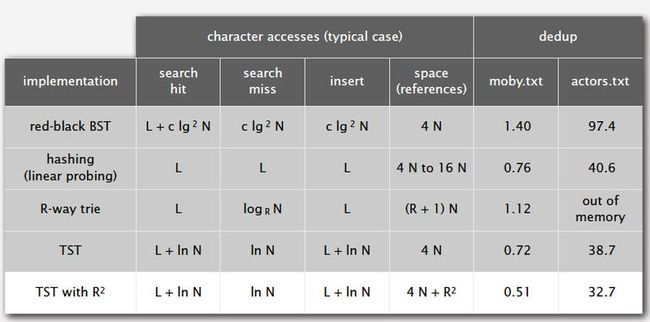
1. String symbol table implementations cost summary (in terms of how many characters are compared)
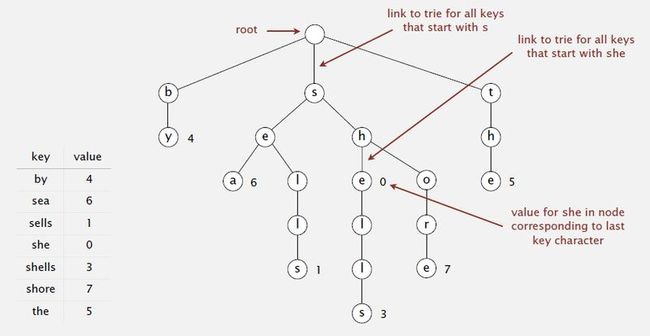
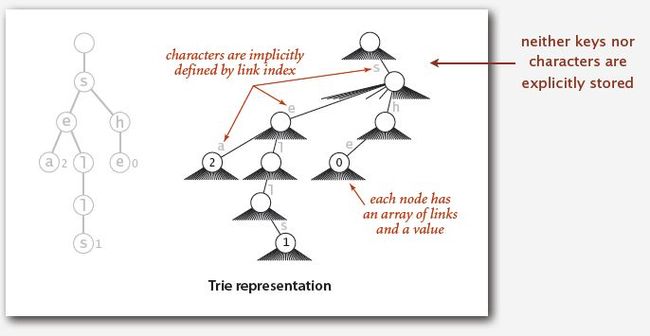
2. Tries [from retrieval, but pronounced "try"]
-- Store characters in nodes (not keys).
-- Each node has R children, one for each possible character.
-- For now, we do not draw null links.
-- Search in a trie: Follow links corresponding to each character in the key.
- Search hit: node where search ends has a non-null value.
- Search miss: reach null link or node where search ends has null value.
-- Insertion into a trie: Follow links corresponding to each character in the key.
- Encounter a null link: create new node.
- Encounter the last character of the key: set value in that node.
-- To delete a key-value pair:
- Find the node corresponding to key and set value to null.
- If node has null value and all null links, remove that node (and recur).
-- Java implementation:
public class TrieST<Value>
{
private static final int R = 256;
private Node root = new Node();
private static class Node
{
private Object value;
private Node[] next = new Node[R];
}
public void put(String key, Value val)
{ root = put(root, key, val, 0); }
private Node put(Node x, String key, Value val, int d)
{
if (x == null) x = new Node();
if (d == key.length()) { x.val = val; return x; }
char c = key.charAt(d);
x.next[c] = put(x.next[c], key, val, d+1);
return x;
}
public boolean contains(String key)
{ return get(key) != null; }
public Value get(String key)
{
Node x = get(root, key, 0);
if (x == null) return null;
return (Value) x.val;
}
private Node get(Node x, String key, int d)
{
if (x == null) return null;
if (d == key.length()) return x;
char c = key.charAt(d);
return get(x.next[c], key, d+1);
}
public void delete(String key) {
delete(root, key, 0);
}
private Value delete(Node x , String key, int d) {
if ( x == null) return null;
if ( d == key.length() ) {
x.val = null;
} else {
char c = key.charAt(d);
x.next[c] = delete(x.next[c] , key, d+1);
}
if ( empty(x) ) x = null;
return x;
}
private boolean empty(Node x) {
if ( x.val != null ) return false;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < x.next.length ; i ++ ) {
if ( x.next[i] != null ) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
-- Performance:
-- Search hit. Need to examine all L characters for equality.
-- Search miss.
- Could have mismatch on first character.
- Typical case: examine only a few characters (sublinear).
-- Space. R null links at each leaf.
(but sublinear space possible if many short strings share common prefixes)
3. Ternary search tries
-- Store characters and values in nodes (not keys).
