上一篇博客当中提到了哈弗曼树的构建与编码,详情请参见:http://cq520.iteye.com/blog/1870454
这一次主要是跟大家探讨一下哈弗曼压缩的原理及实现,由于过程化的实现更加容易理解也更加直观,所以这里首先会分步骤跟大家讲解一下哈弗曼压缩的具体实现方法,然后再与大家分享一下对象化的实现。
首先,我们要知道文件为什么能压缩?
文件是由字节所组成的,一个字节的长度为8位,所以最多只存在256种字节,而一个文件中一般存在许多相同的字节,我们把相同的字节以一种更加精简的方式表示,就完成了我们所说的压缩。
哈弗曼压缩的原理是什么?
上次博客中提到了哈弗曼编码,但是只是粗略的带过了,这一次举一个具体的例子来更加直观的说明哈弗曼压缩的原理。
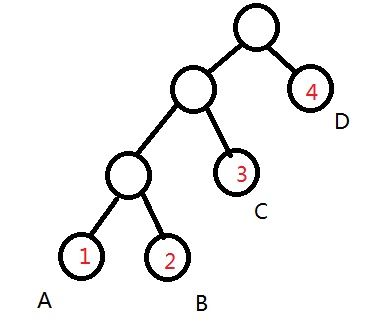
假设一个文件中是这样的一串字节ABBCCCDDDD,那么这个文件的大小就是10个byte。那么接下来就是我们的哈弗曼压缩的第一步:
一.读取文件,统计每一种字节出现的次数,将出现的字节种类与对应的次数保存起来(可采用数组或者是HashMap,或者是其他的数据结构)
保存完了之后干什么呢??当然是构建哈弗曼树呀。第二步:
二. 利用得到的字节与对应的频次构建哈弗曼树,需要注意的是,构建树的时候是以字节出现的频次作为我们的评判标准,出现次数越多的放在越上层。
比如我们上面所说的这个文件,它所构成的树应该是这样的:
我们现在得到的树还处于未编码的状态,那么第三步毫无疑问就是我们所说的编码了:
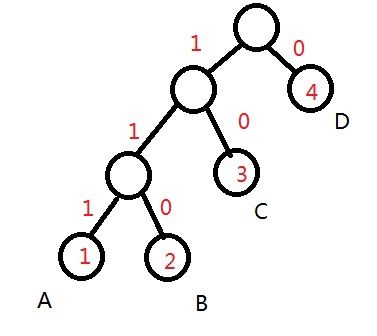
三. 将得到的哈弗曼树进行编码
编码之后的树就变成这个样子了(采取向左编1的方式):
到了这一步其实我们的压缩就已经完成一半了,听到这里,你可能纳闷了,不对呀,不是还没开始么??
下面我们就来看一下哈弗曼压缩的精华所在:
编码之后,A所对应的的编码就是111,B就是110,C是10,D是0,那么我们的文件就变成了11111011,01010100,000,是不是有一种亲切感?下面只要把这些10串每8个作为一组编码成一个新的字节(2进制转10进制),我们的压缩工作就大功告成了,所以这里每8位我也特别用逗号表示出来了,怎么样一个10个byte的文件瞬间变成了3个byte,是不是很神奇呢?
等一下,做到这一步其实是远远不够的,有几个问题:
1. 怎么样把这一串的01变成我们所说的byte数?
需要注意的是,我们把文件中的字节变成这个样子只是把它们变成了一个01的字符串,那么这个问题就要用编程方法来解决了,具体方法有很多种,下面会给大家介绍一两种。
2.如果最后几位不满8个怎么办?
我们可以定义这样一个规则,在最后的位置补0,在文件的末尾再加一位表示最后一个数补0的个数,这样的话这个问题就变得很简单了。
3. 压缩之后我们怎么知道压缩前每种字节对应的编码是什么样子的?
