The Workflow
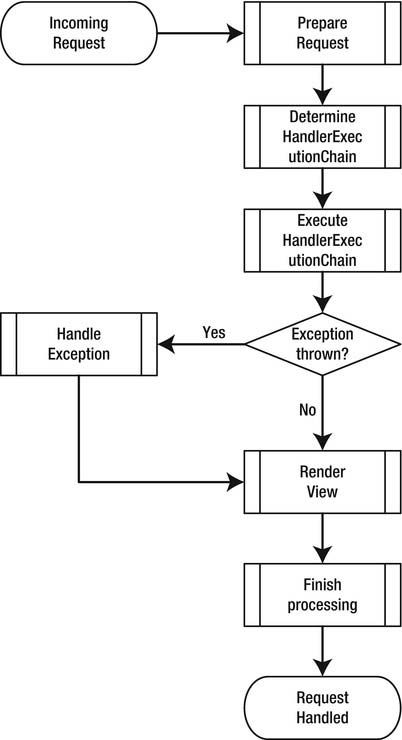
A high-level overview of the request processing workflow
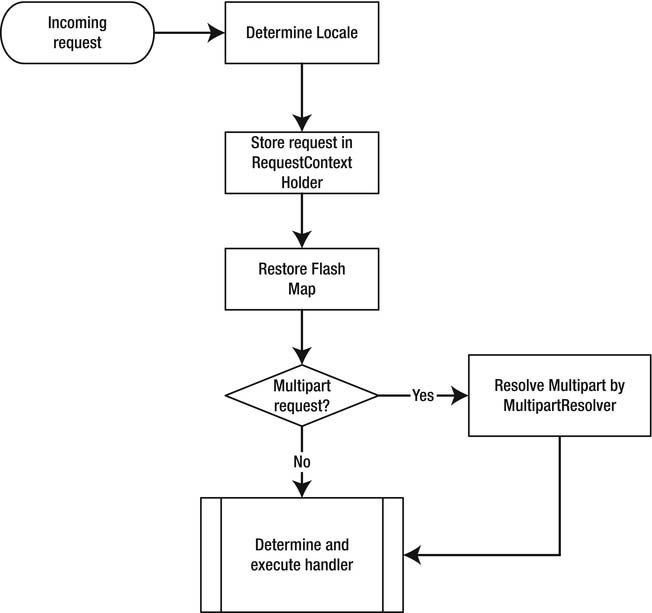
A more complete view of the request processing workflow
Prepare a Request
Before the DispatcherServlet will start dispatching and handling the request, it first does some
preparation and preprocessing of the request. The servlet starts by determining and exposing the
current java.util.Locale for the current request using the org.springframework.web.servlet
.LocaleResolver. Next, it prepares and exposes the current request in org.springframework.web
.context.request.RequestContextHolder. This gives the framework code easy access to the current
request, instead of passing it around.
Next, the servlet will construct a so-called org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMap. It does this
by calling the org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager, which will try to resolve the input
FlashMap. This map contains attributes that were explicitly stored in the previous request. In general, this is used when a redirect is made to go to the next page.
Next, the incoming request is checked for whether it is a multipart HTTP request (this is used when
doing file uploads). If so, the request is wrapped in an org.springframework.web.multipart
.MultipartHttpServletRequest by passing it through an org.springframework.web.multipart
.MultipartResolver. After this, the request is ready to be dispatched to the correct handler.