-- Each node has 3 children: smaller (left), equal (middle), larger (right).
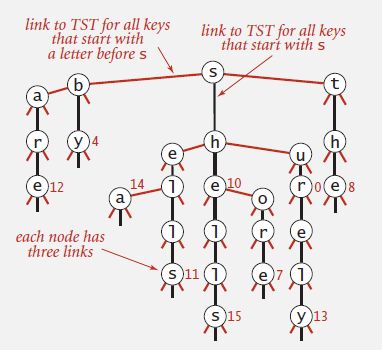
-- Search in a TST: Follow links corresponding to each character in the key.
-- If less, take left link; if greater, take right link.
-- If equal, take the middle link and move to the next key character.
-- Search hit. Node where search ends has a non-null value.
-- Search miss. Reach a null link or node where search ends has null value.
-- Java Implementation:
public class TST<Value>
{
private Node root;
private class Node
{
private Value val;
private char c;
private Node left, mid, right;
}
public void put(String key, Value val)
{ root = put(root, key, val, 0); }
private Node put(Node x, String key, Value val, int d)
{
char c = key.charAt(d);
if (x == null) { x = new Node(); x.c = c; }
if (c < x.c) x.left = put(x.left, key, val, d);
else if (c > x.c) x.right = put(x.right, key, val, d);
else if (d < key.length() - 1) x.mid = put(x.mid, key, val, d+1);
else x.val = val;
return x;
}
public boolean contains(String key)
{ return get(key) != null; }
public Value get(String key)
{
Node x = get(root, key, 0);
if (x == null) return null;
return x.val;
}
private Node get(Node x, String key, int d)
{
if (x == null) return null;
char c = key.charAt(d);
if (c < x.c) return get(x.left, key, d);
else if (c > x.c) return get(x.right, key, d);
else if (d < key.length() - 1) return get(x.mid, key, d+1);
else return x;
}
}
4. TST with R^2 branching at root: Hybrid of R-way trie and TST.
-- Do R^2-way branching at root.
-- Each of R^2 root nodes points to a TST.
5. String symbol table implementation cost summary:
6. TST vs. hashing
-- Hashing:
-- Need to examine entire key.
-- Search hits and misses cost about the same.
-- Performance relies on hash function.
-- Does not support ordered symbol table operations.
-- TSTs:
-- Works only for strings (or digital keys).
-- Only examines just enough key characters.
-- Search miss may involve only a few characters.
-- Supports ordered symbol table operations (plus others!).
-- Bottom line. TSTs are:
-- Faster than hashing (especially for search misses).
-- More flexible than red-black BSTs.
7. Ordered iteration: To iterate through all keys in sorted order:
-- Do inorder traversal of trie; add keys encountered to a queue.
-- Maintain sequence of characters on path from root to node.
public Iterable<String> keys()
{
Queue<String> queue = new Queue<String>();
collect(root, "", queue);
return queue;
}
private void collect(Node x, String prefix, Queue<String> q)
{
if (x == null) return;
if (x.val != null) q.enqueue(prefix);
for (char c = 0; c < R; c++)
collect(x.next[c], prefix + c, q);
}
8. Character-based operations:
-- Prefix match: Find all keys in a symbol table starting with a given prefix.
-- Ex. Keys with prefix sh: she, shells, and shore.
-- application:
- Autocomplete in a cell phone, search bar, text editor, or shell.
- User types characters one at a time.
- System reports all matching strings.
public Iterable<String> keysWithPrefix(String prefix)
{
Queue<String> queue = new Queue<String>();
Node x = get(root, prefix, 0);
collect(x, prefix, queue);
return queue;
}
-- Wildcard match. Keys that match .he: she and the.
-- Longest prefix: Find longest key in symbol table that is a prefix of query string.
-- Ex. Key that is the longest prefix of shellsort: shells.
public String longestPrefixOf(String query)
{
int length = search(root, query, 0, 0);
return query.substring(0, length);
}
private int search(Node x, String query, int d, int length)
{
if (x == null) return length;
if (x.val != null) length = d;
if (d == query.length()) return length;
char c = query.charAt(d);
return search(x.next[c], query, d+1, length);
}
9. String symbol tables summary:
-- Red-black BST.
- Performance guarantee: log N key compares.
- Supports ordered symbol table API.
-- Hash tables.
- Performance guarantee: constant number of probes.
- Requires good hash function for key type.
-- Tries. R-way, TST.
- Performance guarantee: log N characters accessed.
- Supports character-based operations.