apache doc
http://www.aslibra.com/blog/go.php/category/16/
apache download
http://httpd.apache.org/download.cgi
http://apache.mirror.phpchina.com/httpd/httpd-2.2.8.tar.gz
http://apache.mirror.phpchina.com/httpd/httpd-2.2.8.tar.bz2
http://apache.mirror.phpchina.com/httpd/httpd-2.2.8-win32-src.zip
http://apache.mirror.phpchina.com/httpd/binaries/win32/apache_2.2.8-win32-x86-no_ssl.msi
http://apache.mirror.phpchina.com/httpd/binaries/win32/apache_2.2.8-win32-x86-openssl-0.9.8g.msi
http://apache.mirror.phpchina.com/httpd/
http://labs.xiaonei.com:8081/apache-mirror/httpd/binaries/win32/
http://labs.xiaonei.com:8081/apache-mirror/httpd/binaries/win32/apache_2.2.11-win32-x86-no_ssl.msi
apache montior (server-status)
http://192.168.121.123/server-status
每秒刷新一次
http://192.168.121.123/server-status?refresh=1
10秒刷新一次
http://192.168.121.123/server-status?refresh=10
自动刷新参数值
http://192.168.119.13/server-status?refresh=auto
Total Accesses: 1788997
Total kBytes: 22202823
CPULoad: 4.49397
Uptime: 27953
ReqPerSec: 64.0002
BytesPerSec: 813354
BytesPerReq: 12708.6
BusyWorkers: 100
IdleWorkers: 200
Scoreboard: __K___________K_K__
如何开启Apache server-status,并禁止直接通过IP访问
(注:如此操作纯属无意义配置,仅作了解,可由它法替代)
http://syq871206.iteye.com/blog/1073585
2.禁止直接通过IP访问
(1)新增一个virtual Host
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName 192.168.119.32
DocumentRoot /
<Directory />
Order deny,allow
Deny from all
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
(2)重启一下Apache进程
apache tools webalizer
http://baike.baidu.com/view/1376028.htm
webalizer是一个高效的、免费的web服务器日志分析程序。
其分析结果以HTML文件格式保存,从而可以很方便的通过web服务器进行浏览。
Webalizer具有以下一些特性:
1. 为是用C写的程序,所以其具有很高的运行效率。在主频为200Mhz的机器上,webalizer每秒钟可以分析10000条记录,所以分析一个40M大小的日志文件只需要15秒。
2. webalizer支持标准的一般日志文件格式(Common Logfile Format);除此之外,也支持几种组合日志格式(Combined Logfile Format)的变种,从而可以统计客户情况以及客户操作系统类型。并且现在webalizer已经可以支持wu-ftpd xferlog日志格式以及squid日志文件格式了。
3. 支持命令行配置以及配置文件。
4. 可以支持多种语言,也可以自己进行本地化工作。
5. 支持多种平台,比如UNIX、linux、NT, OS/2 和 MacOS等。
安装:
1.从webalizer的官方站点http://www.mrunix.net/webalizer/下载webalizer,当前的最新版本是webalizer-2.01-06-src.tgz。
2.首先解开源代码包:
tar xvzf webalizer-2.01-06-src.tgz
3.在生成的目录中有个lang目录,该目录中保存了各种语言文件,但是只有繁体中文版本,可以自己转换成简体,或者自己重新翻译一下。
4.然后进入生成的目录:
./configure
make --with-language=chinese
5.编译成功后,会产生一个webalizer可执行文件,可以将其拷贝到/usr/sbin/目录下:
cp webalizer /usr/sbin/
然后就可以开始配置webalizer了。
配置:
上面说过,可以通过命令行配置webalizer,也可以通过配置文件进行配置,在本文中我们将介绍使用命令行参数进行配置,需要了解配置文件使用方法的朋友可以参考README文件,里面有很详细的介绍。
可以执行webalizer –h得到所有命令行参数:
Usage: webalizer [options] [log file]
-h = 打印帮助信息
-v -V = 打印版本信息
-d = 打印附加调试信息
-F type = 日志格式类型. type= (clf | ftp | squid)
-i = 忽略历史文件
-p = 保留状态 (递增模式)
-q = 忽略消息信息
-Q = 忽略所有信息
-Y = 忽略国家图形
-G = 忽略小时统计图形
-H = 忽略小时统计信息
-L = 忽略彩色图例
-l num = 在图形中使用数字背景线
-m num = 访问超时 (seconds)
-T = 打印时间信息
-c file = 指定配置文件
-n name = 使用的主机名
-o dir = 结果输出目录
-t name = 指定报告题目上的主机名
-a name = 隐藏用户代理名称
-r name = 隐藏访问链接
-s name = 隐藏客户
-u name = 隐藏URL
-x name = 使用文件扩展名
-P name = 页面类型扩展名
-I name = index别名
-A num = 显示前几名客户类型
-C num = 显示前几名国家
-R num = 显示前几名链接
-S num = 显示前几名客户
-U num = 显示前几名URLs
-e num = 显示前几名访问页面
-E num = 显示前几名不存在的页面
-X = 隐藏个别用户
-D name = 使用dns缓存文件
-N num = DNS 进程数 (0=禁用dns)
假设,web服务器主机名为www.test.com,统计站点域名为 www.test.com, 访问日志为/var/log/httpd/access_log, 我们将webalizer分析结果输出到/var/www/html/log下面。则我们可以建立以下脚本/etc/rc.d/webalizer:
#!/bin/sh
run=/usr/sbin/webalizer
$run -F clf -p -n " " -t "www.test.com"
-o /var/www/html/log /var/log/httpd/access_log
说明:
-F clf 指明我们的web日志格式为标准的一般日志文件格式(Common Logfile Format)
-p 指定使用递增模式,这就是说每作一次分析后,webalizer会生产一个历史文件,这样下一次分析时就可以不分析已经处理过的部分。这样我们就可以在短时间内转换我们的日志文件,而不用担心访问量太大时日志文件无限增大了。
-n “ “ 指定服务器主机名为空,这样输出结果会美观一些。
-o “www.test.com” 指定输出结果标题.