如果你理解了压缩的前三步,你一定会想到这个问题,确实,我们如果按照这种方式压缩,我们所得到的文件将会无法复原。那么要完成压缩,最关键的一步,还要将压缩时所得到的每个字节对应的码表写入文件,这样我们才能保证,我们所做的工作是可逆的。
好的,说完了这些,压缩剩下来的步骤相信你也已经明了了,压缩第四步:
四.根据每种字节对应的哈弗曼编码,将文件转换成01字符串
五.将得到的01串重新编码成新的byte数组写入文件
当然,第四步与第五步可以同时完成,而且,每生成8个以上的字符串就将其前8位转换成byte数组的效率要比一次性转换的效率要高,这是因为,当文件转换成编码之后,长度增大,JVM中需要开辟一个很大的内存空间去存放这个字符串,这显然是很耗时的。
不过在过程化实现的代码中,楼主并没有将这一层优化,具体的优化工作需要读者们自己去做。
下面就是过程化实现的代码了:
package 哈弗曼压缩;
/**
* 哈弗曼压缩
* @author 陈强
*
*/
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Set;
public class HFMCondense {
public static void main(String args[]){
String file="D://b.txt";
HFMCondense condense=new HFMCondense();
//System.out.println("元素与对应的频次表:");
//System.out.println(condense.readFiletoMap(file));
//System.out.println("生成的哈弗曼树");
HFMNode hfmTree=condense.HashMapToHFMTree(condense.readFiletoMap(file));
//condense.PreOrderTraverse(hfmTree);
//System.out.println();
//System.out.println("产生的哈弗曼编码表:");
//condense.HuffmanCode(hfmTree,"");
condense.HuffmanCoding(hfmTree, "");
//转译后的字符串
//String codeString=condense.FileToString(file);
//System.out.println(codeString);
//压缩后的字符串
//String newString=new String(condense.createByteArray(codeString));
//System.out.println(newString);
System.out.println("开始压缩...");
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
//System.out.println(condense.FileToString(file));
//System.out.println(condense.CodeToString(file));
//condense.CompressFile(condense.createByteArray(condense.CodeToString(file)),"D://c");
condense.CompressFile(condense.createByteArray(condense.FileToString(file)),"D://c");
System.out.println("压缩结束...用时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start));
//打印数组最后一个补0的个数
//byte content[]=condense.createByteArray(condense.FileToString(file));
//System.out.println(content[content.length-2]);
}
/**
* 读取将要被压缩的文件,统计每一个字符出现的频率,并将得到的内容存入HashMap中
* @param fileName 将要被压缩的文件
* @return 每一个字节数出现的频率所对应的HashMap
*/
public HashMap<Byte,Integer> readFiletoMap(String fileName){
HashMap<Byte,Integer> hashMap=new HashMap<Byte,Integer>();
File file=new File(fileName);
if(file.exists()){
try{
InputStream in=new FileInputStream(file);
//创建与文件大小相同的字节数组
byte[] content=new byte[in.available()];
//读取文件
in.read(content);
//存入HashMap中
for(int i=0;i<content.length;i++){
//如果表中存在某一个键
if(hashMap.containsKey(content[i])){
//获取该字节当前的键值
int rate=hashMap.get(content[i]);
//键值增大
rate++;
hashMap.put(content[i], rate);
}
//如果不存在某一个字节对象,则将它存入HashMap当中
else{
hashMap.put(content[i],1);
}
}
in.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
else{
System.out.println("文件不存在");
}
return hashMap;
}
/**
* 将HashMap中的元素取出来封装到哈弗曼树中,树中叶子结点保存的是HashMap中的每一个键值与频率
* @param map 读取的Map
* @return 哈夫曼树的根结点
*/
public HFMNode HashMapToHFMTree(HashMap<Byte,Integer> map){
