转自:http://zhangjunhd.blog.51cto.com/113473/128174/
当选择使用
JPanel
和顶层容器的
content pane
时,需要考虑布局管理。
JPanel
缺省是初始化一个
FlowLayout
,而
content pane
缺省是初始化一个
BorderLayout
。
下面将分别介绍几种最常用的布局管理器:
FlowLayout
、
BorderLayout
、
BoxLayout
、
CardLayout
、
GridLayout
和
GridBagLayout
。
代码演示
每一个布局管理器都会有一个代码演示,
xxxLayoutDemo.java
(见附件)。这些文件主要有三个方法组成:
addComponentsToPane()
提供布局逻辑(依据不同的布局管理器和
UI
内容)。
|
public
static
void
addComponentsToPane(Container pane) {
。。。
}
|
createAndShowGUI()
实例化一个
JFrame
,通过它的
ContentPane
加载布局逻辑内容。
|
private
static
void
createAndShowGUI() {
// Create and set up the window.
JFrame frame =
new
JFrame(
"FlowLayoutDemo"
);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.
EXIT_ON_CLOSE
);
// Set up the content pane.
addComponentsToPane(frame.getContentPane());
// Display the window.
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(
true
);
}
|
main()
程序入口,单独起一个线程,实例化
UI
。
|
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
javax.swing.SwingUtilities.invokeLater(
new
Runnable() {
public
void
run() {
createAndShowGUI();
}
});
}
|
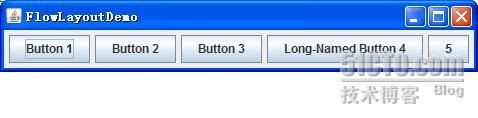
FlowLayout
FlowLayout
类是最简单的布局管理器。它按照和页面上排列单词的类似方式来安排组件
----
从左到右,直至没有多余的空间,然后转到下一行。
效果:
内容面板代码:
|
public
static
void
addComponentsToPane(Container pane) {
pane.setLayout(
new
FlowLayout());
pane.add(
new
JButton(
"Button 1"
));
pane.add(
new
JButton(
"Button 2"
));
pane.add(
new
JButton(
"Button 3"
));
pane.add(
new
JButton(
"Long-Named Button 4"
));
pane.add(
new
JButton(
"5"
));
}
|
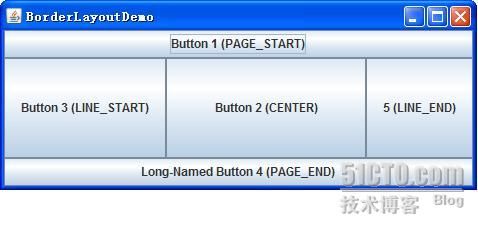
BorderLayout
一个
BorderLayout
对象将界面分成五大区域,分别用
BorderLayout
类的静态常量指定:
-PAGE_START
-PAGE_END
-LINE_START
-LINE_END
-CENTER
效果:
内容面板代码:
|
public
static
void
addComponentsToPane(Container pane) {
JButton button =
new
JButton(
"Button 1 (PAGE_START)"
);
pane.add(button, BorderLayout.
PAGE_START
);
button =
new
JButton(
"Button 2 (CENTER)"
);
button.setPreferredSize(
new
Dimension(200, 100));
pane.add(button, BorderLayout.
CENTER
);
button =
new
JButton(
"Button 3 (LINE_START)"
);
pane.add(button, BorderLayout.
LINE_START
);
button =
new
JButton(
"Long-Named Button 4 (PAGE_END)"
);
pane.add(button, BorderLayout.
PAGE_END
);
button =
new
JButton(
"5 (LINE_END)"
);
pane.add(button, BorderLayout.
LINE_END
);
}
|
BoxLayout
BoxLayout
可以将组件由上至下或由左至右依次加入当前面板。
效果:
内容面板代码:
|
public
static
void
addComponentsToPane(Container pane) {
JPanel xPanel =
new
JPanel();
xPanel.setLayout(
new
BoxLayout(xPanel, BoxLayout.
X_AXIS
));
addButtons(xPanel);
JPanel yPanel =
new
JPanel();
yPanel.setLayout(
new
BoxLayout(yPanel, BoxLayout.
Y_AXIS
));
addButtons(yPanel);
pane.add(yPanel, BorderLayout.
PAGE_START
);
pane.add(xPanel, BorderLayout.
PAGE_END
);
}
private
static
void
addAButton(String text, Container container) {
JButton button =
new
JButton(text);
button.setAlignmentX(Component.