/var/log/httpd/access_log:指定日志文件
然后在/etc/crontab中加入:
01 1 * * * root /etc/rc.d/webalizer
即每天凌晨1点执行该脚本。
然后运行/etc/rc.d/init.d/crond reload重载入crond服务。
测试:
执行以下命令:
# /etc/rc.d/webalizer
然后在浏览器中访问http://www.test.com/log/就可以看到webalizer的分析结果了。
注意:如果您使用了中文语言文件,但是您的linux不支持中文,则在产生的图片中文字可能为乱码。
apache setup
RedHat Apache
[root@localhost /]# which apachectl
/usr/sbin/apachectl
[root@localhost /]# whereis apachectl
apachectl: /usr/sbin/apachectl /usr/share/man/man8/apachectl.8.gz
[root@localhost /]# find / -name "apachectl" -print
/usr/sbin/apachectl
#查看Apache版本
[root@localhost /]# /usr/sbin/apachectl -v
Server version: Apache/2.2.3
Server built: Jan 11 2008 08:19:18
或
[root@localhost /]# apachectl -v
#查看Apache httpd版本
http://www.chinalinuxpub.com/bbs/archive/index.php/t-21446.html
在2.0版本以前,是叫做apache的,比如1.3、1.4等等 2.0版本以后,开始叫做httpd了
[root@localhost conf]# rpm -q httpd
httpd-2.2.3-11.el5_1.3
[root@localhost /]# /usr/sbin/httpd -v
Server version: Apache/2.2.3
Server built: Jan 11 2008 08:19:18
#Apache 启停服务
[root@localhost sbin]# apachectl stop --停止apache
[root@localhost sbin]# apachectl start --启动apache
[root@localhost sbin]# apachectl restart --重启apache
#Apache httpd 启停服务
[root@localhost /]# /usr/sbin/httpd -k stop --停止Apache httpd
[root@localhost /]# /usr/sbin/httpd -k start --启动Apache httpd
[root@localhost /]# /usr/sbin/httpd -k restart --重启Apache httpd
[root@localhost /]# which httpd
/usr/sbin/httpd
[root@localhost /]# whereis httpd
httpd: /usr/sbin/httpd /usr/sbin/httpd.worker /etc/httpd /usr/lib/httpd /usr/share/man/man8/httpd.8.gz
[root@localhost /]# find / -name "httpd" -print
/etc/httpd
/etc/sysconfig/httpd
/etc/rc.d/init.d/httpd
/etc/logrotate.d/httpd
/var/lock/subsys/httpd
/var/log/httpd
/usr/lib/httpd
/usr/sbin/httpd
[root@localhost /]# ps -ef | grep httpd
[root@localhost /]# ps -ef | grep httpd | wc -l
#统计Apache的在线用户数方法,并发请求数及TCP状态
[root@localhost /]# netstat -n | awk '/^tcp/ {++S[$NF]} END {for(a in S) print a, S[a]}'
#如何取出特定内容的access_log
[root@localhost /]# grep /var/log/httpd/access_log_2012-02-12-00_00_53 "GET /webapp/wcs/stores/prdprice" access_log_2012-02-13-16_09_02|awk -F ',' '{ print $6}'|awk '{print $2}'|more
#根据access_log 进行数据分析
url 日期 访问总次数 总访问大小 总响应时间 平均大小 平均时间
/emall/v4secondView 20120306(15:00-16:00) 43125 140886906 2440293299 3267 56587
Red Hat Linux 下配置Apache服务
http://www.linux521.com/2009/system/200907/7396_2.html
http://www.newasp.net/tech/server/14356.html
http://www.newasp.net/tech/server/14356_2.html
http://tech.163.com/06/0206/11/299AMBLT0009159K.html
1.检查是否安装Apache服务
[root@localhost /]#rpm -qa|grep httpd
2.Apache服务在第一张安装光盘上
[root@localhost /]#rpm -ivh /mnt/cdrom/RedHat/RPMS/httpd-2.0.40-21.i386.rpm
3.配置Apache
。。。
4.
[root@localhost /]# /etc/init.d/httpd start --启动apache
[root@localhost /]# /etc/init.d/httpd resatart --重启apache
[root@localhost /]# /etc/init.d/httpd stop --停止apache
绿色安装方法
把安装过的安装目录保留,以后不用在安装了 直接bin/httpd.exe -k install -n servicename, mysql也是。
自己动手打造Apache和Mysql绿色免安装版
http://inshect.iteye.com/blog/343044
自己动手打造Apache和Mysql绿色免安装版
我自己用了很久了,虽然很简单,但相信许多人还不知道,就写出来和大家共享
下载原版,第一次安装时,装到D盘或其他盘
再次安装系统时,不需要再重新安装Apache和MySQL,只需要打几个简单的命令即可!