//得到存储键值的系
Set<Byte> keys=map.keySet();
//得到迭代器对象
Iterator<Byte> iter=keys.iterator();
//如果还有值
while(iter.hasNext()){
byte key=iter.next();//获取系中的键
int value=map.get(key);//得到该键出现的频率
//创建结点并将结点对象加入到队列当中
HFMNode node=new HFMNode(key,value);
nodeQueue.add(node);
nodeList.add(node);
}
//当所剩的结点数还大于两个
while(nodeQueue.size()>=2){
//得到键值频率最小的两个结点
HFMNode left=nodeQueue.poll();
HFMNode right=nodeQueue.poll();
//将这两个结点组合起来生成新的结点
HFMNode node=new HFMNode(left.data,left.value+right.value,left,right);
nodeQueue.add(node);
}
//获取队列中的最后一个结点作为根结点
HFMNode hfm=nodeQueue.poll();
return hfm;
}
/**
* 为生成的哈弗曼树进行编码,产生对应的哈弗曼编码表
* @param hfm 对应的哈弗曼树
* @param code 对应生成的哈弗曼编码
* @return 哈弗曼编码表
*/
//创建一个新的哈弗曼编码表
HashMap<Byte,String> codeMap=new HashMap<Byte,String>();
public HashMap<Byte,String> HuffmanCoding(HFMNode hfm,String code){
//如果左子树不为空,则左子树编码加1
if(hfm.lchild!=null){
HuffmanCoding(hfm.lchild,code+"1");
}
//如果右子树不为空,则右子树编码加0
if(hfm.rchild!=null){
HuffmanCoding(hfm.rchild,code+"0");
}
//如果到达叶子结点,则将元素放入HashMap中生成哈弗曼编码表
if(hfm.lchild==null&&hfm.rchild==null){
codeMap.put(hfm.data,code);
hfm.code=code;
}
return codeMap;
}
/**
* 将哈弗曼编码转换成字符串
* @param fileName 读取的文件名
* @return 编码之后的哈弗曼字符串
*/
public String CodeToString(String fileName){
File file=new File(fileName);
String codeString="";
//如果文件存在
if(file.exists()){
try{
InputStream in=new FileInputStream(file);
byte content[]=new byte[in.available()];
in.read(content);
int i=0;
int len=content.length;//得到文件的字节长度
int size=nodeList.size();//得到队列的长度
while(i<len){
for(int j=0;j<size;j++){
if(content[i]==nodeList.get(j).data){
codeString+=nodeList.get(j).code;
break;
}
}
i++;
}
in.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else {
System.out.println("文件不存在");
}
return codeString;
}
/**
* 将文件按照对应的哈弗曼编码表转成01字符串
* @param fileName 读入的文件名
* @return 转译后的字符串
*/
public String FileToString(String fileName){
File file=new File(fileName);
String StringContent="";
//如果文件存在
if(file.exists()){
try{
InputStream in=new FileInputStream(file);
byte content[]=new byte[in.available()];
in.read(content);
//循环转译
int len=content.length;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
StringContent+=codeMap.get(content[i]);
}
in.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else{
System.out.println("文件不存在");
}
return StringContent;
}
/**
* 将转译后的01字符串重新转换后放入新的字节数组当中
* @param code 转译后的01字符串
* @return 新的字节数组,里面包含了压缩后的字节内容
*/
public byte[] createByteArray(String code) {
//将每8位字符分隔开来得到字节数组的长度
int size=code.length()/8;
//截取得到字符串8整数后的最后几个字符串
String destString=code.substring(size*8);
byte dest[]=destString.getBytes();
//s用来记录字节数组的单字节内容
int s = 0;
int i=0;
int temp = 0;
// 将字符数组转换成字节数组,得到字符的字节内容,方便将二进制转为十进制
byte content[] = code.getBytes();
