第五个设计模式:合成模式
第五个设计模式:合成模式
合成模式 把部分和整体关系用树结构表示,是属于对象的结构模式。
合成模式 要对组合的对象进行管理,所以在一定位置给予对象的相关管理方法,如:add(),remove()等.
合成模式 中对象的管理有两种方案。
1.安全方式:此方式只允许树枝构件有对象的管理方法。
2.透明方式:此方式只允许树枝和树叶都有对象的管理方法,但树叶对象中的管理方法无实际意义。
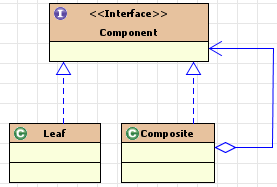
一.UML
示意图
二.组成部分
抽象构件:抽象组合对象的公共行为接口
树叶构件:树叶对象,没有下级子对象
树枝构件:树枝对象,树枝对象可以包含一个或多个其他树枝或树叶对象
三.代码例子:我以一个超市购物为例
(一)、安全方式
1.
抽象物品 (抽象构件)
package
com.eekq.structure.composite.security;
/*
* 抽象构件,物品
* */
public
interface
IRes {
/**
购物买单,示意性的商业方法
*/
public
void
pay();
}
2.
单一物品 (树叶构件)
package
com.eekq.structure.composite.security;
public
class
SingleResImpl
implements
IRes {
/**
物品名称
*/
private
String
name
;
/**
价钱
*/
private
float
money
;
public
SingleResImpl(String name,
float
money) {
this
.
name
= name;
this
.
money
= money;
}
public
void
pay() {
System.
out
.println(
"购买了一件物品["
+getName()+
"],价钱是["
+ getMoney()+
"]元"
);
}
public
float
getMoney() {
//
TODO
自动生成方法存根
return
this
.
money
;
}
public
String getName() {
//
TODO
自动生成方法存根
return
this
.
name
;
}
/**重写equals*/
public
boolean
equals(Object obj){
SingleResImpl res = (SingleResImpl)obj;
return
res.getName().equals(getName()) && res.getMoney()==getMoney();
}
}
3.多个物品 (树枝构件)
package
com.eekq.structure.composite.security;
import
java .util.Iterator;
import
java .util.Vector;
/*
* 对多个物品的管理
* */
public
class
MultiResImpl
implements
IRes {
/**
购物车
*/
private
Vector
car
=
new
Vector();
private
static
float
totle
= 0.0f;
public
void
pay() {
if
(!
car
.isEmpty()){
System.
out
.println(
"名称 价格\n"
);
shopping();
System.
out
.println(
"\n总价:"
+
totle
+
"元"
);
}
else
{
System.
out
.println(
"您好,你没有购买任何物品,不用买单!"
);
}
}
public
void
shopping() {
if
(
car
!=
null
|| !
car
.isEmpty()) {
Iterator it =
car
.iterator();
SingleResImpl res =
null
;
Object temp =
null
;
// 临时对象
while
(it.hasNext()) {
temp = it.next();
if
(temp
instanceof
MultiResImpl) {
((MultiResImpl) temp).shopping();
}
else
{
res = (SingleResImpl) temp;
synchronized
(
this
) {
totle
+= res.getMoney();
}
System.
out
.println(res.getName() +
" "
+ res.getMoney()
+
"元"
);
}
}
}
}
/**
加入新的物品
*/
public
void
addRes(IRes res) {
car
.add(res);
}
/**
放回物品
*/
public
void
removeRes(IRes res) {
car
.remove(res);
}
}
4.收银台买单
package
com.eekq.structure.composite.security;
public
class
Main {
/**
*
@param
args
*/
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
/**
买支雪糕
*/
IRes singleRes =
new
SingleResImpl(
"雪糕"
, 1.5f);
/**
买单
*/
singleRes.pay();
/**
快过年了,我推了个购物车,多买点东西
*/
IRes allRes =
new
MultiResImpl();
/**
在一楼买的食物
*/
IRes one =
new
MultiResImpl();
((MultiResImpl) allRes).addRes(one);
//把一楼的东西装在购物车里
/**
因为是安全方式的组合模式,因此不够透明,只能明确的向下转型,然后再加入购物车了
*/
((MultiResImpl) one).addRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"旺旺"
, 28.5f));
((MultiResImpl) one).addRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"糖果"
, 38.0f));
((MultiResImpl) one).addRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"可乐"
, 8.5f));
/**
二楼去买的衣服和袜子
*/
IRes two =
new
MultiResImpl();
((MultiResImpl) allRes).addRes(two);
// 把二楼的东西装也装在购物车里
((MultiResImpl) two).addRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"衣服"
, 130.5f));
((MultiResImpl) two).addRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"袜子"
, 10f));
/** 二楼再买了个手表,我放在bao里 */
IRes bao =
new
MultiResImpl();
((MultiResImpl) two).addRes(bao);
//把购物小包装在二楼购物车里
((MultiResImpl) bao).addRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"手表"
, 100f));
/**回到一楼,又买了苹果和梨*/
((MultiResImpl) one).addRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"苹果"
, 10.0f));
((MultiResImpl) one).addRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"梨"
, 3.0f));
/**
在买单之前我把可乐退了,因为家里还有的嘛
*/
((MultiResImpl) one).removeRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"可乐"
, 8.5f));
/**
在收银台一次性对购物车所有物品买单
*/
allRes.pay();
}
}
5.运行结果
购买了一件物品[雪糕],价钱是[1.5]元
名称 价格
旺旺 28.5元
糖果 38.0元
苹果 10.0元
梨 3.0元
衣服 130.5元
袜子 10.0元
手表 100.0元
总价:320.0元
(二)、透明方式
透明方式与安全方式的不同点在于抽象构件,透明方式使用的是统一接口。
1.
