一家大企业 A、B系统间通信
(如银行,假设它有
客户关系管理(CRM),
客户信息系统(CIS),
证券结算系统,
账户管理系统 等等,
客户信息系统 需要发送客户信息给 证券结算系统;
客户信息系统 需要发送客户信息给 账户管理系统 等;
若A系统 发送消息给 B系统,A 理解为 B 的上游系统
),
且A、B系统运行于两个独立的JBoss服务器中,A提供了MQ服务,那么B 需读取上游系统A的MQ信息来获取消息;
其实也可以自己根据前面的示例来模拟实现下;
思路:
建立两个JBoss,修改其中一个的端口,
一个模拟A系统,配置了JBossMQ信息;A系统发送一条消息到JBossMQ;
一个模拟B系统,B系统有个MDB来远程访问JBossMQ服务,并把消息打印出来;
环境: JBoss 5.1,JDK1.6
1、拿一个Jboss,copy一份,分别修改其名称为jboss-5.1.0_Sender、jboss-5.1.0_Receiver
修改 jboss-5.1.0_Sender 下的端口(同一机器上,避免冲突,其实也就是两个独立的 AS)
修改%JBOSS_HOME_Sender%\server\default\deploy\jbossweb.sar\server.xml 中的所有端口;
修改%JBOSS_HOME_Sender%\server\default\conf\bindingservice.beans\META-INF\bindings-jboss-beans.xml 中的所有端口;
为了简单快捷,就在端口前加个1,如8080 -> 18080,1099 -> 11099
注意:为防止冲突,需修改全部接口,模拟两个不同的JBOSS
2. 在 jboss-5.1.0_Sender中,进入%JBOSS_HOME_Sender%\server\default\deploy,新建Sender-service.xml文件:
(这里就是配置JBossMQ,集成在JBoss中,这样启动 A 的JBoss 就提供了MQ服务,即构造发送到的目的地址destination)
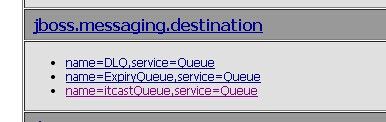
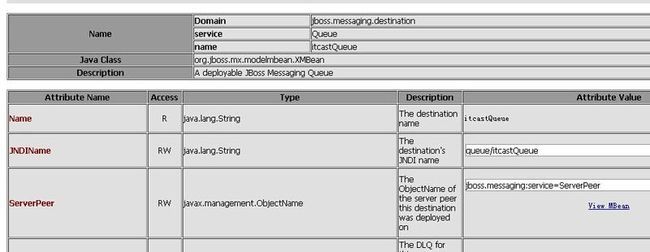
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <server> <mbean xmbean-dd="xmdesc/Queue-xmbean.xml" name="jboss.messaging.destination:service=Queue,name=itcastQueue" code="org.jboss.jms.server.destination.QueueService"> <attribute name="JNDIName">queue/itcastQueue</attribute> <depends optional-attribute-name="ServerPeer">jboss.messaging:service=ServerPeer</depends> <depends>jboss.messaging:service=PostOffice</depends> </mbean> </server>
Queue的name为itcastQueue
3. 创建Java Project,创建文件QueueSender.java:
(这里就是模拟 A 中的系统往 MQ 发送消息,注意classpath加上JBoss的jar文件)
注意:此处注意导入的是jboss中client下的包,而不是其他
Jboss的client下已经有jboss-javaee.jar,不要再额外引入javaee.jar
javaee.jar冲突:
Absent Code attribute in method that is not native or abstract
https://community.jboss.org/thread/176424?_sscc=t
package com;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.jms.Destination;
import javax.jms.JMSException;
import javax.jms.MessageProducer;
import javax.jms.QueueConnection;
import javax.jms.QueueConnectionFactory;
import javax.jms.QueueSession;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class QueueSender{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("java.naming.factory.initial",
"org.jnp.interfaces.NamingContextFactory");
props.setProperty("java.naming.provider.url", "localhost:11099");
props.setProperty("java.naming.factory.url.pkgs",
"org.jboss.naming");
/**
* Context不指定props会报错:
* javax.naming.NoInitialContextException: Need to specify class name in environment or system property,
* or as an applet parameter, or in an application resource file: java.naming.factory.initial
*/
try {
InitialContext ctx = new InitialContext(props);
QueueConnectionFactory factory = (QueueConnectionFactory) ctx.lookup("ConnectionFactory");
QueueConnection conn = factory.createQueueConnection();
QueueSession session = conn.createQueueSession(false,QueueSession.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
Destination destination = (Destination) ctx.lookup("queue/itcastQueue");