本文出处: http://www.21andy.com/
作者: Andy
重装完系统后
1. 运行CMD进入命令行
2. 进入apache所在的目录下的bin目录,如 d:\apache\bin 运行
httpd -k install
只要这一步apache服务就安装好了
3. 进入mysql所在的目录下的bin目录,如 d:\mysql\bin 运行
mysqld -install
也只要这一步Mysql服务就安装好了
卸载
和上面2步一样,进入bin目录
apache卸载命令
httpd -k uninstall
mysql卸载命令
mysqld -remove
RedHat6.2 服务器安装 Apache
http://www.bdqnht.com/html/wangluo/fuqi/webf/20071219/1639.html
http://www.drupal8.com/
http://mirror.stormreact.org/
http://cnsuning.com/investors/stocks/1064.html
http://fpdownload.macromedia.com/get/flashplayer/current/licensing/win/install_flash_player_active_x.exe
Ubuntu Apache 安装
http://wiki.ubuntu.org.cn/Apache%E5%AE%89%E8%A3%85%E8%AE%BE%E7%BD%AE?highlight=(Apache)
Apache Http Server server status为查看当前系统用户数
Linux 下Apache Http Session为:ps aux grep|httpd wc -l
http://user.qzone.qq.com/170475387/blog/1203489758
Apache使用.htaccess实现图片防盗链
http://blog.usle.cn/article.asp?id=541
apache 防盗链两例
http://hi.baidu.com/snoworld/blog/item/d9fa5066161fb926ab184c77.html
1. 利用rewrite 确认你的apache 能使用rewrite mod
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^http://80yh.com.cn /.*$ [NC]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^http://80yh.com.cn $ [NC]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^http://www.80yh.com.cn /.*$ [NC]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^http://www.80yh.com.cn $ [NC]
RewriteRule .*.(gif|jpb|png|css|js|swf] )$ http://www.80yh.com.cn [R,NC]
其中有色的地方都是要改为你的:
红色 :就是改为你提供下载页面的地址,也就是只有通过这个地址才可以下载你所提供的东东。
蓝色 :就是要保护文件的扩展名( 以| 分开) ,也就是说以这些为扩展名的文件只有通过红色 的地址才可以访问。
绿色 :如果不是通过红色 的地址访问蓝色 这些为扩展名的文件时就回重定向到绿色 地址上。
2. 利用SetEnvIfNoCase 和 access
SetEnvIfNoCase Referer "^http://80yh.com.cn " local_ref=1
SetEnvIfNoCase Referer "^http://80yh.com.cn " local_ref=1
<FilesMatch ".(gif|jpb|png|css|js|swf )">
Order Allow,Deny
Allow from env=local_ref
</FilesMatch>
红色 为信任站点,蓝色 为受保护的文件扩展名。
出处:http://www.phpwind.net/read-htm-tid-153039-fpage-1.html
Apache安装设置
http://wiki.ubuntu.org.cn/Apache%E5%AE%89%E8%A3%85%E8%AE%BE%E7%BD%AE
apache 封 IP 的方法
http://17zouguo.iteye.com/blog/998929
以Apache 2.2作为服务器:
1. 在配置文件httpd.conf里设置:
- < Directory “/home/www” >
- Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
- AllowOverride None
- Order allow,deny
- Allow from all
- Deny from 172.17.18.80
- Deny from 60.99.125.110
- ……
- </ Directory >
2.在网站根目录下建立或打开.htaccess文件,加入如下内容
- Order allow,deny
- Allow from all
- Deny from 172.17 . 18.80
- Deny from 60.99 . 125.110
- ……
D:\Program Files\Apache Software Foundation\Apache2.2\conf\httpd.conf
配置ApacheSSL 转发
http://whb.iteye.com/blog/368514
The Apache + SSL on Win32 HOWTO
http://www.apacheforum.com/archive/index.php/t-8.html
http://www.apacheforum.com/showthread.php?t=8
配置SSL
参考:http://tud.at/programm/apache-ssl-win32-howto.php3
1 安装apache
apache_2.2.11-win32-x86-openssl-0.9.8i.msi
按照提示一步一步,安装即可。
*下文中用{apache}代表apache安装目录,本例中是:D:/devel/apache2.2/
2 配置SSL
(1)apache_2.2.11-win32-x86-openssl-0.9.8i.msi已经安装了 OpenSSL and mod_ssl
(2)下载OpenSSL配置文件
openssl.cnf ,下载文件,保存到{apache}\bin下
(3)生成证书
Command代码
1. openssl req -config openssl.cnf -new -out my-server.csr
2. openssl rsa -in privkey.pem -out my-server.key
3. openssl x509 -in my-server.csr -out my-server.cert -req -signkey my-server.key -days 365
第一条命令提示比较多,大概的输入些数据就可以了。
“密码”必须输入;
“Common Name (eg, your websites domain name) []:”也必须输入,没有域名就随便写一个。
(4)配置SSL
去除conf/httpd.conf下面两句的注释,使之生效:
Apache config代码
1. LoadModule ssl_module modules/mod_ssl.so
2. Include conf/extra/httpd-ssl.conf
复制{apache}目录下的, 上述生成的文件:
bin/my-server.cert => conf/ssl/my-server.cert
bin/my-server.key => conf/ssl/my-server.key
修改conf/extra/httpd-ssl.conf
Apache config代码
1. SSLCertificateFile "D:/devel/apache2.2/conf/server.crt" =>
2. SSLCertificateFile "D:/devel/apache2.2/conf/ssl/my-server.cert"
3.
