CodeSmith 使用教程(15) 为Yii Framework 创建生成ActiveRecord的代码模板
在CodeSmith 使用教程(3): 自动生成Yii Framework ActiveRecord我们通过SchemaExploer为Yii Framework从数据库生成简单的ActiveRecord类,没有考虑到表和表之间的关系。本例我们使用CodeSmith为Yii Framework创建一个通用的代码模板,可以使用上例介绍的SchemaExploer,不过在查看CodeSmith自带的例子中有个生成Hibernate的例子,这个模板的使用可以参见CodeSmith 使用教程(1): 概述,CodeSmith提供了这个模板的源码,使用到了CodeSmith.SchemaHelper (CodeSmith没有提供相应的文档),不过可以通过阅读NHiberante的模板了解其一般用法。
为生成Yii Framework ActiveRecord类之间的relation ,先要了解一下表和表之间的关系:
两个 AR 类之间的关系直接通过 AR 类所代表的数据表之间的关系相关联。 从数据库的角度来说,表 A 和 B 之间有三种关系:一对多(one-to-many,例如tbl_user和tbl_post),一对一( one-to-one 例如tbl_user和tbl_profile)和 多对多(many-to-many 例如tbl_category和tbl_post)。 在 AR 中,有四种关系:
-
BELONGS_TO(属于): 如果表 A 和 B 之间的关系是一对多,则 表 B 属于 表 A (例如Post属于User); -
HAS_MANY(有多个): 如果表 A 和 B 之间的关系是一对多,则 A 有多个 B (例如User有多个Post); -
HAS_ONE(有一个): 这是HAS_MANY的一个特例,A 最多有一个 B (例如User最多有一个Profile); -
MANY_MANY: 这个对应于数据库中的 多对多 关系。 由于多数 DBMS 不直接支持 多对多 关系,因此需要有一个关联表将 多对多 关系分割为 一对多 关系。 在我们的示例数据结构中,tbl_post_category就是用于此目的的。在 AR 术语中,我们可以解释MANY_MANY为BELONGS_TO和HAS_MANY的组合。 例如,Post属于多个(belongs to many)Category,Category有多个(has many)Post.
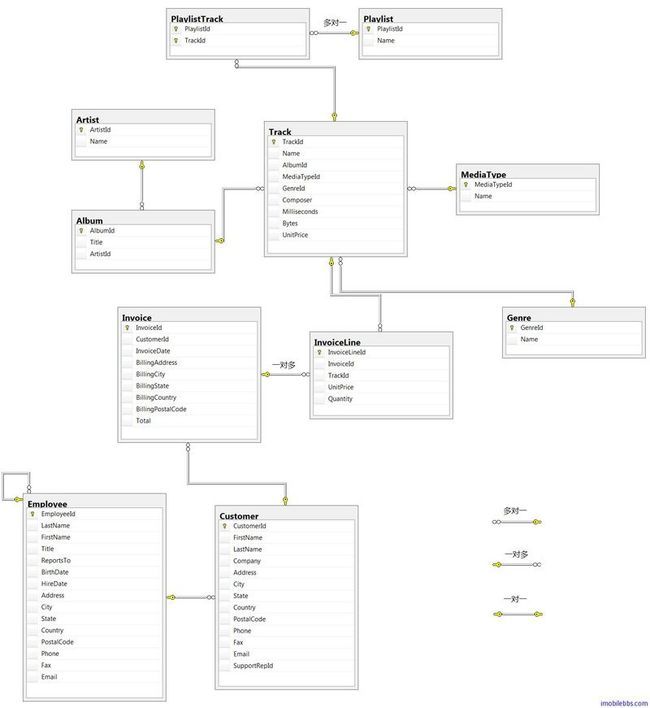
本例还是使用Chinook数据库,修改Yii Framework 开发教程(27) 数据库-关联Active Record示例。数据表之间的关系如下:
CodeSmith 中PLINQO-NH代码位置:
缺省目录为C:\Program Files (x86)\CodeSmith\v6.5\Samples\Templates\Frameworks\PLINQO-NH
CodeSmith.SchemaHelper定义的主要类有:
几个主要的类为
- EntityManager 管理所有的Entity(对应于整个数据库)
- Entity实体类(对应到单个表,视图)
- IAssoication 关系(定义表和表之间的关系)
- AssoicationType 关系的类型 (见下表)
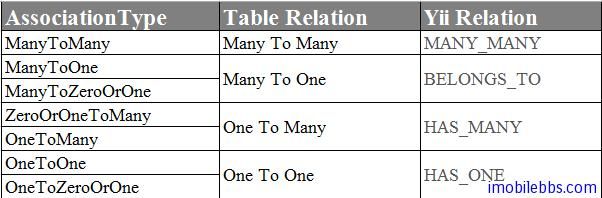
根据AssociationType ,数据库之间的关系以及Yii AR支持的几种关系,可以定义下表:
整个模板也是采用主-从模板的方式,主模板枚举EntityManager中的每个Entity,然后调用子模板为每个表生成AR类:
public void Generate()
{
EntityManager entityManager = CreateEntityManager();
foreach(IEntity entity in entityManager.Entities)
{
if (!(entity is CommandEntity)) {
RenderEntity(entity);
}
}
}
...
private void RenderEntity(IEntity entity)
{
string folder=@"../models/";
EntityTemplate entityTemplate = this.Create<EntityTemplate>();
entityTemplate.SourceEntity = entity;
entityTemplate.RenderToFile(folder+entity.Name+".php", true);
}
