SQL:使用关系模型的数据库语言,用于和各类数据库的交互,提供通用的数据管理和查询功能:
改变数据库结构
更改系统安全设置
设置用户对数据库或表的许可权限
在数据库中检索需要的信息
对数据库的信息进行更新
常用SQL指令:select ,insert, delete ,update ,create , drop
Select 查询语句
DML数据操作语句(insert、updata、delete、merge)
DDL数据定义语句(create、 alter、drop、truncate)
DCL数据控制语句(grant、revoke)
TCL事务控制语句(commit、rollback、savepoint)
数据字典
1)user_tables 用户所有的数据表
2) user_constraints 用户所有的约束条件
3) user_objects 用户所有的对象( 表、视图、索引等 )
4) all_tables 用户能访问的数据表包括自己的和别的用户允许自己访问的
5) all_constraints 用户能访问的约束条件
6) all_objects 用户能访问的对象( 表、视图、索引等 )
数据字典的格式如:
User_XXX: 用户自己的对象
All_XXX: 用户能访问的对象
Dba_XXX:数据库所有的对象
数据库中的主要对象:
表 Table--存储的基本单元关系型数据库中表是一个二维结构由行( Row )和列( Record )组成
视图View--虚拟的表,视图对应一条Select 语句,查询得到的结果集被赋予一个名字即视图的名字
索引Index--用来在数据库中加速表查询的数据库对象
序列Sequence--用来生成唯一数字值的数据库对象,值由Oracle 按递增或递减顺序自动生成
表操作
1. 创建表
Create table student( name varchar2(20), age number(3));
Create table student( 姓名 varchar2(20), 年龄 number(3));
create sequence student_seq; 为表student创建序列(自动生成id的列“seq”)
create table student(id number(3) , name char(20) not null , email char(50) unique,
majorid number(2) ,
constraint stu_id_pk primary key(id) ,
constraint stu_mid_fk foreign key(majorid) references major(id)
) ; 建表同时建立约束(主键、外键)
2.创建视图(实质:对复杂查询语句的替换)
视图不包含任何数据,是基表数据的投影,其用法和表相同
create view v_student as select name, email from student where age=20视图定义为单表子集
select e.empno,e.ename,e.job,d.hiredate,d.sal, d.dname
from emp e left join dept d on d.deptno = e.deptno 视图定义为多表子集
create or replace view v_king AS
select count(*),e.empno,e.ename,e.job,d.hiredate,sum(d.sal), d.dname
from emp e left join dept d on d.deptno = e.deptno 视图定义为多表子集
create or replace view v_king AS
select * from emp e left join dept d on d.deptno = e.deptno 视图定义为多表并集
select text from user_views where view_name ='v_king '; 查看视图的定义
2. 更改表结构
alter table student add(id varchar(10)) ; 增加列
alter table student ADD COLUMN_NAME NUMBER(1) DEFAULT 1; 增加列并附值
alter table student drop column id ; 删除列
alter table student rename column column_old to column_new; 修改列名
alter table student modify column_name varchar2(20); 修改列数据类型
alter table student add constraint student_id_pk primary key(id); 追加主键约束
alter table student drop primary key; 删除主键约束
alter table student add constraint student_mid_fk foreign key(majorid)
references major_ning(id);追加外键约束
alter table student add constraint student_email_uk unique(eamil); 追加唯一键
alter table student add constraint student_g_ck check(gender in('M','F'));检查约束
3.创建约束