抽象构件
package
com.eekq.structure.composite.clarity;
/*
* 抽象构件,物品
* */
public
interface
IRes {
/**
购物买单,示意性的商业方法
*/
public
void
pay();
/**
加入新的物品
*/
public
void
addRes(IRes res);
/**
放回物品
*/
public
void
removeRes(IRes res);
}
2.
单一物品 (树叶构件)
package
com.eekq.structure.composite.security;
public
class
SingleResImpl
implements
IRes {
/**
物品名称
*/
private
String
name
;
/**
价钱
*/
private
float
money
;
public
SingleResImpl(String name,
float
money) {
this
.
name
= name;
this
.
money
= money;
}
public
void
pay() {
System.
out
.println(
"购买了一件物品["
+getName()+
"],价钱是["
+ getMoney()+
"]元"
);
}
public
float
getMoney() {
//
TODO
自动生成方法存根
return
this
.
money
;
}
public
String getName() {
//
TODO
自动生成方法存根
return
this
.
name
;
}
/**重写equals*/
public
boolean
equals(Object obj){
SingleResImpl res = (SingleResImpl)obj;
return
res.getName().equals(getName()) && res.getMoney()==getMoney();
}
}
3.多个物品 (树枝构件)
同安全模式代码一样!
4.收银台买单
package
com.eekq.structure.composite.clarity;
public
class
Main {
/**
*
@param
args
*/
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
/**
买支雪糕
*/
IRes singleRes =
new
SingleResImpl(
"雪糕"
, 1.5f);
/**
买单
*/
singleRes.pay();
/**
快过年了,我推了个购物车,多买点东西
*/
IRes allRes =
new
MultiResImpl();
/**
在一楼买的食物
*/
IRes one =
new
MultiResImpl();
allRes.addRes(one);
// 把一楼的东西装在购物车里
/**
因为是透明方式的组合模式,因此直接调用就是了
*/
one.addRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"旺旺"
, 28.5f));
one.addRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"糖果"
, 38.0f));
one.addRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"可乐"
, 8.5f));
/**
二楼去买的衣服和袜子
*/
IRes two =
new
MultiResImpl();
allRes.addRes(two);
// 把二楼的东西装也装在购物车里
two.addRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"衣服"
, 130.5f));
two.addRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"袜子"
, 10f));
/**
二楼再买了个手表,我放在bao里
*/
IRes bao =
new
MultiResImpl();
two.addRes(bao);
// 把购物小包装在二楼购物车里
bao.addRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"手表"
, 100f));
/**
回到一楼,又买了苹果和梨
*/
one.addRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"苹果"
, 10.0f));
one.addRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"梨"
, 3.0f));
/**
在买单之前我把可乐退了,因为家里还有的嘛
*/
one.removeRes(
new
SingleResImpl(
"可乐"
, 8.5f));
/**
在收银台一次性对购物车所有物品买单
*/
allRes.pay();
}
}
5.
运行结果
同安全模式一样的结果!
四.总结
合成模式 是对象的结构模式,以上演示合成模式 。在以后的项目中,如果遇到对象组合的情况,即也符合树结构的。可以考虑下此模式。此模式中讲述了安全方式和透明方式。
安全方式:抽象构件上只提供树叶和树枝公共的方法,没提供树枝独有的管理等方法(add(),remove())。这样的好处是安全,用户不会在树叶上使用add()等管理方法,缺点是不够透明,用户必须知识当前对象为树叶还是树枝(向下转型)。
透明方式:抽象构件 上提供了满足树枝的所有方法(包括add(),remove()),这样做的好处是,用户可以任意执行对象的add()和remove()管理对象。缺点 是如果用户在树叶上执行管理方式(add(),remove())时,在编译期不会有错,但在执行期会报错,这样不容易被发觉错误出在哪.
作者:飞行鱼 QQ:6868861 推荐J2EE群:7715552