for (int k = 0; k < content.length; k++) {
content[k] = (byte) (content[k] - 48);
}
//转译后的字节内容数组
byte byteContent[];
if (content.length % 8 == 0) {// 如果该字符串正好是8的倍数
byteContent = new byte[content.length / 8 + 1];
byteContent[byteContent.length - 1] = 0;// 那么返回的字节内容数组的最后一个数就补0
} else {
//否则该数组的最后一个数就是补0的个数
byteContent = new byte[content.length / 8 + 2];
byteContent[byteContent.length - 1] = (byte) (8 - content.length % 8);
}
int bytelen=byteContent.length;
int contentlen=content.length;
// byteContent数组中最后一个是补0的个数,实际操作到次后个元素
//Math.pow返回第一个参数的第二个参数次幂的值
while (i < bytelen - 2) {
for (int j = 0; j < contentlen; j++) {
if (content[j] == 1) {// 如果数组content的值为1
s =(int)(s + Math.pow(2, (7 - (j - 8 * i))));// 累积求和
}// if
if ((j+1)%8==0) {// 当有8个元素时
byteContent[i] = (byte) s;// 就将求出的和放入到byteContent数组中去
i++;
s = 0;// 并重新使s的值赋为0
}// if
}// for
}// while
int destlen=dest.length;
for(int n=0;n<destlen;n++){
temp+=(dest[n]-48)*Math.pow(2, 7-n);//求倒数第2个字节的大小
}
byteContent[byteContent.length - 2] = (byte) temp;
return byteContent;
}
/**
* 压缩并输出新文件
* @param content 压缩后产生的新的字节数组
* @param fileName 输出文件名
*/
public void CompressFile(byte[] content,String fileName){
File file=null;
//统一后缀名
if(!fileName.endsWith("hfm")){
file=new File(fileName+".hfm");
}else if(fileName.endsWith("hfm")){
file=new File(fileName);
}
int len=content.length;
if(len>0){
try{
OutputStream out=new FileOutputStream(file);
//将字节内容写入文件
out.write(content);
out.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else{
System.out.println("压缩出错");
}
}
/**
* 测试一下哈弗曼树建立是否正确
* @param hfm
*/
public void PreOrderTraverse(HFMNode hfm){
if(hfm!=null){
System.out.print(hfm.value+" ");
PreOrderTraverse(hfm.lchild);
PreOrderTraverse(hfm.rchild);
}
}
/**
* 存储哈弗曼树结点的优先队列
*/
ArrayList<HFMNode> nodeList=new ArrayList<HFMNode>();
PriorityQueue<HFMNode> nodeQueue=new PriorityQueue<HFMNode>(11,new MyComparator());
/**
* 实例化的一个比较器类
*/
class MyComparator implements Comparator<HFMNode>{
public int compare(HFMNode o1, HFMNode o2) {
return o1.value-o2.value;
}
}
}
结点类:
package 哈弗曼压缩;
public class HFMNode {
byte data; //存储字节的数据域
int value; //字节出现的频率
String code;//叶子结点的哈弗曼编码
HFMNode lchild,rchild;//左右孩子的引用
//只指定数据的构造体
public HFMNode(byte data,int rate){
this(data,rate,null,null);
}
//同时指定左右孩子的构造体
public HFMNode(byte data,int value,HFMNode lchild,HFMNode rchild){
this.data=data;
this.value=value;
this.lchild=lchild;
this.rchild=rchild;
}
}
大家也看到了里面有两个方法做了同样一件事情,而经过测试之后发现两个方法的效率差不多,我们注意到的是,上面所做的每一步都是下一步的前提,所以在做过程化的实现时,一定要先理清楚前后的逻辑关系,此外,上文也提到了,这样做完之后还有几个问题没有解决。
1. 码表还未写入文件。(写入码表的方法有很多种,可以使用DataOutputStream类或者ObjectOutputStream类里面所提供的方法,大家自己查看一下API吧)
2. 压缩的效率很低(上面这一种实现的方法效率几乎是最低了,优化有几个方向,例如引入缓冲,生成编码的同时进行转译,采用更加快速的存储方式(采用数组存储的效率要高于HashMap)).