4. SSLCertificateKeyFile "D:/devel/apache2.2/conf/server.key" =>
5. SSLCertificateKeyFile "D:/devel/apache2.2/conf/ssl/my-server.key"
现在SSL配置完成。下面配置代理
配置代理
去除conf/httpd.conf下面两句的注释,使之生效:
Apache config代码
1. LoadModule proxy_module modules/mod_proxy.so
2. LoadModule proxy_connect_module modules/mod_proxy_connect.so
3. LoadModule proxy_http_module modules/mod_proxy_http.so
在conf/httpd.conf结尾添加如下配置:
Apache config代码
1. ProxyRequests Off
2. <Proxy *>
3. Order deny,allow
4. Allow from all
5. </proxy>
6. ProxyPass / https://{those_compute_ip}/
7. ProxyPassReverse / https://{those_compute_ip}/
修改conf/extra/httpd-ssl.conf,添加
Apache config代码
1. SSLProxyEngine on
Apache按照端口号配置反向代理
http://whb.iteye.com/blog/402746
Xml代码
1. Listen 8001
2. Listen 8002
3.
4. < VirtualHost _default_:8001 >
5. ProxyPass /bob http://192.168.254.30:8001/bob
6. ProxyPassReverse /bob http://192.168.254.30:8001/bob
7. </ VirtualHost >
8.
9. < VirtualHost _default_:8002 >
10. ProxyPass /bob https://192.168.254.30:8002/bob
11. ProxyPassReverse /bob https://192.168.254.30:8002/bob
12. </ VirtualHost >
Apache Portable Runtime apr
ref
http://redalx.iteye.com/blog/162246
http://blog.csdn.net/tingya/archive/2006/04/15/664304.aspx
apr说白了就是如何在Tomcat中使用JNI的方式来读取文件以及进行网络传输, 提高tomcat 的IO效率。
apr可以大大提升Tomcat对静态文件的处理性能,同时如果你使用了HTTPS方式传输的话,也可以提升SSL的处理性能。
doc
http://apr .apache.org/
http://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-5.5-doc/apr.html
http://tomcat .apache.org/tomcat -6.0-doc/apr .html
down
http://tomcat.heanet.ie/native/
http://tomcat.heanet.ie/native/1.1.9/binaries/win32/tcnative-1.dll
setup for Windows
直接下载编译好的二进制版本的dll库文件
http://tomcat.heanet.ie/native/1.1.9/binaries/win32/tcnative-1.dll来使Tomcat启用APR
如何删除windows 服务apache2.2
C:\Users\Lindows>sc delete Apache2.2
[SC] DeleteService SUCCESS
setup for linux
在Linux下,可以直接解压和安装bin目录下的tomcat_native.tar.gz文件,编译之前要确保apr库已经安装,安装的方式:
# ./configure --with-apr=/usr/local/apr
# make
# make install
安装成功后还需要对tomcat设置环境变量,方法是在catalina.sh文件中增加一行:
CATALINA_OPTS="-Djava.library.path=/usr/local/apr/lib"
怎么才能判断Tomcat是否已经启用了APR库呢?方法是通过看Tomcat的启动日志
如果没有启用APR,则启动日志一般有这么一条:
org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Protocol start
如果启用了APR,则这条日志就会变成:
使用了apr 之后,如果使用了https,https的配置也需要作改变。需要用到openssl来进行证书文件的生成。
<!-- ssl for apr -->
<Connector port="8443" maxHttpHeaderSize="8192"
maxThreads="150" minSpareThreads="25" maxSpareThreads="75"
enableLookups="false" disableUploadTimeout="true"
acceptCount="100" scheme="https" secure="true"
clientAuth="false"
SSLEngine="on"
SSLCertificateFile="..\conf\ca\server.crt"
SSLCertificateKeyFile="..\conf\ca\server.key" />
linux下编译
cd apache-tomcat -5.5.14/bin/tomcat -native-1.1.1/jni/native/
./configure --with-apr =/usr/bin/apr -1-config --with-java-home=/usr/java/jdk1.5.0_06/
make
make install
bin/catalina.sh
加上
CATALINA_OPTS="-Djava.library.path=/usr/local/apr /lib"
分割apache日志 access.log / 截取access.log特定行段内容
[root@SmartEDM3 ~]# cat /etc/httpd/logs/access_log.1 | gawk 'BEGIN{i=0;}{i=i+1;if((i>1)&&(i<54)) print $0;}' > /etc/httpd/logs/access_cut.log
分割apache日志 rotatelogs cronolog
如何快速统计RoR网站的访问量
http://robbin.iteye.com/blog/97287
webServer tomcat 5 / tomcat6 / tomcat7
http://lindows.iteye.com/blogs/213348
http://www.iteye.com/topic/810862
Linux下运行的Web服务器Apache,默认日志文件是不分割的,一个整文件既不易于管理,也不易于分析统计。
安装cronolog后,可以将日志文件按时间分割,易于管理和分析。
http://blog.jianghu.taobao.com/u/Nzg0MjkwNTY=/blog/blog_detail.htm?aid=22448334
方法一:
配置httpd.conf,找到CustomLog logs/access.log common,用#注解掉这行,在下面加入:
ErrorLog "|bin/rotatelogs.exe logs/error_%Y-%m-%d.log 86400 480"
CustomLog "|bin/rotatelogs.exe logs/access_%Y-%m-%d.log 86400 480" combined
86400表示1天,480是与UTC相差的时间,8×60=480分钟。
方法二:
去http://cronolog.org/download/index.html下载一个合适版本,我用的是 Win 32 version,
将cronolog.exe解压到 Apache的bin目录下,
配置httpd.conf
找到CustomLog logs/access.log common,用#注解掉这行,在下面加入:
CustomLog "|bin/cronolog.exe logs/access_%Y-%m-%d.log" combined
Mcrypt响应慢的一个原因
http://www.laruence.com/2012/09/24/2810.html
Linux随机数发生器导致Apache进程全部Block的问题追查
http://jarfield.iteye.com/blog/1739834#comments
Linux服务器在运行时,既没有键盘事件,也没有鼠标事件,如何快速积累熵池呢?