MessageProducer producer = session.createProducer(destination);
producer.send(session.createTextMessage("First JMS 消息!"));
session.close();
conn.close();
} catch (NamingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (JMSException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println();
}
}
注意此处的localhost:11099,需跟下面一致
企业B(或B系统)
4. 在 jboss-5.1.0_Receiver中,进入%JBOSS_HOME%\server\default\deploy,新建Receiver-service.xml文件:
(这里就是 A 提供给 B 的MQ中间件配置信息,B根据A提供的信息配置在自己的JBoss中)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<server>
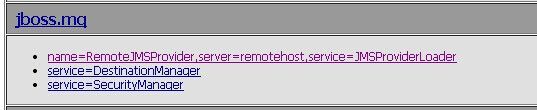
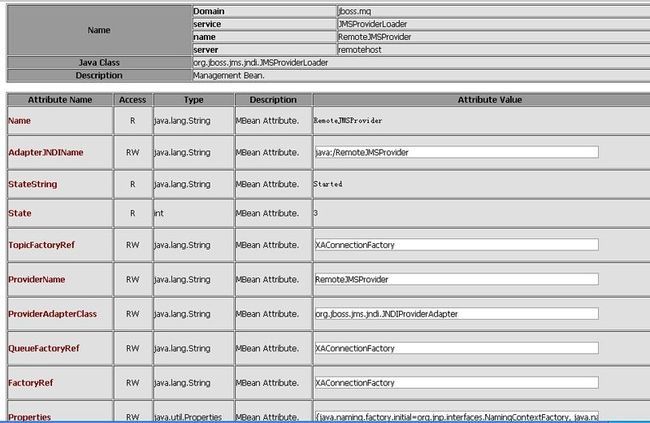
<mbean code="org.jboss.jms.jndi.JMSProviderLoader" name="jboss.mq:service=JMSProviderLoader,name=RemoteJMSProvider,server=remotehost">
<attribute name="ProviderName">RemoteJMSProvider</attribute>
<attribute name="ProviderAdapterClass">org.jboss.jms.jndi.JNDIProviderAdapter</attribute>
<attribute name="FactoryRef">XAConnectionFactory</attribute>
<attribute name="QueueFactoryRef">XAConnectionFactory</attribute>
<attribute name="TopicFactoryRef">XAConnectionFactory</attribute>
<attribute name="Properties">
java.naming.factory.initial=org.jnp.interfaces.NamingContextFactory
java.naming.factory.url.pkgs=org.jnp.interfaces
java.naming.provider.url=localhost:11099
</attribute>
</mbean>
</server>
注意此处的localhost:11099,需跟上面构造InitialContext时的环境一致,上面引用此处
MQ的name为RemoteJMSProvider
5. 创建EJB Project,新建MDB:
(这里就是当A发送消息到MQ中时,B通过此EJB就能监听收到消息)
import javax.ejb.ActivationConfigProperty;
import javax.ejb.MessageDriven;
import javax.jms.JMSException;
import javax.jms.Message;
import javax.jms.MessageListener;
import javax.jms.TextMessage;
@MessageDriven(activationConfig = {
@ActivationConfigProperty(propertyName = "destinationType", propertyValue = "javax.jms.Queue"),
@ActivationConfigProperty(propertyName = "destination", propertyValue = "queue/itcastQueue"),
@ActivationConfigProperty(propertyName = "providerAdapterJNDI", propertyValue = "java:/RemoteJMSProvider")
})
public class MDBean implements MessageListener {
public void onMessage(Message message) {
TextMessage msg = (TextMessage) message;
try {
System.out.println(msg.getText());
} catch (JMSException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
此处的propertyValue = "java:/RemoteJMSProvider"
6. 打包部署EJB到%JBOSS_HOME_Reveiver%\server\default\deploy
7、进入 jboss-5.1.0_Sender下的bin目录,运行run.bat文件,也即启动了A提供的MQ服务器;
(可以http://localhost:18080/jmx-console/查看MQ的JNDI信息)
8、进入 jboss-5.1.0_Receiver下的bin目录,运行run.bat文件,也即启动了B的系统来接受消息;
(可以http://localhost:8080/jmx-console/查看remote JMS Provider的JNDI配置信息,也就是MQ服务器的JNDI信息)
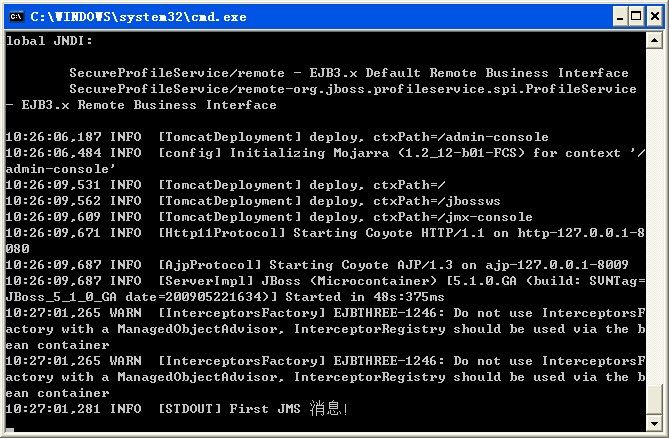
9、直接运行A中的系统QueueSender,发送消息;检查B中JBoss Console:
接收端B JBOSS的Console:
上面就是一个简单的模拟: A -> MQ -> B
如果客户端运行在应用服务器内,我们不需要为InitialContext设置应用服务器的上下文信息,也不建议设置。因为应用服务器启动时会把JNDI驱动类等上下文信息添加进系统属性,创建InitialContext对象时如果没有指定Properties参数,InitialContext内部会调用System.getProperty()方法从系统属性里获取必要的上下文信息。
因此要是在两台机器上测试,不需要修改端口;
实例参考:http://bbs.51cto.com/thread-965361-1.html