压缩完成之后就要进行解压了,相信掌握了压缩技术的你,解压已经不成难题了,需要注意的是,
1. 码表最好放在压缩文件的前半部分,(这是因为,你可以在码表的最后用两个0表示码表的结束,而在文件的尾部,你可能也可以碰到两个0,这样你就无法判断哪里是码表的开始了)
2. 读出来码表之后记得保存起来,解压时需要一个一个字节的去对照码表
说到这里,我们的过程化实现就已经基本结束了,但是大家可能想起来了,不是要讲对象化的实现么??怎么讲了这么久还没开始呀?别急别急,上面只是为了让大家更好的理解哈弗曼压缩的原理。下面就是对象化实现的具体代码,由于对象化的实现难于理解,所以很多地方都给予了注释,甚至一些不必要的地方都写上了,(当然注释中可能有些不到位的地方)不过我想写好注释或许才是我们真正所需要的,湖大的陆亮学长就曾说过,我可能写不出一行有技术含量的代码,但我能写出一行规范的代码。
对象化的实现方法中,提供了按位输入与输出的类,这些类都是自定义的,因为在编程中我们所能操作的计算机的最小单元是byte,那么在这个类中是怎么做的呢?将一个字节进行8次移位按位与运算,我们就得到了这个字节的8个bit的表示方式。
里面还有很多比较实用的方法,希望大家能够耐心的看一下,好的,话不多说了,方法如下:
基本数据接口:
package 哈弗曼完全压缩;
public interface BitUtils {
public static final int BITS_PER_BYTES=8;//位与byte之间的转换单位
public static final int DIFF_BYTES=256;//0x100
public static final int EOF=256;//EndOfFile 资料源无更多的资料可读取
}
位输入类:
package 哈弗曼完全压缩;
/**
* InputStream的包装类,提供按位输入
*/
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class BitInputStream {
private InputStream in;//基本输入流
private int buffer;//byte缓冲区
private int bufferPos;//表示缓冲区中有多少未被使用的空间
/**
* 封装InputStream的构造方法,初始化byte缓冲区的大小
* @param is InputStream对象
*/
public BitInputStream(InputStream is){
in=is;
bufferPos=BitUtils.BITS_PER_BYTES;//初始化缓冲区的剩余空间
}
/**
* 读取一位的方法,每8次对其进行调用就会从基本输入流中读出一个byte
* @return 1位数据,1或者0
* @throws IOException
*/
public int readBit() throws IOException{
//如果缓冲区还未被使用
if(bufferPos==BitUtils.BITS_PER_BYTES){
//输入流读取一位
buffer=in.read();
//读到文件的末尾了
if(buffer==-1)
return -1;
//清空缓冲区
bufferPos=0;
}
//扩张缓冲区
return getBit(buffer,bufferPos++);
}
/**
* 关闭输入流
* @throws IOException
*/
public void close() throws IOException{
in.close();
}
/**
* 获取一个byte中每一位的方法
* @param pack
* @param pos
* @return
*/
private static int getBit(int pack,int pos){
//将一个字节进行8次按位与运算,得到这个字节的8位
return (pack&(1<<pos))!=0?1:0;
}
}
位输出类:
package 哈弗曼完全压缩;
/**
* OutputStream的包装类,提供按位输出的方法
*/
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
public class BitOutputStream {
private OutputStream out; //基本输出流
private int buffer;//输出的缓冲区
private int bufferPos;//缓冲区中剩余的位数
/**
* 封装OutputStream的构造方法,初始化缓冲区大小
* @param os
*/
public BitOutputStream(OutputStream os){
bufferPos=0;
buffer=0;
out=os;
}
/**
* 写入一串的位
* @param val 包含有位数据的数组
* @throws IOException
*/
public void writeBits(int []val) throws IOException{
int len=val.length;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
writeBit(val[i]);
}
}
/**
* 写入位的方法(0或1),每8次对其进行调用就从基本流中写入一个byte
* @param val 当前写入的位数据
* @throws IOException
*/
public void writeBit(int val) throws IOException{
buffer=setBit(buffer,bufferPos++,val);//将缓冲数据转换成位数据
//每读到一个byte就刷新一次
if(bufferPos==BitUtils.BITS_PER_BYTES)//缓冲区已满则刷新缓冲区
flush();
}
/**
* 刷新此缓冲的输出流
* @throws IOException
*/
public void flush() throws IOException{
if(bufferPos==0)//如果缓冲中没有数据则不执行
return;
//将缓冲区中的数据写入
out.write(buffer);
//重置缓冲区
bufferPos=0;
buffer=0;
}
/**
* 关闭流的方法
* @throws IOException
*/
public void close() throws IOException{
flush();
out.close();
}
/**
* 进行位数据转换的方法
* @param pack
* @param pos
* @param val 当前位
* @return
*/
private int setBit(int pack,int pos,int val){
if(val==1)
//按位或运算
pack|=(val<<pos);
return pack;
}
}
结点类:
package 哈弗曼完全压缩;