约束包括:主键primary key、非空not null、唯一unique、检查check、外键foreign key
建议约束命名规则:表名_列名_约束条件的类型
建立约束条件的时机:建表同时建立约束条件,在创建完表以后创建约束
create table dept(
deptno number(2) primary key, --主键约束(列级)
dname varchar2(20)
);
create table dept(
deptno number(2) primary key,
dname varchar2(20),
constraint dept_deptno_pk primary key (deptno) --主键约束(表级)
);
create table student(
id number(4),
name varchar2(10) not null, -- 非空约束(只有列级)
);
create table student(
id number(4),
name varchar2(10) constraint student_name_nn not null, -- 给非空约束命名
);
create table student(
id number(4),
name varchar2(10),
email varchar2(30) unique, --唯一键约束(列级)
);
create table student(
id number(4),
name varchar2(10),
email varchar2(30),
constraint student_email_uk unique(email) --唯一键约束(表级)
) ;
create table student(
id number(4),
name varchar2(10),
age number(2) check(age > 10),
gender char(1) check(gender in('F', 'M') ) --检查约束(列级)
);
create table student(
id number(4),
name varchar2(10),
age number(2),
gender char(1),
constraint student_age_ck check(age > 10),
constraint student_gender_ck check(gender in('F', 'M', 'f', 'm')) --检查约束(表级)
);
create table major(
id number(2) primary key, 外键表1
name char(20)
);
create table student(
sid number(3),
name varchar2(20),
majorid number(2),
constraint stu_mid_fk foreign key (majorid) references major(id) -- 外键约束
);
alter table student drop constraint stu_mid_fk; --删除外键约束
alter table student add constraint stu_mid_fk foreign key (majorid) references major(id) on delete set null; --重建外键约束(主表数据被删除从表关联数据置为 null)
alter table student add constraint stu_mid_fk foreign key (majorid) references major(id) on delete cascade;
--重建外键约束(主表数据被删除从表关联数据置为 null)
3.创建索引
自动创建索引:如果表有 PK/Unique 两种约束索引自动创建 , 除此以外索引必须手动创建
自定义索引:create index 索引名 on 表名(列名) ;
create unique index name_uniidx on student (name varchar2(20), age number(3));
凡是对有约束条件的字段查询会使用索引:select * from student where id = 1001 ;
select constraint_name from user_constraints where table_name ='student'; 查询约束
select index_name from user_indexes where table_name = 'student'; 查询索引
3.创建序列
(序列对象在 Oracle、db2 等数据库中有,在 mysql、sql server 中没有)
create sequence stu_seq ; 创建序列stu_seq
create sequence stu_seq start with 1000 increment by 2 ;建立序列主键值从1000开始步进为2
select stu_seq.nextval from dual ; 查看序列产生的值
insert into student(id,name)values(stu_seq.nextval , 'amy') ;用序列产生的值作为表的主键值
drop sequence stu_seq ; 删除序列
3. 复制表头
create table student_1 as select * from student where 1 = 2 ; 复制表头