子模板则根据每个Entity的Assoications(关系属性)为AR 生成relations函数,
<?php
class <%= SourceEntity.Name %> extends CActiveRecord
{
public static function model($className=__CLASS__)
{
return parent::model($className);
}
public function tableName()
{
return '<%= SourceEntity.GetSafeName() %>';
}
<%if (SourceEntity.Associations.Count>0){ %>
public function relations()
{
return array(
<% IEnumerable<IAssociation> associations = SourceEntity.Associations; %>
<% foreach(IAssociation association in associations) { %>
<% if(association.Entity.Name!=association.ForeignEntity.Name) {%>
<% if (association.AssociationType == AssociationType.ManyToOne
|| association.AssociationType==AssociationType.ManyToZeroOrOne) { %>
'<%= ToCameral(association.Name) %>'=>array(self::BELONGS_TO,
'<%= association.ForeignEntity.Name %>',
<%=GetBelongToKey(association) %>
<% } %>
<% if (association.AssociationType == AssociationType.OneToMany
|| association.AssociationType==AssociationType.ZeroOrOneToMany) { %>
'<%= ToCameral(association.Name) %>'=>array(self::HAS_MANY,
'<%= association.ForeignEntity.Name %>',
<%=GetKey(association) %>
<% } %>
<% if (association.AssociationType == AssociationType.OneToOne
|| association.AssociationType==AssociationType.OneToZeroOrOne) { %>
'<%= ToCameral(association.Name) %>'=>array(self::HAS_ONE,
'<%= association.ForeignEntity.Name %>',
<%=GetKey(association) %>
<% } %>
<% if (association.AssociationType == AssociationType.ManyToMany) { %>
'<%= ToCameral(association.Name) %>'=>array(self::MANY_MANY,
'<%= association.IntermediaryAssociation.Entity.Name %>',
<%=GetManyToManyKey(association) %>
<% } %>
<% } %>
<% } %>
);
}
<% } %>
}
?>
<script runat="template">
public string ToCameral(string name)
{
return StringUtil.ToCamelCase(name);
}
public string GetKey(IAssociation association)
{
string retString=string.Empty;
if(association.Properties.Count>1)
{
retString="array(";
foreach (AssociationProperty associationProperty in association.Properties)
{
retString+="'"+associationProperty.ForeignProperty.GetSafeName()+"',";
}
retString+="),";
}else{
foreach (AssociationProperty associationProperty in association.Properties)