/**
* 哈弗曼结点类
*/
public class HuffNode implements Comparable<HuffNode>{
public int value;//结点数据
public int weight;//权重
HuffNode left,right;//左右孩子结点
HuffNode parent;//父亲结点
/**
* 初始化结点的数据,权重,左右孩子结点与父亲结点
* @param v 数据
* @param w 权重
* @param lchild 左孩子结点
* @param rchild 右孩子结点
* @param pt 父亲结点
*/
HuffNode(int v,int w,HuffNode lchild,HuffNode rchild,HuffNode pt){
value=v;
weight=w;
left=lchild;
right=rchild;
parent=pt;
}
/**
* 比较两个结点的权重
*/
public int compareTo(HuffNode rhs) {
return weight-rhs.weight;
}
}
字符统计类:
package 哈弗曼完全压缩;
/**
* 字符统计类,获取输入流(通常是文件)中所含的字符数
* 8位字节认为是ASCII字符
*/
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class CharCounter {
//字节的下标表示字节的种类,对应的值表示出现的次数
private int theCounts[]=new int[BitUtils.DIFF_BYTES];//字节的种类总共有256种
/**
* 默认的无参的构造方法
*/
public CharCounter(){
}
/**
* 封装了基本的InputStream,读取数据并进行字符的频次统计
* @param input InputStream对象
* @throws IOException
*/
public CharCounter(InputStream input) throws IOException{
int ch;//读到的字节
//一直读到文件的末尾,每一种byte出现了多少次
while((ch=input.read())!=-1){
theCounts[ch]++;
}
}
/**
* 获取该字符统计数组的某一个字符出现的次数
* @param ch 数组下标
* @return 该下标位置字符出现的次数
*/
public int getCount(int ch){
return theCounts[ch&0xff];
}
/**
* 设置某一个字符出现的次数
* @param ch 数组下标
* @param count 字符出现次数
*/
public void setCount(int ch,int count){
theCounts[ch&0xff]=count;
}
}
哈弗曼树类:
package 哈弗曼完全压缩;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class HuffmanTree {
private CharCounter theCounts;//字符统计类对象
private HuffNode root;//根结点
private HuffNode[] theNodes=new HuffNode[BitUtils.DIFF_BYTES+1];//存储HuffNode的数组
public static final int ERROR=-3;//错误
public static final int INCOMPLETE_CODE=-2;//不完全的结点编码
public static final int END=BitUtils.DIFF_BYTES;//字节的溢出位
/**
* 实例化一个字符统计类对象
*/
public HuffmanTree(){
theCounts=new CharCounter();
root=null;
}
/**
* 可以通过CharCounter对象来创建一个huffmanTree对象
* @param cc CharCounter对象
*/
public HuffmanTree(CharCounter cc){
theCounts=cc;
root=null;
createTree();//创建HuffmanTree
}
/**
* 得到要寻找的字符编码所在的树结点,如果该字符不在树上,则返回null表示出错,否则,通过父亲链逆向查找,直到到达根结点
* @param ch 当前结点的下标
* @return 结点相对的字符编码数组
*/
public int[] getCode(int ch){
HuffNode current=theNodes[ch];
if(current==null)
return null;
String v="";//结点的编码
HuffNode parent=current.parent;
while(parent!=null){
if(parent.left==current)
v="0"+v;//左结点编码
else
v="1"+v;//右结点编码
//向下遍历
current=current.parent;
parent=current.parent;
}
int len=v.length();
int [] result=new int[len];//创建一个与编码相同大小数组
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
result[i]=v.charAt(i)=='0'?0:1;
return result;
}
/**
* 获取编码对应的字符
* @param code 哈弗曼编码
* @return 存储在结点中的值(如果结点不是叶子结点,则返回符号INCOMPLETE)
*/
public int getChar(String code){
HuffNode leaf=root;//获取根结点
int len=code.length();
//按照编码向左或向右遍历到叶子结点
for(int i=0;leaf!=null&&i<len;i++)
if(code.charAt(i)=='0')
leaf=leaf.left;
else
leaf=leaf.right;
//根结点为空
if(leaf==null)
return ERROR;
return leaf.value;
}
/**
* 写入编码表的方法
* @param out 写入的数据流
* @throws IOException
*/
public void writeEncodingTable(DataOutputStream out) throws IOException{
for(int i=0;i<BitUtils.DIFF_BYTES;i++){
if(theCounts.getCount(i)>0){
out.writeByte(i);//将字节写入(通常是文件)