google了一下资料,发现有一些程序可以自动补充熵池,例如rngd 或rng-tools 。
我在Linode VPS上尝试了一下rngd,效果非常明显。
先观察rngd启动前的熵池大小: watch cat /proc/sys/kernel/random/entropy_avail ,在100~200之间。
然后启动rngd:sudo rngd -r /dev/urandom -o /dev/random -f -t 1
熵池立刻飙升到3712,接近4096的上限。
网站项目性能之个人谈
http://wangxizhao.iteye.com/blog/651992
对于并发量很大的网站项目,最容易产生数据库瓶颈问题。因此我们要优化我们的网站,最常用的莫过于使用网页静态化和缓存技术,当然这里的静态化不包括伪静态。有人静态化生成.html文件,可是如何在html文件中包含其他文件呢?,有人想到iframe,没错,可以实现,但是效率不好。因此个人更建议使用SSI技术生成.shtml文件,纵观新浪,sohu等几大门户网站无不使用此技术。
SSI技术优点:SSI技术是通用技术,它不受限于运行环境,在java、dotnet、CGI、ASP、PHP下都可以使用SSI技术;解释SSI的效率比解释JSP的效率快很多,因为JSP规范提供了太多的功能,这些功能都需要servlet引擎一一进行解释,所以效率比较低。
生成.shtml文件,我选用velocity模板引擎,但是要注意在生成.shtml文件的时候,模板会将<!--#include file="" --> 中的include指令解析成自己的模板语言,此时我们需要将#转义成普通字符。
解释.shtml文件最佳服务器是APACHE HTTP SERVER。同时对于静态文件我们更需要专业的apache 帮我们解析。其性能远远高于tomcat等servlet容器。此刻我们又不得不使用负载均衡将apache和tomcat整合了。之前一直困扰于负载均衡之后的apache如何访问tomcat上的静态文件这个问题?百思不得其解,终于在一阵“摸爬滚打”中找到了答案,其实在apache的配置文件httpd.conf中可以配置:DocumentRoot "D:/apache-tomcat-6.0.18/webapps" 。如此我们怎么知道我们现在服务器上的应用已经动静态分离了呢?可以用这个方法简单测试下:分别访问一个应用中存在的文件和不存在的文件,查看浏览器报错信息。
对于缓存,个人更建议使用全局缓存策略(缓存静态页),比如oscache,jbosscache等,而不是使用hibernate的二级缓存。这里就不作详细介绍了.
查看apache连接数
http://hi.baidu.com/kson34/blog/item/4b16a77a824928e12f73b37d.html
查看Apache并发请求数及其TCP连接状态
http://brucectl.iteye.com/blog/284783
Apache查看连接数和限制当前的连接数
http://zhengdl126.iteye.com/blog/802520
http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2010-10/29069.htm
起因:线上的一台服务器,最近总是出现 访问 很慢的情况发生,点击一个链接要2秒钟以上才能打开,按照我们对于访问人数的估计,服务器应该不至于响应这么慢,从而需要针对这个问题进行分析,来解决网站访问过慢。
分析:
1、首先,在页面访问变慢情况发生时,使用 top 命令查看了服务器的负载情况,发现负载并不高,初步估计不是程序的问题。
2、然后,查看了线程中的 httpd 的数量, ps -aux | grep httpd | wc -l 发现,线程数已经达到了 apache 设置的最大值。由此断定是网站访问人数过多造成了访问过慢。
3、为了验证,查看了连接数和当前的连接数,分别是
netstat -ant | grep $ip:80 | wc -l
netstat -ant | grep $ip:80 | grep EST | wc -l
发现果然,连接数特别多,远远超过我们的估计值。
4、刚开始的时候,对于服务器的 MPM 配置方式不是特别的熟悉,认为修改服务器配置可以解决问题。主要的配置部分包括 prefork 模式 或者 work 模式的配置,
5、后来想到需要查看用户都是访问的那些页面,将配置中的 access_log 打开,发现85%以上的访问都是直接访问的资源文件,由此判定,用户可能使用了多线程的下载工具,或者这些资源遭受了盗链。
6、找到了问题所在,进行解决也就比较好办了。想到了两个方法:
A、对单个IP进行连接的线程限制,不允许多线程连接资源。
B、添加URL重写,防止盗链。
修改Linux内核参数,减少TCP连接中的TIME-WAIT sockets
http://brucectl.iteye.com/blog/284763
[root@b2cwebserver02 ~]# netstat -na|grep ESTABLISHED|awk '{print $5}'|awk -F: '{print $1}'|sort|uniq -c|sort -r +0n
[root@b2cwebserver02 ~]# netstat -na|grep SYN|awk '{print $5}'|awk -F: '{print $1}'|sort|uniq -c|sort -r +0n
[root@b2cwebserver02 ~]# netstat -an | grep 80 | awk '{print $6}' | sort | uniq -c | sort -rn
179 TIME_WAIT
140 ESTABLISHED
6 FIN_WAIT2
6 FIN_WAIT1
4 CONNECTED
2 LISTEN
2
1 STREAM
1 CLOSE_WAIT
1 8804
1 6980
apache域名绑定
http://javantsky.iteye.com/blog/852982
需求背景:
系统中用户注册后会根据id生成其主页,如http://www.test.com/index/2
用户希望实现一级域名绑定,即,通过访问http://www.demo.com也能直接访问到其主页
....balabala....
