4.web
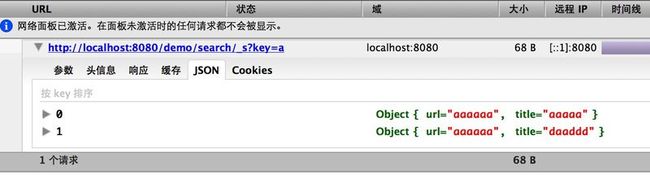
接下来是这次demo的另一个bundle.而且是个拥有spring-mvc能力的web-bundle(WAB).先来看一下结构
首先来看一下web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"
version="2.5">
<display-name>Search Web Module</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>search</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.phantom.web.virgo.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextClass</param-name>
<param-value>org.eclipse.virgo.web.dm.ServerOsgiBundleXmlWebApplicationContext</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>search</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
在这个demo中,我们使用的是Spring-MVC,所以,这里加入Spring-MVC支持.这里用到了一个自定义扩展类org.phantom.web.virgo.servlet.DispatcherServlet。说明一下这个类的作用。在OSGI中,每个bundle都是独立的,它拥有独立的ClassLoad,独立的Spring ApplicationContext.但是我们要通过spring从一个bundle中获取另一个bundle的服务,即我们需要这些applicationContext互相认识.怎么做到呢?virgo对这事做了支持.它提供了一个类org.eclipse.virgo.web.dm.ServerOsgiBundleXmlWebApplicationContext.这个类就相当于一个OSGI全局的applicationContext.我们这里就是要将这个类注入到Spring-MVC的DispatcherServlet中.这里通过扩展默认的DispatcherServlet来达到目的
public class DispatcherServlet extends org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet{
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
String contextClass = config.getInitParameter("contextClass");
if (contextClass != null) {
try {
setContextClass(Class.forName(contextClass));
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new ServletException(String.format("Context class %s not found", contextClass), e);
}
}
super.init(config);
}
} 然后来看一下OSGI描述.
Manifest-Version: 1.0
Bundle-ManifestVersion: 2
Bundle-Name: search web module
Bundle-SymbolicName: org.phantom.demo.web
Bundle-Version: 1.0.0.SNAPSHOT
Import-Template: org.springframework.*;version="[3.0.5,4)"
Import-Package: org.springframework.context.config;version="[3.0.5,4)",
org.springframework.web.servlet.config;version="[3.0.5,4)"
Excluded-Imports: org.phantom.demo.web
Snap-Host: org.phantom.demo.host;version="1.0.0.SNAPSHOT"
Snap-ContextPath: /search
这里要介绍Snap-ContextPath:/search.前文已经介绍过Host-Snap,这一句配置就是配置当前bundle的请求路径,即第二级路径.还有一句Snap-Host:org.org.phantom.demo.host.这句配置将当前snap挂载到了某个host上.于是,根据前文的介绍,当进入到/demo后,SnapHostFilter开始工作,拿到请求的第二级/search,分发到当前bundle.
接下来的配置就是Spring-MVC的配置了.在WEB-INF/创建与DispatcherServlet同名的search-servlet.xml即可
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/utils"
xmlns:osgi="http://www.springframework.org/schema/osgi"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/osgi http://www.springframework.org/schema/osgi/spring-osgi-1.2.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="org.phantom.demo.web" />
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<mvc:resources location="/" mapping="*.html"/>
<mvc:resources location="/resources/" mapping="/resources/**" />
<osgi:reference id="pictureSearch" interface="org.phantom.demo.api.SearchHandler" bean-name="pictureSearch"/>
</beans>
一句句解释一下.第一句,打开包扫描,将Controller加入到Spring管理中
<context:component-scan base-package="org.phantom.demo.web" />
接下来打开mvc的支持.将一些Spring-MVC默认的View、Convertor加入进来。
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
后面两句,是对一些静态资源放行的配置,因为我们servlet的拦截模式是/*,所以,静态资源直接放行
<mvc:resources location="/" mapping="*.html"/>
<mvc:resources location="/resources/" mapping="/resources/**" />
这句就是通过Spring-DM获取一个OSGI服务的配置.这里我们只获取图片搜索的实现,MP3的我们留在后续章节,用来说明OSGI的动态性如何体现.
