* its prevlen field. */
nextdiff = (p[0] != ZIP_END) ? zipPrevLenByteDiff(p,reqlen) : 0;
/* Store offset because a realloc may change the address of zl. */
offset = p-zl;
//resize下ziplist
zl = ziplistResize(zl,curlen+reqlen+nextdiff);
p = zl+offset;
/* Apply memory move when necessary and update tail offset. */
if (p[0] != ZIP_END) {
/* Subtract one because of the ZIP_END bytes */
memmove(p+reqlen,p-nextdiff,curlen-offset-1+nextdiff);
/* Encode this entry's raw length in the next entry. */
//写入reqlen,相当于下一个entry的prevlen
zipPrevEncodeLength(p+reqlen,reqlen);
/* Update offset for tail */
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+reqlen);
/* When the tail contains more than one entry, we need to take
* "nextdiff" in account as well. Otherwise, a change in the
* size of prevlen doesn't have an effect on the *tail* offset. */
tail = zipEntry(p+reqlen);
if (p[reqlen+tail.headersize+tail.len] != ZIP_END) {
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+nextdiff);
}
} else {
/* This element will be the new tail. */
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(p-zl);
}
/* When nextdiff != 0, the raw length of the next entry has changed, so
* we need to cascade the update throughout the ziplist */
if (nextdiff != 0) {//此处后面再讲
offset = p-zl;
zl = __ziplistCascadeUpdate(zl,p+reqlen);
p = zl+offset;
}
/* Write the entry */
//像zipmap一样的方式写入entry
p += zipPrevEncodeLength(p,prevlen);
p += zipEncodeLength(p,encoding,slen);
if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) {//在这里判断一下类型
memcpy(p,s,slen);
} else {
zipSaveInteger(p,value,encoding);
}
ZIPLIST_INCR_LENGTH(zl,1);//将entry的个数加1
return zl;
} 图解:
再lpush('123',3),注意会转化为int哦
图解:
再lpush('aa...',255),插入一个长度于255的字符串,255大于254,所以其slen将占用2个字节
上面提到的zipEncodeLength方法:
else if (rawlen <= 0x3fff) {
len += 1;
if (!p) return len;
buf[0] = ZIP_STR_14B | ((rawlen >> 8) & 0x3f);
buf[1] = rawlen & 0xff; 第一个字节为ZIP_STR_14B ,第二个字节为255,而且因为所值大于254,倒置prenlen所占用的字节也将发生改变,就会有上面提到的nextdiff=4
/* When nextdiff != 0, the raw length of the next entry has changed, so
* we need to cascade the update throughout the ziplist */
if (nextdiff != 0) {
offset = p-zl;
zl = __ziplistCascadeUpdate(zl,p+reqlen);
p = zl+offset;
}
/* When an entry is inserted, we need to set the prevlen field of the next
* entry to equal the length of the inserted entry. It can occur that this
* length cannot be encoded in 1 byte and the next entry needs to be grow
* a bit larger to hold the 5-byte encoded prevlen. This can be done for free,
* because this only happens when an entry is already being inserted (which
* causes a realloc and memmove). However, encoding the prevlen may require
* that this entry is grown as well. This effect may cascade throughout
* the ziplist when there are consecutive entries with a size close to
* ZIP_BIGLEN, so we need to check that the prevlen can be encoded in every
* consecutive entry.
*
* Note that this effect can also happen in reverse, where the bytes required
* to encode the prevlen field can shrink. This effect is deliberately ignored,
* because it can cause a "flapping" effect where a chain prevlen fields is
* first grown and then shrunk again after consecutive inserts. Rather, the
* field is allowed to stay larger than necessary, because a large prevlen
* field implies the ziplist is holding large entries anyway.
*
* The pointer "p" points to the first entry that does NOT need to be
* updated, i.e. consecutive fields MAY need an update. */
static unsigned char *__ziplistCascadeUpdate(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p) {
size_t curlen = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl)), rawlen, rawlensize;
size_t offset, noffset, extra;
unsigned char *np;
zlentry cur, next;
while (p[0] != ZIP_END) {
cur = zipEntry(p);
rawlen = cur.headersize + cur.len;
rawlensize = zipPrevEncodeLength(NULL,rawlen);
/* Abort if there is no next entry. */
if (p[rawlen] == ZIP_END) break;
next = zipEntry(p+rawlen);
/* Abort when "prevlen" has not changed. */
if (next.prevrawlen == rawlen) break;
if (next.prevrawlensize < rawlensize) {
/* The "prevlen" field of "next" needs more bytes to hold
* the raw length of "cur". */
offset = p-zl;
extra = rawlensize-next.prevrawlensize;
zl = ziplistResize(zl,curlen+extra);
p = zl+offset;
/* Current pointer and offset for next element. */
np = p+rawlen;
noffset = np-zl;
/* Update tail offset when next element is not the tail element. */
if ((zl+intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))) != np) {
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+extra);
}
/* Move the tail to the back. */
memmove(np+rawlensize,
np+next.prevrawlensize,
curlen-noffset-next.prevrawlensize-1);
zipPrevEncodeLength(np,rawlen);
/* Advance the cursor */
p += rawlen;
curlen += extra;
} else {
if (next.prevrawlensize > rawlensize) {
/* This would result in shrinking, which we want to avoid.
* So, set "rawlen" in the available bytes. */
zipPrevEncodeLengthForceLarge(p+rawlen,rawlen);
} else {
zipPrevEncodeLength(p+rawlen,rawlen);
}
/* Stop here, as the raw length of "next" has not changed. */
break;
}
}
return zl;
} 这里也是ziplist最难理解之处,当一个prenlen所占用的字节数发生变化,就会倒置下一个prenlen的值发生变化
图解:
最后看一下取list长度
/* Return length of ziplist. */
unsigned int ziplistLen(unsigned char *zl) {
unsigned int len = 0;
if (intrev16ifbe(ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl)) < UINT16_MAX) {
len = intrev16ifbe(ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl));
} else {//大于则要遍历list
unsigned char *p = zl+ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE;
while (*p != ZIP_END) {
p += zipRawEntryLength(p);
len++;
}
/* Re-store length if small enough */
if (len < UINT16_MAX) ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) = intrev16ifbe(len);
}
return len;
}
文件的其他方法不做分析
总结&注意:list在存数据时做了转int,如果为int,其所占用的字节数最少为2,比 map要多,而且相对map每存一个entry,要多一个prevlen,以达到双向链表的目的。当插入的数据长度大于254时,有可能__ziplistCascadeUpdate操作,相对比较复杂。当插入过多数据需要遍历list。