create table student_1 as select 姓名 from student where 1=2; 复制姓名列
4.复制表
create table 表名 as 查询语句 复制表不复制约束条件
create table student_1 as select * from student
create table student_1 as select 姓名 from student; 复制表student中一列
5. 查看表
desc student ;
6. 插入记录
Insert into student values(‘tom’ , 18 ,1) ;
Insert into student columns(姓名,年龄) values('tom' , 18) ;
insert into student_1 select 姓名 from student where 姓名='tom'
把student中符合条件的值插入到student_1中
7. 更改记录
update student set 姓名='king' where姓名='tom'; 将tom修改成king
update student set 姓名=’ king’ where 姓名 is null;
8. 查看记录
Select * from student;
9. 删除记录
delete from student ; 删除表中所有数据
delete from student where name=12; 删除一行where后可以是所删行的任一值,null值除外
update Basic_Goodscode set GOODS_NUMPROPERTY2=null;删除一列的数据(列项不删)
alter table tablename drop column columnname ;删除一列(包括列项)
10.删除表
Drop table student ;
11.表、字段添加注释
添加表注释:
comment on table 表名 is '个人信息';
添加字段注释:
comment on column 字段名 is '注释内容';
字符类型文字值用单引号,不能用双引号,双引号表示列别名
12.使用算术运算符
Select语句中,number型数据可以使用算术运算符、小括号创建表达式
(运算优先级和所学的相同)
select BILLCODE_ID,BILLTYPE_CODE,MEMBER_CODE,MEMBER_CODE*3+1from system_billcode;
select BILLCODE_ID,BILLTYPE_CODE,MEMBER_CODE,MEMBER_CODE*(3+1) from system_billcode
13.连接运算符“||”:
可以把列与字符、或其他表达式拼接到一起,得到一个新字符串
select BILLCODE_ID,BILLTYPE_CODE || MEMBER_CODE, MEMBER_CODE *2from system_billcode
select BILLCODE_ID,BILLTYPE_CODE || MEMBER_CODE, MEMBER_CODE *2 || 'king查询结果的字符拼接'from system_billcode
14.使用字段别名
字段别名:重命名查询结果中的字段,以增强可读性;如果别名使用特殊字符或强制大小写敏感需要使用双引号
格式:Select 字段列或表达式 as 字段别名, … from 表名 (as可省略)
select BILLCODE_ID as单据号,MEMBER_CODE*3as king from system_billcode
(查询结果中列名:BILLCODE_ID MEMBER_CODE 变为:单据号king)
15.空值
空值:无效、未指定、未知的或不可预知的值;不等同于空格或0
在表达式中使用空值:
1>.算术表达式中如果出现空值,则整个表达式结果为空
2>.连接表达式中如果出现空值,则被作为一个空的(长度为0的)字符串处理
3>.null值不能与任何值比较,包括自身。测试一列是否有null值,用is null运算符
16.去除重复行
缺省条件下,查询出的结果包含所有符合条件的记录行,包括重复行
使用关键字distinct 可从插叙结果中去掉重复行(distinct作用范围是后面所有字段的组合)
Select * from system_billcode -------> Select distinct * from system_billcode
Select distinct BILLCODE_ID, MEMBER_CODE from system_billcode
17.查询结果排序
查询结果缺省按照记录的插入顺序进行排序,可使用oder by 子句对查询结果排序
排序方式:升序 ASC(缺省),降序DESC
Select distinct BILLCODE_ID, MEMBER_CODE from system_billcodeorder by BILLCODE_ID
Select distinct BILLCODE_ID, MEMBER_CODE from system_billcodeorder by BILLCODE_ID ASC
Select distinct BILLCODE_ID, MEMBER_CODE from system_billcodeorder by BILLCODE_ID DESC
多字段排序:
Select distinct * from system_billcodeorder by BILLCODE_ID , BILLCODE_NAME