out.writeInt(theCounts.getCount(i));//将字节出现的次数写入(通常是文件)
}
}
//最后写入0表示编码的结束
out.writeByte(0);
out.writeInt(0);
}
/**
* 读取编码表的方法
* @param in 数据输入流对象
* @throws IOException
*/
public void readEncodingTable(DataInputStream in) throws IOException{
for(int i=0;i<BitUtils.DIFF_BYTES;i++)
theCounts.setCount(i, 0);
byte ch;
int num;
for(;;){
ch=in.readByte();//读到的字节
num=in.readInt();//字符出现的次数
if(num==0)//如果读到0表示编码表的结束
break;
theCounts.setCount(ch, num);
}
createTree();//创建HuffmanTree
}
/**
* 构造哈弗曼编码树的方法
*/
public void createTree(){
//创建一个优先队列来保存HuffNode
PriorityQueue<HuffNode> pq=new PriorityQueue<HuffNode>();
for(int i=0;i<BitUtils.DIFF_BYTES;i++){
if(theCounts.getCount(i)>0){//如果某一个字节出现过
HuffNode newNode=new HuffNode(i,theCounts.getCount(i),null,null,null);
theNodes[i]=newNode;
pq.add(newNode);//将新结点添加到队列中
}
}
theNodes[END] =new HuffNode(END,1,null,null,null);
pq.add(theNodes[END]);
//当剩余的结点多于一个时
while(pq.size()>1){
//每次取出当前最小的两个结点
HuffNode n1=pq.remove();//remove方法与poll方法的唯一不同之处在于:此队列为空时将抛出一个异常
HuffNode n2=pq.remove();
//将最小的两个结点链接形成新结点
HuffNode result=new HuffNode(INCOMPLETE_CODE,n1.weight+n2.weight,n1,n2,null);
n1.parent=n2.parent=result;
//将新结点添加到队列当中
pq.add(result);
}
root=pq.element();//根结点就是队列中的最后一个结点
}
}
解压缩类:
package 哈弗曼完全压缩;
/**
* 包含解压缩的包装类
*/
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class HZIPInputStream extends InputStream{
private BitInputStream bin;//位输入流
private HuffmanTree codeTree;//编码的HuffmanTree对象
/**
* 封装InputStream对象,实例化HuffmanTree对象与BitInputStream对象,并读入哈弗曼编码
* @param in
* @throws IOException
*/
public HZIPInputStream(InputStream in) throws IOException{
//数据输入流
DataInputStream din=new DataInputStream(in);
codeTree=new HuffmanTree();
codeTree.readEncodingTable(din);
bin=new BitInputStream(in);
}
/**
* 读取文件的方法
*/
public int read() throws IOException{
String bits="";//哈弗曼编码的字符串
int bit;//位
int decode;//解码后的字符
while(true){
bit=bin.readBit();
if(bit == -1)
throw new IOException("Unexpected EOF");//意外的资源结束
bits+=bit;
decode=codeTree.getChar(bits);//获取编码对应的字符
if(decode==HuffmanTree.INCOMPLETE_CODE)//向下搜索到叶子结点
continue;
else if(decode==HuffmanTree.ERROR)//编码出错
throw new IOException("Unexpected error");
else if(decode==HuffmanTree.END)//编码溢出
return -1;
else
return decode;
}
}
/**
* 关闭输入流
*/
public void close() throws IOException{
bin.close();
}
}
压缩类:
package 哈弗曼完全压缩;
/**
* 包含压缩的包装类
*/
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
public class HZIPOutputStream extends OutputStream{
private ByteArrayOutputStream byteOut=new ByteArrayOutputStream();//实例化的一个字节数组输出流对象
private DataOutputStream dout;//数据输出流对象
/**
* 实例化一个DataOutputStream对象的构造方法
* @param out 输出流对象
* @throws IOException
*/
public HZIPOutputStream(OutputStream out) throws IOException{
dout=new DataOutputStream(out);
}
/**
* 写入编码频率的方法
*/
public void write(int ch) throws IOException{
byteOut.write(ch);
}
/**
* 关闭流的方法
*/
public void close() throws IOException{
byte[] theInput=byteOut.toByteArray();//将字节数组输出流转换数据转换成字节数组进行输入
ByteArrayInputStream byteIn=new ByteArrayInputStream(theInput);//将字节数组封装到字节输入流中