CENTER_ALIGNMENT
);
container.add(button);
}
private
static
void
addButtons(Container container) {
addAButton(
"Button 1"
, container);
addAButton(
"Button 2"
, container);
addAButton(
"Button 3"
, container);
addAButton(
"Long-Named Button 4"
, container);
addAButton(
"5"
, container);
}
|
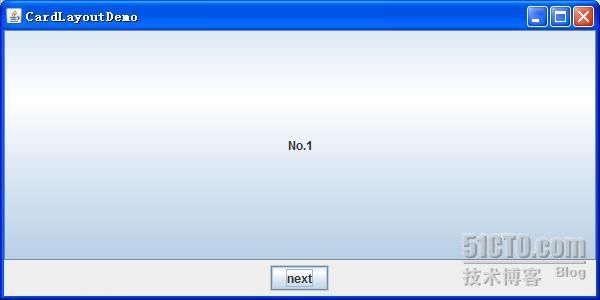
CardLayout
卡片布局和其他布局不同,因为它隐藏了一些组件。卡片布局就是一组容器或者组件,它们一次仅仅显是一个,组中的每个容器称为卡片。
效果:
内容面板代码:
|
public
void
addComponentToPane(Container pane) {
final
JPanel contentPanel =
new
JPanel();
JPanel controlPanel =
new
JPanel();
final
CardLayout cardLayout=
new
CardLayout();;
pane.setLayout(
new
BorderLayout());
pane.add(contentPanel, BorderLayout.
CENTER
);
pane.add(controlPanel, BorderLayout.
PAGE_END
);
controlPanel.setLayout(
new
FlowLayout());
JButton[] b =
new
JButton[10];
for
(
int
i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
b[i] =
new
JButton(
"No."
+ i);
contentPanel.add(b[i]);
}
contentPanel.setLayout(cardLayout);
JButton nextButton =
new
JButton(
"next"
);
nextButton.addActionListener(
new
ActionListener(){
public
void
actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
cardLayout.next(contentPanel);
}});
controlPanel.add(nextButton);
}
|
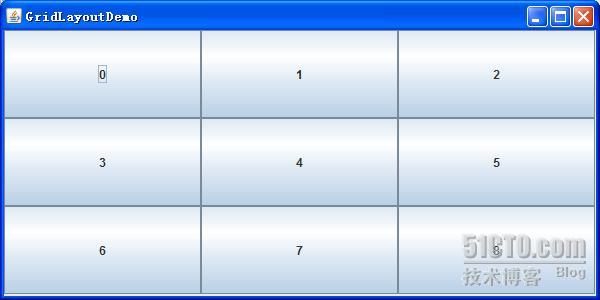
GridLayout
GridLayout
让你建立一个组件表格,并且当组件加入时,会依序又左至右,由上至下填充到每个格子,它不能由你指定想放那个格子就放那个格子
效果:
内容面板代码:
|
public
static
void
addComponentsToPane(Container pane) {
JButton[] buttons =
new
JButton[9];
pane.setLayout(
new
GridLayout(3, 3));
for
(
int
i = 0; i < buttons.
length
; i++) {
buttons[i] =
new
JButton(i +
""
);
pane.add(buttons[i]);
}
}
|
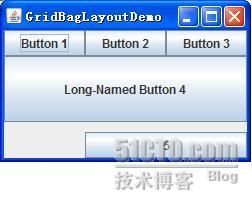
GridBagLayout
GridBagLayout
是所有AWT
布局管理器当中最复杂的,同时他的功能也是最强大的。GridBagLayout
同GridLayout
一样,在容器中以网格形式来管理组件。但GridBagLayout
功能要来得强大得多。
1
、GridBagLayout
管理的所有行和列都可以是大小不同的;
2
、GridLayout
把每个组件限制到一个单元格,而GridBagLayout
并不这样:组件在容器中可以占据任意大小的矩形区域。
GridBagLayout
通常由一个专用类来对他布局行为进行约束,该类叫GridBagConstraints
。其中有11
个公有成员变量,
GridBagConstraints
可以从这
11
个方面来进行控制和操纵。这些内容是:
1
、
gridx—
组件的横向坐标;
2
、
girdy—
组件的纵向坐标;
3
、
gridwidth—
组件的横向宽度,也就是指组件占用的列数;
4
、
gridheight—
组件的纵向长度,也就是指组件占用的行数;
5
、
weightx—
指行的权重,告诉布局管理器如何分配额外的水平空间;
6
、
weighty—
指列的权重,告诉布局管理器如何分配额外的垂直空间;