使用子都别名排序:
selectdistinct BILLCODE_ID b,MEMBER_CODE from system_billcode orderby b
18.条件查询:
格式:select * | {[distinct] 字段名 | 表达式 [别名] ,…}
from 表名
where 查询条件
查询语句中使用字符串和日期:
字符串和日期要用单引号括起来,字符串大小写敏感,日期格式敏感,缺省的日期格式是‘DD-MON-RR’
Select * from emp where name=’tom’
Select * from emp where date=’02-4月-8’;
获取当前缺省日期格式:
Select sysdate from dual;
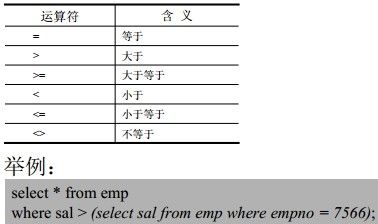
19. 比较运算符:
1)、“= 、> 、>= 、< 、<= 、<>”
Select * from emp where age >30;
Select * from emp where age <>30; 不等于
2)、beteen … and … 介于两者之间,包括边界
In (set) 出现在集合中
Like 模糊查询(%表示0或多个字符、_表示一个字符、特殊字符可用escape标识符来查找)
Is null 为空值
Select * from emp where age between 16 and 30;
Select * from emp where age in(15,20,25,30);
Select * from emp where name like ‘t%’;名字包含‘t’
Select * from emp where name like ‘_t%’;名字包含一个’t’
Select * from emp where name like ‘%\_%’escape ‘\’;
Select * from emp where job is null;
20. 逻辑运算符:
And
Or
Not
Select * from emp where age=20 and age > 30;
Select * from emp where age=20 or age >30;
Select * from emp where age not in (20,30,40)
21.运算符优先级:
1、 * /
2、 + -
3、 ||
4、 = > >= < <= <>
5、 Is[not] null like [not]in
6、 [not]between …and…
7、 Not
8、 And
9、 Or
使用小括号可强行改变运算顺序
Select * from emp where name=’tom’ or name=’jack’ and age >=30;
Select * from emp where (name=’tom’ or name=’jack’) and age >=30;
函数
一、单行函数:
单行函数功能:
对数据进行计算
控制数据的输出格式
设置/改变日期的显示格式
进行数据类型转换
使用NVL函数处理空值
实现if-then-else 多路分支逻辑
操作数据项、接受参数并返回处理结果、对每一个返回行起作用、可修改数据类型、可嵌套
单行函数分类:
字符函数、数值函数、日期函数、转换函数、通用函数
字符函数:
1、字符大小写转换函数:
select lower(BILLCODE_COLUMN)from system_billcode 查询结果全部转换为小写
select upper(BILLCODE_COLUMN)from system_billcode 查询结果全部转换为大写
select initcap(BILLCODE_COLUMN)from system_billcode查询结果单词首字母大写
2、字符处理函数
Concat()字符串连接: concat(‘hello’,’world)--->helloworld
select concat(BILLCODE_ID,BILLCODE_COLUMN) from system_billcode 将查询结果的两个字符串连接
select concat('hello','world') from system_billcode
将两个字符串连接(此字符串在该表不存在,作为查询结果的附加列)
字符串处理函数concat()和拼接运算符||联合使用:
select concat(BILLCODE_ID,BILLCODE_COLUMN) || MEMBER_CODE from system_billcode 将查询结果先连接后拼接
select concat('BILLCODE_ID','BILLCODE_COLUMN') || MEMBER_CODE from system_billcode
将两个字符串连接然后再和查询结果拼接
Substr()截取字符串: substr(‘helloworld’,4,3)--->low
Length()返回字符串长度: length(‘helloworld’)------->11
Instr()定位字符串: instr(‘helloworld’,’or’)-------->8
Lpad()左侧填充: lpad(‘smith’,10,’*’)----->*****smith
Rpad()右侧填充: rpad(‘smith’,10,’*’)----->smith*****
Trim()过滤首尾空格: trim(‘ mr smith ’)-------->mr smith
Replace()替换: replace(‘mr smith and mr white’,’mr’,’mrs’)