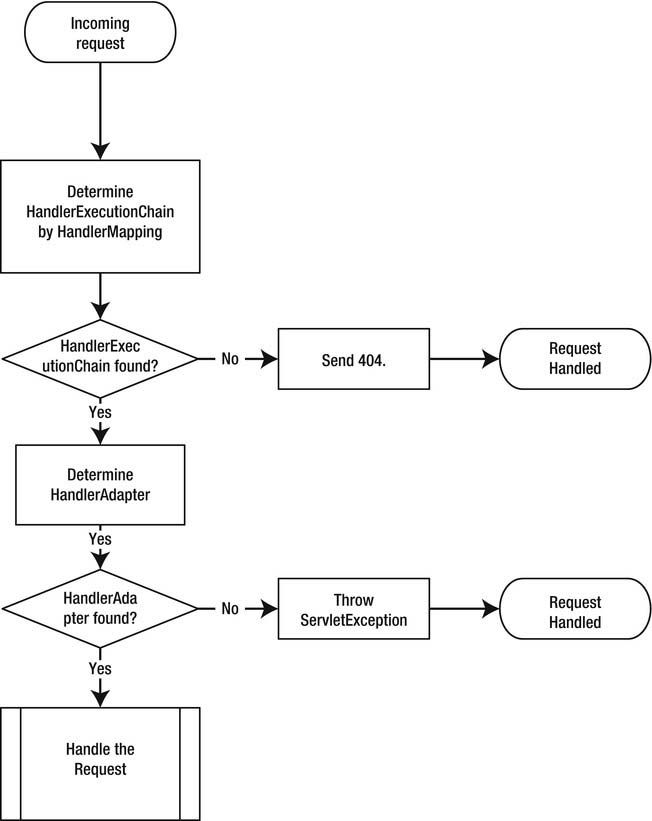
Determine the HandlerExecutionChain
A couple of components are involved in dispatching the request . When a request is ready
for dispatching, the DispatcherServlet will consult one or more org.springframework.web.servlet
.HandlerMapping implementations to determine which handler can handle the request. If no handler is
found, an HTTP 404 response is send back to the client. The HandlerMapping returns an
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExecutionChain (you will learn more about this in the next
section). When the handler has been determined, the servlet will attempt to find an org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter to actually execute the found handler. If no suitable HandlerAdapter can be found, a javax.servlet.ServletException is thrown.
Execute the HandlerExecutionChain
To handle the request, the DispatcherServlet uses the HandlerExecutionChain to determine what to
execute. This class holds a reference to the actual handler that needs to be invoked; however, it also
(optionally) references org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor implementations that are
executed before (preHandle method) and after (postHandle method) the execution of the handler. These interceptors can be used to apply crosscutting functionality. If the code executes successfully, the interceptors are called again; and finally, when needed, the view is rendered.
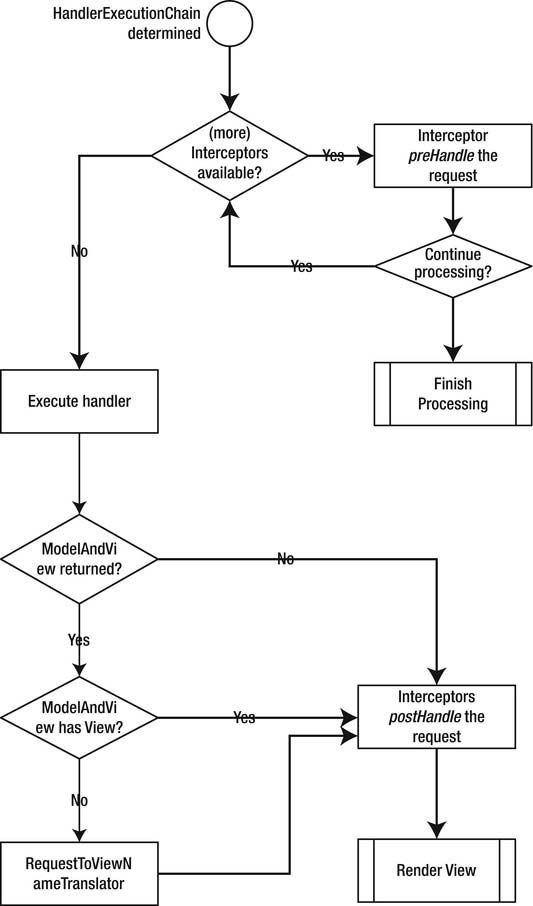
The execution of the handler is delegated to the selected HandlerAdapter that was determined in the
previous step. It knows how to execute the selected handler and how to translate the response into an
org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView. If there is no view in the returned ModelAndView, an
org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator is consulted to generate a view name
based on the incoming request.