<osgi:reference id="pictureSearch" interface="org.phantom.demo.api.SearchHandler" bean-name="pictureSearch"/>
同样,我们与普通OSGI进行一下对比.在普通OSGI中,想要或者一个服务如何编写
try {
SearchHandler handler = null;
ServiceReference<SearchHandler>[] srs = (ServiceReference<SearchHandler>[]) bundleContext.getServiceReferences(SearchHandler.class.getName(),"(bean-name='picutreSearch')");
if(srs!=null && srs.length>0)
handler = bundleContext.getService(srs[0]);
} catch (InvalidSyntaxException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
最后来看一下Controller如何编写
package org.phantom.demo.web;
import java.util.List;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.phantom.demo.api.SearchBean;
import org.phantom.demo.api.SearchHandler;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/_s")
public class SearchController {
@Resource
private SearchHandler handler = null;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseEntity<List<? extends SearchBean>> doSearch(String key) {
List<? extends SearchBean> list = handler.doSearch(key);
return new ResponseEntity<List<? extends SearchBean>>(list, HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
在Controller中,将获取到的服务注入进来.
@Resource
private SearchHandler handler = null;
ok,然后编写一个很简单的页面.点击按钮发送请求页面上发送一个get请求到Controller,Controller调用service完成整个流程.
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<script type="text/javascript" src="../resources/jquery-1.6.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function(){
$(":button").click(function(){
$.ajax({
url:'_s',
type:'get',
data:{key:$(":text").val()},
success:function(result){
alert(result);
}
});
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input/><input type="button" value="search"/>
</body>
</html>
所有bundle开发完后,按照依赖关系,依次执行mvn install安装到本地maven仓库.之前已经配置了maven仓库与virgo关联.所以这种开发流程基本是:开发完—install—启动virgo.
然后到${virgo_home}/pickup/新建一个plan,即一次部署计划.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<plan name="com.faben.demo.plan" version="1.0.0.SNAPSHOT" scoped="false" atomic="false"
xmlns="http://www.eclipse.org/virgo/schema/plan"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.eclipse.org/virgo/schema/plan
http://www.eclipse.org/virgo/schema/plan/eclipse-virgo-plan.xsd">
<artifact type="bundle" name="org.phantom.demo.host" version="1.0.0.SNAPSHOT"/>
<artifact type="bundle" name="org.phantom.demo.web" version="1.0.0.SNAPSHOT"/>
<artifact type="bundle" name="org.phantom.demo.search.picture" version="1.0.0.SNAPSHOT"/>
</plan>
部署计划中只需要写实现包和web包,被依赖的包比如api不用写,Virgo会根据MANIFEST.MF中的依赖定义,在maven库中找到api并加载.
做完这些后,启动virgo,访问http://localhost:8080/demo/search/index.html.
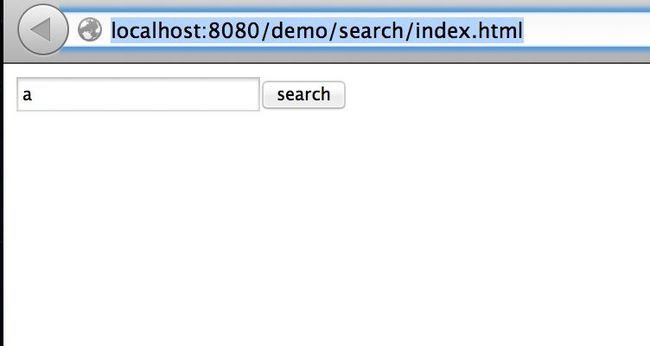
点击按钮,通过firebug查看请求和返回的数据