---->mrs smith and mrs white
数值函数:
Abs()去绝对值: abs(-3.14)--------------------- -3.14
Round()四舍五入: round(3.1415)--------------------- 3
Round(3.1415 ,3)------------------3.142
Round(314.1592 ,-2)---------------300
Trunk()截断: round(3.1415 ,3)------------------3.141
Ceil()向上取整 ceil(3.14)------------------------4
Floor()向下取整 floor(3.14)-----------------------3
Sign()判断数值正负 sign(-3.14)------------------------1
Sin()…三角函数 sin(3.14)-------------------------.001592653
Power()幂运算 power(4.5 ,2)---------------------power(4.5 ,2)
Sqrt()开平方根 sqrt(9)---------------------------3
Mod()取模 mod(10 ,3)------------------------1
Exp()基数为e幂运算 exp(1)----------------------------2.71828183
Log()对数运算 log(4 ,16.0)----------------------2
Ln()自然对数运算 ln(7)-----------------------------1.94591015
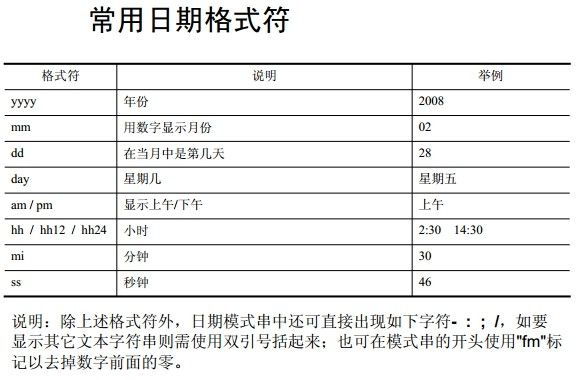
日期函数:
Oracle内部以数字格式存储日期和时间信息:世纪,年,月,日,小时,分钟,秒
缺省的日期格式是:DD-MON-YY
设定日期格式的方式:
1、改变运行环境(session交互环境)的日期格式:
alter session set nls_date_format ='yyyy mm dd hh24:mi:ss'
alter session set nls_date_format ='yyyy mm dd hh12:mi:ss'
通过改变session的日期格式,改变的select语句 的返回结果形式
2、运用转换函数对日期显示格式进行字符串转换
可使用sysdate函数获取当前系统日期和时间
日期型数据的算术运算:
日期型数据可以直接加减一个数值,结果仍为日期
两个日期型数据可以直接相减,结果为两者相差多少天
add_months(x ,y)计算在日期x基础上增加y个月的日期:add_months(sysdate ,2)
last_day(x)返回日期x当月最后一天的日期:last_day(sysdate)
months_between(x ,y)返回日期x,y之间相差的月数:months_between(sysdate,hiredate)
round(x ,y)将日期x四舍五入到y所指定的日期单位(月或年)的第一天:
round(sysdate ,’month’); round(sysdate ,’year’);
trunk(x ,y)将日期x截断到y所指定的日期单位(月或年)的第一天:
trunk(sysdate ,’month’); trunk(sysdate ,’year’);
next_day(x ,y)计算指定日期x后的第一个星期几(由参数y指定)对应的日期:
next_day(sysdate ,’星期二’);
转换函数:
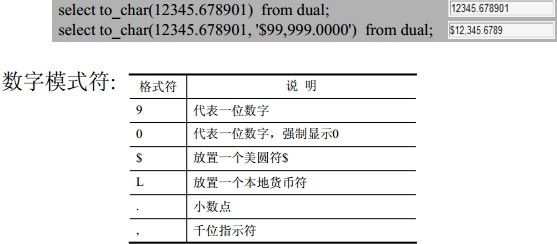
to_char(): to_char(date)--------------缺省转换为“dd-mm-yy”格式
to_char(date ,’format_model’)—转换成指定的格式
select name,age,to_char(sysdate ,’yyyy-mm-dd’)from student
to_char(number)-----------
to_char(number,’format_model’)
select to_char(12345.678901) from dual;
select to_char(12345.678901 ,’$99999.0000’) from dual;
to_date(): to_date(char)-------------按缺省格式“dd-mm-yy”解析
to_date(char ,’format_model’)---按指定格式解析
insert into student values(‘tom’,to_date(‘2008-02-28’,’yyyy-mm-dd’));
to_number(): to_number(char)------------
to_number(char ,’format_model’)
![]()
通用函数:
Nvl()函数:用于将空值null替换为指定的缺省值,使用于字符、数字、日期等类型
格式:nvl(exp1 , exp2)
如果表达式exp1的值为null,则返回exp2的值,否则返回exp1的值
Select name , age ,sal ,comm , sal +nvl(comm , 0) from student;
Select name , age , nvl(hiredate , sysdate) from student ;