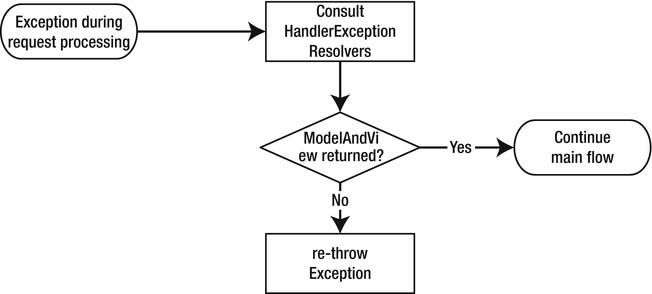
Handle Exceptions
When an exception is thrown during the handling of the request, the DispatcherServlet will consult the
configured org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolvers to handle the thrown
exception. The resolver can translate the exception to a view to show the user. For instance, if there is an exception related to database errors, you could show a page indicating the database is down. If the
exception isn’t resolved, it is rethrown and handled by the servlet container, which generally results in
an HTTP 500 response code (internal server error).
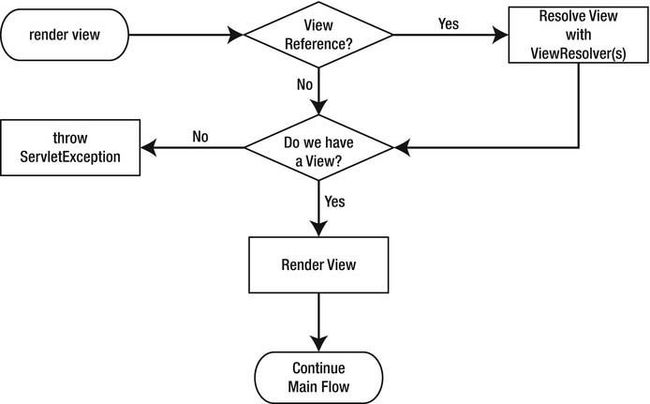
Render a View
If a view has been selected during the request processing workflow, the DispatcherServlet first checks
whether it is a view reference (this is the case if the view is a java.lang.String). If so, the configured
org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolvers are consulted to resolve the view reference to an
actual org.springframework.web.servlet.View implementation. If there is no view and one cannot be
resolved, a javax.servlet.ServletException is thrown.
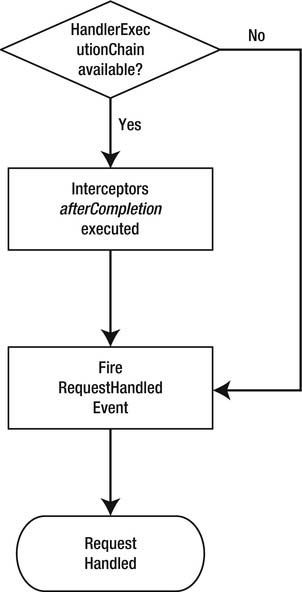
Finish the Processing
Each incoming request passes through this step of the request processing flow, regardless of whether
there are exceptions. If an HandlerExecutionChain is available, then the afterCompletion method of the
interceptors is called. Only the interceptors where the preHandle method was successfully invoked will
have their afterCompletion method called. Next, these interceptors are executed in the reverse order
that their preHandle method was called. This mimics the behavior seen in servlet filters, where the first
filter called is also the last one to be called.
Finally, the DispatcherServlet uses the event mechanism in the Spring Framework to fire an
org.springframework.web.context.support.RequestHandledEvent. You could create and
configure an org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener to receive and log these events.
The Request Processing Summary
The DispatcherServlet is a key component in processing requests with Spring MVC. It is also highly
flexible and configurable. This flexibility comes from the fact that the servlet uses a lot of different
components to fulfill its role, and these components are expressed as interfaces.
The DispatcherServlet Components Used in Request Processing Workflow