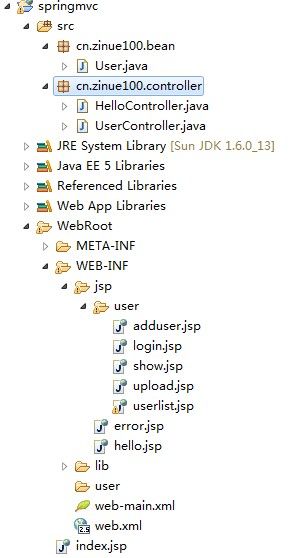
这是项目的包图
我只是想颠三倒四,然后把该记住的知识记住
环境:win7 MyEclipse10 jdk1.6 tomcat7 SpringMVC2.5
目标:CRUD
本文是根据这个小例子修改而来,感谢这位前辈
http://download.csdn.net/download/wxwzy738/5224307
总结的肯定有不对,不完整的地方,权当笔记。
首先是web.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="2.5"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd">
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>WEB-INF/web-main.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.htm</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
这是springmvc的前端控制器,也就是说所有请求都将在这里找到url
servlet-mapping中定义的是路径,熟悉servlet的都知道,这里表示以url结尾的请求将进入控制器
init-param大概是服务器初始化时会加载到内存的配置,contextConfigLocation这个应该是spring容器会去读的配置文件。
web-main.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <mvc:annotation-driven/> <mvc:resources location="/resources/" mapping="/resources/**"/> <context:component-scan base-package="cn.zinue100.controller"/> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"></property> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property> </bean> <bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver"> <property name="maxUploadSize" value="5000000"></property> </bean> </beans>
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
大概是把spring默认配置成注解,而不是用xml
<mvc:resources location="/resources/" mapping="/resources/**"/>
这样根目录下面的resource的文件(.css,.js等)就不会被spring的DispatchServlet进行过滤
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.zinue100.controller"/>
配置注解扫描的包路径,也就是说,这个文件夹下注解中的路径,将起作用
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"></property>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property>
</bean>
配置action中返回的视图配置
这个配置是controller向jsp跳转的配置,在jsp中海油自定义标签,但我现在不太懂这个配置,姑且放在一边
来看实体类吧
package cn.zinue100.bean;
import javax.validation.constraints.Size;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Email;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotEmpty;
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
private String email;
public User(){
}
public User(String username, String password, String email) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.email = email;
}
@NotEmpty(message = "用户名不能为空")
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
@NotEmpty(message = "密码不能为空")
@Size(min = 4, max = 8, message = "密码在4~8位之间")
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@NotEmpty(message = "email不能为空")
@Email(message = "email格式不正确")
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return username+"#"+password+"#"+email;
}
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello")
表示要访问这个action的时候都要加上这个/hello路径
HelloController
package cn.zinue100.controller;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
//@RequestMapping(value = "/hello")
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello.htm")
public String hello(int id){
System.out.println("hello action:"+id);
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello1.htm")
public String hello(int id,Map<String,Object> map){
System.out.println("hello1 action:"+id);
map.put("name", "huangjie");
return "hello";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello2.htm")
public String hello2(int id,Model model){
System.out.println("hello2 action:"+id);
model.addAttribute("name", "huangjie");
model.addAttribute("ok");
return "hello";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello3.htm")
public String hello3(HttpServletRequest request){
String id = request.getParameter("id");
System.out.println("hello3 action:"+id);
return "hello";
}
}
接收参数getParameter()的时候:
如果地址栏/springmvc/hello.htm上面没有传递参数,那么当id为int型的时候会报错,当id为Integer的时候值为null
当地址栏为/springmvc/hello.htm?id=10的时候,action中有三种接收方式
1、String hello(@RequestParam(value = "userid") int id),这样会把地址栏参数名为userid的值赋给参数id,如果用地址栏上的参数名为id,则接收不到
2、String hello(@RequestParam int id),这种情况下默认会把id作为参数名来进行接收赋值
3、String hello(int id),这种情况下也会默认把id作为参数名来进行接收赋值
注:如果参数前面加上@RequestParam注解,如果地址栏上面没有加上该注解的参数,例如:id,那么会报404错误,找不到该路径
其中
第一个方法不能重定向web-info里面的文件,而且需要写上绝对路径
第二个方法是返回页面参数的第一种方式,在形参中放入一个map
第三个方法是回页面参数的第二种方式,在形参中放入一个Model
到request,response,session等,只要在方法形参中声明参数即可
UserController.java
package cn.zinue100.controller;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.validation.Valid;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.SessionAttributes;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.RedirectAttributes;
import cn.zinue100.bean.User;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/user")
@SessionAttributes(value = "loginUser")
public class UserController {
Map<String, User> users = new LinkedHashMap<String, User>();
public UserController() {
System.out.println("初始化....");
users.put("zinue101", new User("zinue101", "123", "[email protected]"));
users.put("zinue102", new User("zinue102", "123", "[email protected]"));
users.put("zinue103", new User("zinue103", "123", "[email protected]"));
users.put("zinue104", new User("zinue104", "123", "[email protected]"));