Select name , age , job , nvl(job ,‘no job yet’) from student;
Nvl2()函数:用于实现条件表达式
格式:nvl2(exp1 ,exp2 ,exp3)
如果表达式exp1的值不为null,则返回exp2的值,否则返回exp3的值
Select name ,age ,sal ,comm ,nvl2(comm ,sal+comm ,sal) total from student;
Nullif()函数:用于数据等价性比较并根据比较结果返回null或其中一个被比较的数值
格式:nullif(exp1 ,exp2)
如果表达式exp1与exp2的值相等则返回null,否则返回exp1的值
Select name 原名,nullif(pen_name ,name) 化名 from student ;
Coalesce()函数:用于实现数据“接合”功能
格式:coalesce(exp1 ,exp2 ,…)
依次考察各参数表达式,遇到非null值即停止并返回该值
Select name , age , sal ,comm ,coalesce(sal +comm ,sal ,0) 总收入 from student
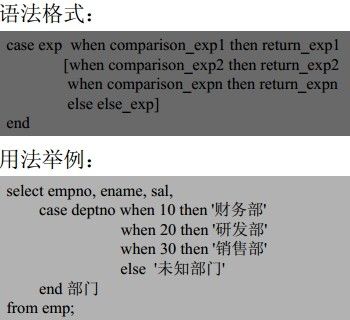
Decode()函数:和case表达式类似,也用于实现多路分支结构
where子语句:(根据条件过滤表里的记录“行过滤”)
语法顺序:select---from---where
执行顺序:from---where---select
后跟条件表达式、列名(用字符类型的列过滤字符串必须用‘’)、常量、比较运算符、文字值; 但不能跟列别名;也可跟多个条件表达式,之间用运算符连接 and、or、或()
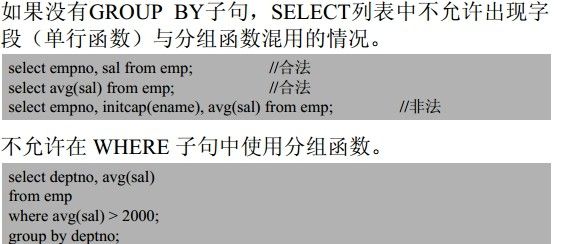
二、分组函数(多行函数):
功能:
对一组数据进行运算,针对一组数据(多行记录)只返回一个结果
分类:
Avg()计算平均值(数值型):
Count()返回查询所得到的记录行数(任何类型):
Max()计算最大值(任何类型):
Min()计算最小值(任何类型):
Sum()求和(数值型):
Select avg(age),max(name),min(name),sum(age) from emp;
Count()函数:
Count(*):返回组中总记录数目
Count(exp):返回表达式exp值非空的记录数目
Count(distinct(exp)):返回表达式exp值不重复的、非空的记录数目
Select count(*) from emp;
Select count(comm) from emp;
Select count(distinct(comm)) from emp;
分组函数与空值
1.分组函数省略列中的空值:
Select avg(comm) from emp ;
Select sum(comm) from emp ;
2.使用nvl()函数强制分组函数处理空值:
Select avg(nvl(comm ,0)) from emp ;
Group by子句
Group by子句:将表中数据分成若干小组
语法顺序:select---from---where--group by---order by
执行顺序:from---where ---group by---order by---select

Select deptno ,job ,avg(sal) from emp group by deptno ,job ;
Having子句:用于过滤分组
语法顺序:select ---from ---where---group by---having---order by
执行顺序:from ---where---group by---select---having---order by

where和having的区别:
1。过滤的对象不同:where过滤的是行(记录);having过滤的是组(组标识、每组数据的聚合结果)
2。后面跟的内容不同:where子句后跟列名、单行函数;having子句后只能跟group by后面的表达式和组函数
3。执行顺序不同:where子句执行在前;having子句执行在后
where和having的共同点:where和having子句都不允许用列别名
多表查询
格式:
Select 字段
from table 1, table 2
where table 1.column 1=table 2.column 2;
where子句指定两表连接条件,当被连接的多个表中存在同名字段时,必须在该字段前加上“表名.”作为前缀
多表连接中:
可使用and操作符增加查询条件
使用表别名可以简化查询
使用表名(表别名)前缀可提高查询效率
为连接n个表,至少需要n-1个连接条件
两个以上的表进行连接时应依次、分别指定相邻的两个表之间的连接条件
通过连接运算符可以实现多个表查询。连接是关系数据库模型的主要特点,也是它区别于其它类型数据库管理系统的一个标志。
在关系数据库管理系统中,表建立时各数据之间的关系不必确定,常把一个实体的所有信息存放在一个表中。当检索数据时,通过连接操作查询出存放在多个表中的不同实体的信息。连接操作给用户带来很大的灵活性,他们可以在任何时候增加新的数据类型。为不同实体创建新的表,尔后通过连接进行查询。
连接可以在SELECT 语句的FROM子句或WHERE子句中建立,而在FROM子句中指出连接时有助于将连接操作与WHERE子句中的搜索条件区分开来。所以,在Transact-SQL中推荐使用这种方法。