7
、
anchor—
当组件小于其显示区域时使用此字段;
8
、
fill—
如果显示区域比组件的区域大的时候,可以用来控制组件的行为。控制组件是垂直填充,还是水平填充,或者两个方向一起填充;
9
、
insets—
指组件与表格空间四周边缘的空白区域的大小;
10
、
ipadx—
组件间的横向间距,组件的宽度就是这个组件的最小宽度加上
ipadx
值;
11
、
ipady—
组件间的纵向间距,组件的高度就是这个组件的最小高度加上
ipady
值。
说明:
1
、
gridx
,
gridy
:其实就是组件行列的设置,注意都是从
0
开始的,比如
gridx=0
,
gridy=1
时放在
0
行
1
列;
2
、
gridwidth
,
gridheight
:默认值为
1
;
GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER
常量,代表此组件为此行或此列的最后一个组件,会占据所有剩余的空间;
3
、
weightx
,
weighty
:当窗口变大时,设置各组件跟着变大的比例。比如组件
A
的
weightx=0.5
,组件
B
的
weightx=1
,那么窗口
X
轴变大时剩余的空间就会以
1
:
2
的比例分配给组件
A
和
B
;
4
、
anchor
:当组件空间大于组件本身时,要将组件置于何处。
有
CENTER
(默认值)、
NORTH
、
NORTHEAST
、
EAST
、
SOUTHEAST
、
WEST
、
NORTHWEST
选择。
5
、
insets
:设置组件之间彼此的间距。它有四个参数,分别是上,左,下,右,默认为(
0
,
0
,
0
,
0
)。
效果:
内容面板代码:
|
public
static
void
addComponentsToPane(Container pane) {
JButton button;
pane.setLayout(
new
GridBagLayout());
GridBagConstraints c =
new
GridBagConstraints();
button =
new
JButton(
"Button 1"
);
c.
fill
= GridBagConstraints.
HORIZONTAL
;
c.
gridx
= 0;
c.
gridy
= 0;
pane.add(button, c);
button =
new
JButton(
"Button 2"
);
c.
fill
= GridBagConstraints.
HORIZONTAL
;
c.
weightx
= 0.5;
c.
gridx
= 1;
c.
gridy
= 0;
pane.add(button, c);
button =
new
JButton(
"Button 3"
);
c.
fill
= GridBagConstraints.
HORIZONTAL
;
c.
weightx
= 0.5;
c.
gridx
= 2;
c.
gridy
= 0;
pane.add(button, c);
button =
new
JButton(
"Long-Named Button 4"
);
c.
fill
= GridBagConstraints.
HORIZONTAL
;
c.
ipady
= 40;
// make this component tall
c.
weightx
= 0.0;
c.
gridwidth
= 3;
c.
gridx
= 0;
c.
gridy
= 1;
pane.add(button, c);
button =
new
JButton(
"5"
);
c.
fill
= GridBagConstraints.
HORIZONTAL
;
c.
ipady
= 0;
// reset to default
c.
weighty
= 1.0;
// request any extra vertical space
c.
anchor
= GridBagConstraints.
PAGE_END
;
// bottom of space
c.
insets
=
new
Insets(10, 0, 0, 0);
// top padding
c.
gridx
= 1;
// aligned with button 2
c.
gridwidth
= 2;
// 2 columns wide
c.
gridy
= 2;
// third row
pane.add(button, c);
}
|
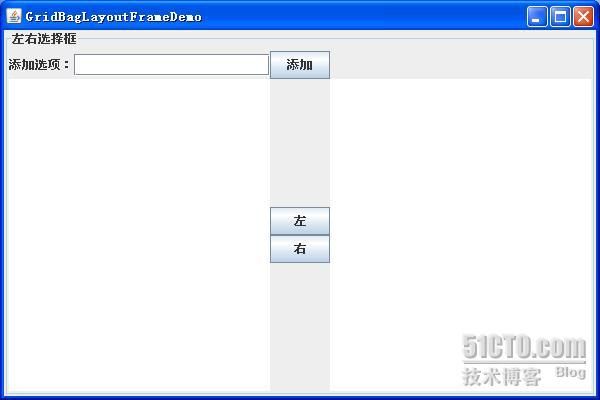
一个
GardBagLayout
布局的左右选择框,代码
GridBagLayoutFrame.java
见附件,效果:
本文出自 “子 孑” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://zhangjunhd.blog.51cto.com/113473/128174