{
retString+="'"+associationProperty.ForeignProperty.GetSafeName()+"'),";
}
}
return retString;
}
public string GetBelongToKey(IAssociation association)
{
string retString=string.Empty;
if(association.Properties.Count>1)
{
retString="array(";
foreach (AssociationProperty associationProperty in association.Properties)
{
retString+="'"+associationProperty.Property.GetSafeName()+"',";
}
retString+="),";
}else{
foreach (AssociationProperty associationProperty in association.Properties)
{
retString+="'"+associationProperty.Property.GetSafeName()+"'),";
}
}
return retString;
}
public string GetManyToManyKey(IAssociation association)
{
string retString="'"+association.ForeignEntity.GetSafeName()+"(";
foreach (AssociationProperty associationProperty in association.Properties)
{
retString+=associationProperty.ForeignProperty.GetSafeName()+",";
}
IAssociation intermidateAssociation=association.IntermediaryAssociation;
if(intermidateAssociation!=null)
{
foreach (AssociationProperty associationProperty in intermidateAssociation.Properties)
{
retString+=associationProperty.ForeignProperty.GetSafeName()+",";
}
}
retString=retString.Substring(0,retString.Length-1);
retString+=")'),";
return retString;
}
</script>
然后generated output 就可以为数据库的表生成对应的AR类,比如生成的Track类
class Track extends CActiveRecord
{
public static function model($className=__CLASS__)
{
return parent::model($className);
}
public function tableName()
{
return 'track';
}
public function relations()
{
return array(
'album'=>array(self::BELONGS_TO,'Album','AlbumId'),
'genre'=>array(self::BELONGS_TO,'Genre','GenreId'),
'mediatype'=>array(self::BELONGS_TO,'Mediatype','MediaTypeId'),
'invoicelines'=>array(self::HAS_MANY,'Invoiceline','TrackId'),
'playlists'=>array(self::MANY_MANY,'Playlist','playlisttrack(TrackId,PlaylistId)'),
);
}
}
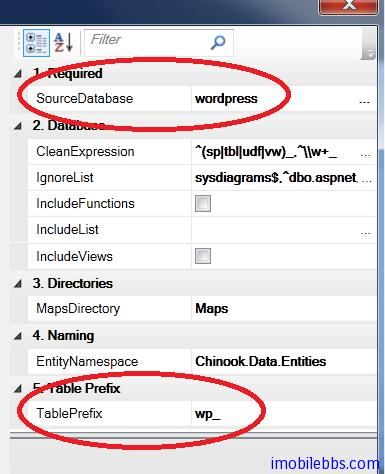
如果实在看不懂本例也无所谓,可以直接使用该模板,只要设置数据源 ,如果数据库的表有前缀,比如Wordpress的表有wp_ 可以设置表前缀(不是必须的)
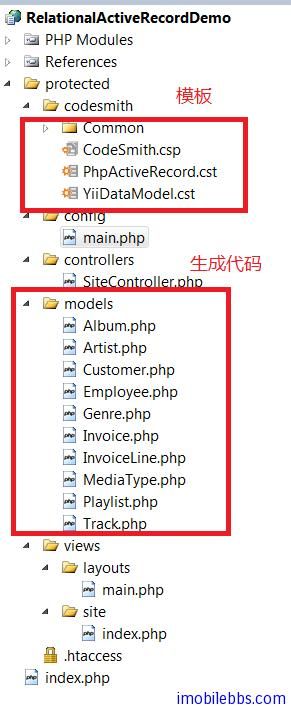
本例下载,如果需要使用本例的模板,直接把项目中protected下的codesmith 目录拷贝到你自己的项目中,然后为codesmith.csp 配置数据源(或者还有表前缀),然后生成代码即可。
本例下载