顺便说一个很简单的二级域名绑定方式
在www.test.com的vhost中添加如下内容:
- RewriteEngine on
- RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^[0 - 9 ]+\.test.com$
- RewriteRule ^/?$ /%{HTTP_HOST}
- RewriteRule ^/([0 - 9 ]+)\.test\.com/?$ /index/$ 1 [R,L]
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^[0-9]+\.test.com$
RewriteRule ^/?$ /%{HTTP_HOST}
RewriteRule ^/([0-9]+)\.test\.com/?$ /index/$1 [R,L]
这样通过访问http://2.test.com也能范围到http://www.test.com/index/2中同样内容了
apache域名绑定的关键是urlrewrite,需要一点正则表达的知识。
apache 多站点配置
怎么在Apache环境下建立N个站点的配置方法
http://www.woplus.com/phptech/apache-website-peizhi/
假设你的主机IP是:127.0.0.1你的主机上有三个域名:
www.a.com 网页文件放在E:\web\www\1
www.b.com 网页文件放在E:\web\www\2
www.c.com 网页文件放在E:\web\www\3
在apache的httpd.conf中加入
#设置不同的域名到不同的目录
NameVirtualHost 127.0.0.1
<VirtualHost 127.0.0.1>
DocumentRoot “E:\web\www\a”
ServerName www.a.com
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost 127.0.0.1>
DocumentRoot “E:\web\www\b”
ServerName www.b.com
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost 127.0.0.1>
DocumentRoot “E:\web\www\c”
ServerName www.c.com
</VirtualHost>
配置好后重启Apache,OK了!
使用Apache做负载均衡Link_out
http://www.iteye.com/articles/280
ab - Apache HTTP server benchmarking tool apache ab压力测试
http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.0/programs/ab.html
ab is a tool for benchmarking your Apache Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) server. It is designed to give you an impression of how your current Apache installation performs. This especially shows you how many requests per second your Apache installation is capable of serving.
apache ab 压力测试的轻量级具体做法
http://www.oschina.net/question/234345_56911
一:压力测试中需要掌握的几个基本概念
1:吞吐率(Requests per second)
服务器并发处理能力的量化描述,单位是reqs/s,指的是某个并发用户数下单位时间内处理的请求数。某个并发用户数下单位时间内能处理的最大请求数,称之为最大吞吐率。
记住:吞吐率是基于并发用户数的。这句话代表了两个含义,1:吞吐率和并发用户数相关;2:不同的并发用户数下,吞吐率一般是不同的。
计算公式:总请求数 / 处理完成这些请求数所花费的时间,即
Request per second = Complete requests / Time taken for tests
2:并发连接数(The number of concurrent connections)
并发连接数指的是某个时刻服务器所接受的请求数目,简单的讲,就是一个会话。
3:并发用户数(The number of concurrent users,Concurrency Level)
要注意区分这个概念和并发连接数之间的区别,一个用户可能同时会产生多个会话,也即连接数。在HTTP/1.1下,IE7支持两个并发连接,IE8支持6个并发连接,FireFox3支持4个并发连接,所以相应的,我们的并发用户数就得除以这个基数。
4:用户平均请求等待时间(Time per request)
计算公式:处理完成所有请求数所花费的时间/ (总请求数 / 并发用户数),即
Time per request = Time taken for tests /( Complete requests / Concurrency Level)
5:服务器平均请求等待时间(Time per request: across all concurrent requests)
计算公式:处理完成所有请求数所花费的时间 / 总请求数,即
Time taken for / testsComplete requests
可以看到,它是吞吐率的倒数。
同时,它也=用户平均请求等待时间/并发用户数,即
Time per request / Concurrency Level
二:具体做法
1:压力测试工具选择
重量级的工具有Visual Studio 自带的工具,还有Loader Runner(LR),轻量级的工具有Apache项目中的ApacheBench,简称ab。你可以在这里下载:ab.zip。
2:ab的简单使用及参数介绍
image
以上测试,基于我的一个asp.net的页面。对于压力测试,必须时时刻刻做,如果不知道自己的应用能够承载多少的并发用户数,那基本上就是在扔定时炸*弹。
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/luminji/archive/2011/09/02/2163525.html
apache ab压力测试
http://blog.chinaunix.net/space.php?uid=12318776&do=blog&cuid=537944
使用Apache AB实现bugfree登录的脚本
http://www.mamicode.com/info-detail-399524.html
apache 自带的ab.exe 测试网站的并发量(网站压力测试)
http://djw0101.iteye.com/blog/1233758
APACHE自带的测试工具AB(apache benchmark).在APACHE的bin目录下。
格式: ./ab [options] [http://]hostname[:port]/path
参数:
-n requests Number of requests to perform
//在测试会话中所执行的请求个数。默认时,仅执行一个请求
-c concurrency Number of multiple requests to make
//一次产生的请求个数。默认是一次一个。
-t timelimit Seconds to max. wait for responses
//测试所进行的最大秒数。其内部隐含值是-n 50000。它可以使对服务器的测试限制在一个固定的总时间以内。默认时,没有时间限制。
-p postfile File containing data to POST
//包含了需要POST的数据的文件.