SQL-92标准所定义的FROM子句的连接语法格式为:
FROM join_table join_type join_table
[ON (join_condition) ]
其中join_table指出参与连接操作的表名,连接可以对同一个表操作,也可以对多表操作,对同一个表操作的连接又称做自连接。
join_type 指出连接类型,可分为三种:内连接、外连接和交叉连接。
内连接(inner join)使用比较运算符进行表间某(些)列数据的比较操作,并列出这些表中与连接条件相匹配的数据行。根据所使用的比较方式不同,内连接又分为等值连接、自然连接和不等连接三种。
外连接分为左外连接(left outer join或left join)、右外连接(right outer join或right join)和全外连接(full outer join或full join)三种。与内连接不同的是,外连接不只列出与连接条件相匹配的行,而是列出左表(左外连接时)、右表(右外连接时)或两个表(全外连接时)中所有符合搜索条件的数据行。
交叉连接(CROSS JOIN)没有WHERE 子句,它返回连接表中所有数据行的笛卡尔积,其结果集合中的数据行数等于第一个表中符合查询条件的数据行数乘以第二个表中符合查询条件的数据行数
连接操作中的ON (join_condition) 子句指出连接条件,它由被连接表中的列和比较运算符、逻辑运算符等构成
无论哪种连接都不能对text、ntext和image数据类型列进行直接连接,但可以对这三种列进行间接连接。例如:
select p1.pub_id , p2.pub_id , p1.pr_info
from pub_info as p1 inner join pub_info as p2
on datalength(p1.pr_info) = datalength(p2.pr_info)
(一)内连接
内连接查询操作列出与连接条件匹配的数据行,它使用比较运算符比较被连接列的列值。内连接分三种:
1、等值连接:在连接条件中使用等于号(=)运算符比较被连接列的列值,其查询结果中列出被连接表中的所有列,包括其中的重复列。
2、不等连接: 在连接条件使用除等于运算符以外的其它比较运算符比较被连接的列的列值。这些运算符包括>、>=、<=、<、!>、!<和<>。
3、自然连接:在连接条件中使用等于(=)运算符比较被连接列的列值,但它使用选择列表指出查询结果集合中所包括的列,并删除连接表中的重复列。
等值连接列出authors和publishers表中位于同一城市的作者和出版社:
SELECT *
FROM authors AS a INNER JOIN publishers AS p
ON a.city=p.city
select ename, a.deptno as a_deptno,b.deptno as b_deptno ,b.dname as 部门
from emp a, dept b
where a.deptno = b.deptno;
非等值连接,在emp表和salgrade表中查找员工的姓名,工资,等级,工资上线,工资下线
select ename as 姓名, sal as 工资, grade as 工资等级,losal as 工资上线,hisal as 工资下线
from emp, salgrade
where sal between losal and hisal;
自然连接,在选择列表中删除authors 和publishers 表中重复列(city和state):
SELECT a.* , p.pub_id , p.pub_name , p.country
FROM authors AS a INNER JOIN publishers AS p
ON a.city = p.city
自然连接 natural join------相当等值连接(natural join基于两个表中的全部同名列建立连接从两个表中选出同名列的值均对应相等的所有行如果两个表中同名列的数据类型不同,则出错 不允许在参照列上使用表名或者别名作为前缀)
select e.ename, d.dname
from emp e natural join dept d;
内连接时,返回查询结果集合中的仅是符合查询条件( WHERE 搜索条件或 HAVING 条件)和连接条件的行。而采用外连接时,它返回到查询结果集合中的不仅包含符合连接条件的行,而且还包括左表(左外连接时)、右表(右外连接时)或两个边接表(全外连接)中的所有数据行。
外连接运算符为(+)
左外连接将论坛内容和作者信息连接起来:
SELECT a.* , b.*
FROM luntan LEFT JOIN usertable as b
ON a.username = b.username
select first_name as 姓名, department_name as 部门名称, d.department_id as 部门编号
from employees e, departments d
where e.department_id= d.department_id(+) ;
右外连
select e.ename, d.dname, e.deptno
from emp e,dept d
where e.deptno = d.deptno(+);
全外连接将city表中的所有作者以及user表中的所有作者,以及他们所在的城市:
SELECT a.* , b.*
FROM city as a FULL OUTER JOIN user as b