CharCounter countObj=new CharCounter(byteIn);//实例化字符统计对象并统计字节数组的字符出现的次数
byteIn.close();//关闭字节输入流
HuffmanTree codeTree=new HuffmanTree(countObj);//通过CharCounter对象实例化一个HuffmanTree对象
codeTree.writeEncodingTable(dout);//将编码写入数据输出流中
BitOutputStream bout=new BitOutputStream(dout);//创建位输出流
//将按编码转换后的位写入
int len=theInput.length;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
bout.writeBits(codeTree.getCode(theInput[i]&0xff));
bout.writeBits(codeTree.getCode(BitUtils.EOF));//文件结束的标示符
//关闭流
bout.close();
byteOut.close();
}
}
压缩与解压方法及测试:
package 哈弗曼完全压缩;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
public class HZIP {
/**
* 压缩文件的方法,此方法需要传入正确的绝对路径名
* @param inFile 需要被压缩的文件
* @param outFile 压缩之后的输出文件
* @throws IOException IO异常
*/
public static void compress(String inFile,String outFile) throws IOException{
String compressFile=null;//创建压缩文件
String extension=inFile.substring(inFile.length()-4);//获取源文件的后缀名
File file=new File(outFile);
//如果文件已经存在
if(file.exists()){
System.out.println("文件已经存在");
}else{
//自动补齐后缀名
if(!outFile.endsWith(".hfm")){
compressFile=outFile+extension+".hfm";
}
else{
compressFile=outFile+extension;
}
//创建文件输入的缓冲流
InputStream in=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(inFile));
//创建文件输出的缓冲流
OutputStream out=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(compressFile));
int ch;
//创建哈弗曼压缩的输入流
HZIPOutputStream hzout=new HZIPOutputStream(out);
while((ch=in.read())!=-1){
hzout.write(ch);
}
//关闭流
in.close();
hzout.close();
}
}
/**
* 解压文件的方法,此方法需要填入正确的绝对路径名
* @param compressedFile 需要被解压的文件
* @param outFile 解压之后的输出文件
* @throws IOException IO异常
*/
public static void uncompress(String compressedFile,String outFile) throws IOException{
String extension;//文件的后缀名
extension =compressedFile.substring(compressedFile.length()-4);
//得到压缩前的文件的后缀名
String suffix=compressedFile.substring(compressedFile.length()-8,compressedFile.length()-4);
//如果文件不合法则不执行解压操作
if(!extension.equals(".hfm")){
System.out.println("文件格式错误或者不是有效的压缩文件");
return;
}
File file=new File(outFile);
//如果已经存在同名文件
if(file.exists()){
System.out.println("该文件已经存在,请重新命名解压后的文件");
}
else{
outFile+=(suffix+".uc");//输出文件的格式统一为uc格式
//创建文件输入的缓冲流
InputStream fin=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(compressedFile));
//创建数据读入流
DataInputStream in=new DataInputStream(fin);
//创建哈弗曼压缩输入流
HZIPInputStream hzin=new HZIPInputStream(in);
//创建文件输出的缓冲流
OutputStream fout=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(outFile));
int ch;
//解压并输出文件
while((ch=hzin.read())!=-1){
fout.write(ch);
}
//关闭流
hzin.close();
fout.close();
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException{
System.out.println("开始压缩");
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
compress("d://a.txt","d://cd");
System.out.println("压缩结束,用时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start));
}
}
这个压缩还有很多值得改进的地方,比如当文件较小或过大时,压缩之后的文件比源文件还大,为什么呢?这是因为:
文件较小时,由于要写入编码表,所以造成了较大的空间占用。
而文件较大时,由于各种字节出现的频率已经趋于了相近的地步,那么我们再来回顾一下哈弗曼的压缩过程时会发现,极端情况下,当所有字节都出现过,且出现的次数相同时,每一种字节的编码长度都达到了8位(哈弗曼树的第9层刚好有256个叶子结点),达不到压缩的效果。
不过既然达不到压缩,做一个文件加密的工作也是不错的,怎么样,自己动手试试吧。