}
public void init(Model model, User user) {
if (user != null) {
users.put(user.getUsername(), user);
}
model.addAttribute("users", users);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/list.htm")
public String list(Model model) {
init(model, null);
return "user/userlist";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/add.htm", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String add(Model model) {
model.addAttribute(new User());
return "user/adduser";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/add.htm", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String add(@Valid User user, BindingResult binding, Model model) {
if (binding.hasErrors()) {
return "user/adduser";
}
init(model, user);
return "redirect:/user/list.htm";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/{username}.htm", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String show(@PathVariable String username, Model model) {
User user = users.get(username);
model.addAttribute("user", user);
return "user/show";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/delete/{username}.htm", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String delete(@PathVariable String username) {
users.remove(username);
return "redirect:/user/list.htm";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/update/{username}.htm", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String update(@PathVariable String username, Model model) {
User user = users.get(username);
model.addAttribute("user", user);
return "user/adduser";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/update/{username}.htm", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String update(@PathVariable String username, @Valid User user,
BindingResult br) {
if (br.hasErrors()) {
return "/user/adduser";
}
users.put(user.getUsername(), user);
return "redirect:/user/list.htm";
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/{username}.htm", params = "json")
public User showJson(@PathVariable String username, Model model) {
System.out.println("username:" + username);
return users.get(username);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/login.htm", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String login() {
return "/user/login";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/login.htm", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String login(String username, String password, Model model) {
if (!users.containsKey(username)) {
throw new RuntimeException("用户名不存在!");
}
if (!password.equals(users.get(username).getPassword())) {
throw new RuntimeException("密码不正确");
}
// 存放入session中,因为前面已经加了@SessionAttributes(value = "loginUser")注解
model.addAttribute("loginUser", users.get(username));
return "redirect:/user/list.htm";
}
@ExceptionHandler(value = { RuntimeException.class })
public String handlerException(Exception ex, HttpServletRequest req) {
req.setAttribute("ex", ex);// 把异常放入request请求中
return "error";// 转到error页面
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/redir.htm")
public String redir(Model model, RedirectAttributes ra) {
// model.addAttribute("movie", "海贼王");//使用这种方式在重定向是传递不了的
ra.addFlashAttribute("movie", "海贼王");// 使用这种可以
return "redirect:/user/list.htm";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "upload.htm", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String uploadPhoto() {
return "user/upload";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "upload.htm", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String uploadPhoto(MultipartFile photo, Model model,
HttpServletRequest req) {
System.out.println(photo.getContentType());
System.out.println(photo.getName());
System.out.println(photo.getOriginalFilename());
String realpath = req.getSession().getServletContext()
.getRealPath("/upload/");
System.out.println(realpath);
try {
FileUtils.copyInputStreamToFile(photo.getInputStream(), new File(
realpath + "/" + photo.getOriginalFilename()));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
model.addAttribute("message", "上传成功");
return "user/upload";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "uploads.htm", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String uploadPhoto(
@RequestParam(required = false) MultipartFile[] photos,
Model model, HttpServletRequest req) {
String realpath = req.getSession().getServletContext()
.getRealPath("/upload/");
try {
for (MultipartFile photo : photos) {
if (photo.isEmpty())
continue;
FileUtils.copyInputStreamToFile(photo.getInputStream(),
new File(realpath + "/" + photo.getOriginalFilename()));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
model.addAttribute("message", "上传成功");
return "user/upload";
}
}
SessionAttributes(value = "loginUser")
写上这个注解的话那么在Model中进行添加key为loginUser的时候会默认添加到session中
我的初步理解Model这个对象就对应页面的dom树。如果页面有对象那么必须传,不然空指针
返回的字符串中
如果redirect打头就是重定向,如果没有就是转发
别的不贴了,放附件中吧