-T content-type Content-type header for POSTing
//POST数据所使用的Content-type头信息。
-v verbosity How much troubleshooting info to print
//设置显示信息的详细程度 - 4或更大值会显示头信息, 3或更大值可以显示响应代码(404, 200等), 2或更大值可以显示警告和其他信息。 -V 显示版本号并退出。
-w Print out results in HTML tables
//以HTML表的格式输出结果。默认时,它是白色背景的两列宽度的一张表。
-i Use HEAD instead of GET
// 执行HEAD请求,而不是GET。
-x attributes String to insert as table attributes
//
-y attributes String to insert as tr attributes
//
-z attributes String to insert as td or th attributes
//
-C attribute Add cookie, eg. 'Apache=1234. (repeatable)
//-C cookie-name=value 对请求附加一个Cookie:行。 其典型形式是name=value的一个参数对。此参数可以重复。
-H attribute Add Arbitrary header line, eg. 'Accept-Encoding: xxxx'
Inserted after all normal header lines. (repeatable)
-A attribute Add Basic WWW Authentication, the attributes
are a colon separated username and password.
-P attribute Add Basic Proxy Authentication, the attributes
are a colon separated username and password.
//-P proxy-auth-username:password 对一个中转代理提供BASIC认证信任。用户名和密码由一个:隔开,并以base64编码形式发送。无论服务器是否需要(即, 是否发送了401认证需求代码),此字符串都会被发送。
-X proxy:port Proxyserver and port number to use
-V Print version number and exit
-k Use HTTP KeepAlive feature
-d Do not show percentiles served table.
-S Do not show confidence estimators and warnings.
-g filename Output collected data to gnuplot format file.
-e filename Output CSV file with percentages served
-h Display usage information (this message)
//-attributes 设置 属性的字符串. 缺陷程序中有各种静态声明的固定长度的缓冲区。另外,对命令行参数、服务器的响应头和其他外部输入的解析也很简单,这可能会有不良后果。它没有完整地实现 HTTP/1.x; 仅接受某些'预想'的响应格式。 strstr(3)的频繁使用可能会带来性能问题,即, 你可能是在测试ab而不是服务器的性能。
参数很多,一般我们用 -c 和 -n 参数就可以了. 例如:
./ab -c 1000 -n 1000 http://127.0.0.1/index.php
这个表示同时处理1000个请求并运行1000次index.php文件.
#/usr/local/xiaobai/apache2054/bin/ab -c 1000 -n 1000 http://127.0.0.1/index.html.zh-cn.gb2312
This is ApacheBench, Version 2.0.41-dev <$Revision: 1.121.2.12 $> apache-2.0
Copyright (c) 1996 Adam Twiss, Zeus Technology Ltd, http://www.zeustech.net/
Copyright (c) 1998-2002 The Apache Software Foundation, http://www.apache.org/
Benchmarking 127.0.0.1 (be patient)
Completed 100 requests
Completed 200 requests
Completed 300 requests
Completed 400 requests
Completed 500 requests
Completed 600 requests
Completed 700 requests
Completed 800 requests
Completed 900 requests
Finished 1000 requests
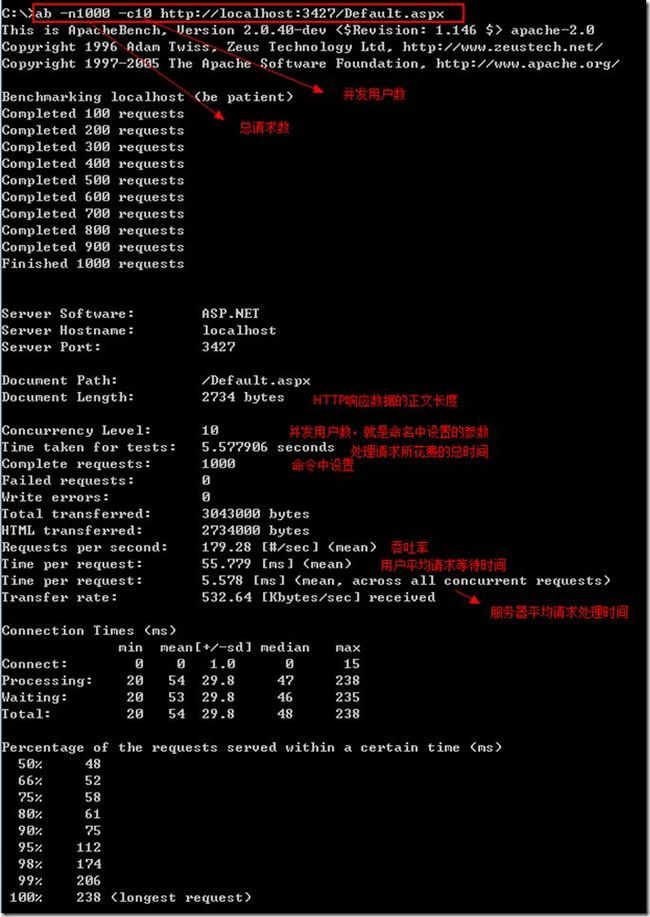
Server Software: Apache/2.0.54
//平台apache 版本2.0.54
Server Hostname: 127.0.0.1
//服务器主机名
Server Port: 80
//服务器端口
Document Path: /index.html.zh-cn.gb2312
//测试的页面文档
Document Length: 1018 bytes
//文档大小
Concurrency Level: 1000
//并发数
Time taken for tests: 8.188731 seconds
//整个测试持续的时间
Complete requests: 1000
//完成的请求数量
Failed requests: 0
//失败的请求数量
Write errors: 0
Total transferred: 1361581 bytes
//整个场景中的网络传输量
HTML transferred: 1055666 bytes
//整个场景中的HTML内容传输量
Requests per second: 122.12 [#/sec] (mean)
//大家最关心的指标之一,相当于 LR 中的 每秒事务数 ,后面括号中的 mean 表示这是一个平均值
Time per request: 8188.731 [ms] (mean)
//大家最关心的指标之二,相当于 LR 中的 平均事务响应时间 ,后面括号中的 mean 表示这是一个平均值
Time per request: 8.189 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
//每个请求实际运行时间的平均值
Transfer rate: 162.30 [Kbytes/sec] received
//平均每秒网络上的流量,可以帮助排除是否存在网络流量过大导致响应时间延长的问题