ON a.username = b.username
(三)交叉连接
交叉连接不带WHERE 子句,它返回被连接的两个表所有数据行的笛卡尔积,返回到结果集合中的数据行数等于第一个表中符合查询条件的数据行数乘以第二个表中符合查询条件的数据行数。
例,titles表中有6类图书,而publishers表中有8家出版社,则下列交叉连接检索到的记录数将等于6*8=48行。
SELECT type , pub_name
FROM titles CROSS JOIN publishers
ORDER BY type
(四)自连接
在同一个表中查询每个员工及上司的工号和姓名
select a.empno as 员工编号, a.ename as 员工姓名, a.mgr as 上司的员工编号, b.ename as 上司姓名
from emp a, emp b
where a.mgr = b.empno;
Using子句:
如果不希望参照被连接表的所有同名列进行等值连接,自然连接将无法满足要求,可以在连接时使用using子句来设置用于等值连接的列(参照列)名
Select emp_no ,ename ,sal ,dep_no ,dname from emp join dep using(dep_no);
不允许在参照列上使用表名或者别名作为前缀
using子句-----使用同名列查询
select e.ename, d.dname
from emp e join dept d
using (deptno);
On子句:如果要参照非同名的列进行等值连接,或想设置任意的连接条件,可以使用on子句
Select emp_no ,ename ,sal ,emp.dep_no ,dname from emp join dep on(emp.dep_no=dep.dep_no);
on子句 ------当列名不同时用on子句
用on查询两张表:
select e.ename, d.dname from emp e join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;
用on查询多张表:
select e.ename, d.dname from emp e join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno join 第三个表 on 列1 = 列2;
子查询
子查询在主查询前执行,主查询使用子查询的结果
使用子查询的方针:
(1)子查询要用括弧“()”括起来;
(2)子查询要放在比较运算符的右边。
(3)Order by子句在子查询中是没有必要的,除非需要Top-N的分析。
(4)单行子查询配单个值的操作符,多行子查询配多个值的操作符。
(5)查询是基于未知的值时应考虑使用子查询。
注:
如果子查询没有返回结果,主查询也不会返回任何结果
如果子查询返回单行结果,则为单行子查询,可以在主查询中对其使用相应的单行记录比较运算符
如果子查询返回多行结果,则为多行子查询,此时不允许对其使用单行记录比较运算符,只能用IN,
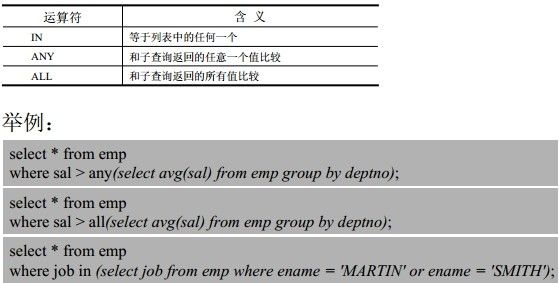
ANY,ALL
子查询按执行方式分为:
『标准子查询』:子查询只执行一次
『关联子查询』:主查询执行一次,子查询就执行一次,子查询依赖于主查询的参数。
select * from jobs a
where job_id>1 and Exists(select * from jobs where job_id=a.job_id-1)
子查询按返回结果集分
1.单行子查询:子查询返回一行记录
单行子查询使用单行记录比较运算符:
2.多行子查询:子查询返回多行记录
多列子查询 :
SELECT deptno,ename,job,sal
FROM EMP
WHERE (deptno,sal) IN (SELECT deptno, MAX(sal) FROM EMP GROUP BY deptno);
查找出工资比scott高的人:
select ename, sal from emp
where sal>(select sal from emp where ename='SCOTT');
查找那些人和scott相同职位的人:
select ename, job from emp
where job=(select job from emp where ename='SCOTT') and ename <> 'SCOTT';
any的用法 < any意味着小于最大、> any大于最小:
select empno, ename, sal, job from emp
where sal<any(select sal from emp where job='SALESMAN');
all的用法 < all:小于所有,即小于最小、> all:大于所有,即大于最大:
select empno, ename, sal, job from emp
where sal<all(select sal from emp where job='SALESMAN');
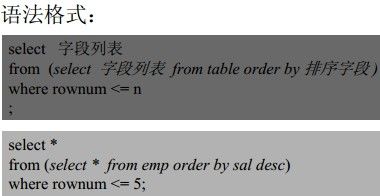
TopN查询
子查询和表连接查询的选择:
子查询最终是针对某张表的数据信息进行筛选,也就是说不管你嵌套了几层子查询,最后还是在基表中筛选数据;
表连接的话,又分了很多种,比如笛卡尔积,这个就是两个表的所有结果乘积,另外还有自然连接那些,通过表连接查询的结果可以是多张表的合集……也就是说最终展现的时候,多表连接可以是多个表的数据结果,而子查询却只是一个基表里面的某些筛选数据