Connection Times (ms)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 4 646 1078.7 89 3291
Processing: 165 992 493.1 938 4712
Waiting: 118 934 480.6 882 4554
Total: 813 1638 1338.9 1093 7785
//网络上消耗的时间的分解,各项数据的具体算法还不是很清楚
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
50% 1093
66% 1247
75% 1373
80% 1493
90% 4061
95% 4398
98% 5608
99% 7368
100% 7785 (longest request)
//整个场景中所有请求的响应情况。在场景中每个请求都有一个响应时间,其中50%的用户响应时间小于1093 毫秒,60% 的用户响应时间小于1247 毫秒,最大的响应时间小于7785 毫秒
由于对于并发请求,cpu实际上并不是同时处理的,而是按照每个请求获得的时间片逐个轮转处理的,所以基本上第一个Time per request时间约等于第二个Time per request时间乘以并发请求数
apache使用的一些心得
http://www.chinaunix.net/jh/13/488448.html
freebsd apache
lindowsmatoMacBook-Pro:varnish-3.0.2 root# /usr/sbin/httpd -v
Server version: Apache/2.2.20 (Unix)
Server built: Sep 12 2011 17:42:56
lindowsmatoMacBook-Pro:varnish-3.0.2 root# whereis httpd
/usr/sbin/httpd
lindowsmatoMacBook-Pro:varnish-3.0.2 root# /usr/sbin/httpd -?
Usage: /usr/sbin/httpd [-D name] [-d directory] [-f file]
[-C "directive"] [-c "directive"]
[-k start|restart|graceful|graceful-stop|stop]
[-v] [-V] [-h] [-l] [-L] [-t] [-T] [-S]
Options:
-D name : define a name for use in <IfDefine name> directives
-d directory : specify an alternate initial ServerRoot
-f file : specify an alternate ServerConfigFile
-C "directive" : process directive before reading config files
-c "directive" : process directive after reading config files
-e level : show startup errors of level (see LogLevel)
-E file : log startup errors to file
-v : show version number
-V : show compile settings
-h : list available command line options (this page)
-l : list compiled in modules
-L : list available configuration directives
-t -D DUMP_VHOSTS : show parsed settings (currently only vhost settings)
-S : a synonym for -t -D DUMP_VHOSTS
-t -D DUMP_MODULES : show all loaded modules
-M : a synonym for -t -D DUMP_MODULES
-t : run syntax check for config files
-T : start without DocumentRoot(s) check
chkconfig 和 systemctl 命令有什么异同呢?
http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/390809658
https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/SysVinit_to_Systemd_Cheatsheet/zh
linux中service与chkconfig的替代者systemctl
http://www.111cn.net/sys/linux/65797.htm
http://dl2.iteye.com/upload/attachment/0105/4485/a134f98d-ef7e-3c07-8262-658306075059.png
最近在玩ubuntu和opensuse时发现了systemctl命令了,后来在试玩centos7时也发现了该命令,systemctl是systemd下的一个工具。网上查了下,该命令已经存在很久了。该命令是用来替代service和chkconfig两个命令的 --- 尽管个人感觉还是后者好用。 为了顺应时间的发展,这里总结下。在目前很多linux的新发行版本里,系统对于daemon的启动管理方法不再采用SystemV形式,而是使用了sytemd的架构来管理daemon的启动。
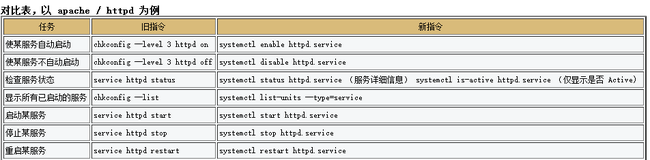
| 任务 | 旧指令 | 新指令 |
| 使某服务自动启动 | chkconfig --level 3 httpd on | systemctl enable httpd.service |
| 使某服务不自动启动 | chkconfig --level 3 httpd off | systemctl disable httpd.service |
| 检查服务状态 | service httpd status | systemctl status httpd.service (服务详细信息) systemctl is-active httpd.service (仅显示是否 Active) |
| 加入自定义服务 | chkconfig --add test | systemctl load test.service |
| 删除服务 | chkconfig --del xxx | 停掉应用,删除相应的配置文件 |
| 显示所有已启动的服务 | chkconfig --list | systemctl list-units --type=service |
| 启动某服务 | service httpd start | systemctl start httpd.service |
| 停止某服务 | service httpd stop | systemctl stop httpd.service |
| 重启某服务 | service httpd restart | systemctl restart httpd.service |
end