基于Spring可扩展Schema提供自定义配置支持(spring配置文件中 配置标签支持)
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/jifeng/archive/2011/09/14/2176599.html
在很多情况下,我们需要为系统提供可配置化支持,简单的做法可以直接基于Spring的标准Bean来配置,但配置较为复杂或者需要更多丰富控制的时候,会显得非常笨拙。一般的做法会用原生态的方式去解析定义好的xml文件,然后转化为配置对象,这种方式当然可以解决所有问题,但实现起来比较繁琐,特别是是在配置非常复杂的时候,解析工作是一个不得不考虑的负担。Spring提供了可扩展Schema的支持,这是一个不错的折中方案,完成一个自定义配置一般需要以下步骤:
设计配置属性和JavaBean
编写XSD文件
编写NamespaceHandler和BeanDefinitionParser完成解析工作
编写spring.handlers和spring.schemas串联起所有部件
在Bean文件中应用
下面结合一个小例子来实战以上过程
1)设计配置属性和JavaBean
首先当然得设计好配置项,并通过JavaBean来建模,本例中需要配置People实体,配置属性name和age(id是默认需要的)
private String id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
2)编写XSD文件
为上一步设计好的配置项编写XSD文件,XSD是schema的定义文件,配置的输入和解析输出都是以XSD为契约,本例中XSD如下:
< xsd:schema
xmlns ="http://blog.csdn.net/cutesource/schema/people"
xmlns:xsd ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:beans ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
targetNamespace ="http://blog.csdn.net/cutesource/schema/people"
elementFormDefault ="qualified"
attributeFormDefault ="unqualified" >
< xsd:import namespace ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" />
< xsd:element name ="people" >
< xsd:complexType >
< xsd:complexContent >
< xsd:extension base ="beans:identifiedType" >
< xsd:attribute name ="name" type ="xsd:string" />
< xsd:attribute name ="age" type ="xsd:int" />
</ xsd:extension >
</ xsd:complexContent >
</ xsd:complexType >
</ xsd:element >
</ xsd:schema >
关于xsd:schema的各个属性具体含义就不作过多解释,可以参见http://www.w3school.com.cn/schema/schema_schema.asp
<xsd:element name="people">对应着配置项节点的名称,因此在应用中会用people作为节点名来引用这个配置
<xsd:attribute name="name" type="xsd:string" />和<xsd:attribute name="age" type="xsd:int" />对应着配置项people的两个属性名,因此在应用中可以配置name和age两个属性,分别是string和int类型
完成后需把xsd存放在classpath下,一般都放在META-INF目录下(本例就放在这个目录下)
3)编写NamespaceHandler和BeanDefinitionParser完成解析工作
下面需要完成解析工作,会用到NamespaceHandler和BeanDefinitionParser这两个概念。具体说来NamespaceHandler会根据schema和节点名找到某个BeanDefinitionParser,然后由BeanDefinitionParser完成具体的解析工作。因此需要分别完成NamespaceHandler和BeanDefinitionParser的实现类,Spring提供了默认实现类NamespaceHandlerSupport和AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser,简单的方式就是去继承这两个类。本例就是采取这种方式:
public class MyNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser( " people " , new PeopleBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}
其中registerBeanDefinitionParser("people", new PeopleBeanDefinitionParser());就是用来把节点名和解析类联系起来,在配置中引用people配置项时,就会用PeopleBeanDefinitionParser来解析配置。PeopleBeanDefinitionParser就是本例中的解析类:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
public class PeopleBeanDefinitionParser extends AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser {
protected Class getBeanClass(Element element) {
return People. class ;
}
protected void doParse(Element element, BeanDefinitionBuilder bean) {
String name = element.getAttribute( " name " );
String age = element.getAttribute( " age " );
String id = element.getAttribute( " id " );
if (StringUtils.hasText(id)) {
bean.addPropertyValue( " id " , id);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(name)) {
bean.addPropertyValue( " name " , name);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(age)) {
bean.addPropertyValue( " age " , Integer.valueOf(age));
}
}
}
其中element.getAttribute就是用配置中取得属性值,bean.addPropertyValue就是把属性值放到bean中。
4)编写spring.handlers和spring.schemas串联起所有部件
上面几个步骤走下来会发现开发好的handler与xsd还没法让应用感知到,就这样放上去是没法把前面做的工作纳入体系中的,spring提供了spring.handlers和spring.schemas这两个配置文件来完成这项工作,这两个文件需要我们自己编写并放入META-INF文件夹中,这两个文件的地址必须是META-INF/spring.handlers和META-INF/spring.schemas,spring会默认去载入它们,本例中spring.handlers如下所示:
以上表示当使用到名为"http://blog.csdn.net/cutesource/schema/people"的schema引用时,会通过study.schemaExt.MyNamespaceHandler来完成解析
spring.schemas如下所示:
以上就是载入xsd文件
5)在Bean文件中应用
到此为止一个简单的自定义配置以完成,可以在具体应用中使用了。使用方法很简单,和配置一个普通的spring bean类似,只不过需要基于我们自定义schema,本例中引用方式如下所示:
xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:cutesource ="http://blog.csdn.net/cutesource/schema/people"
xsi:schemaLocation ="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://blog.csdn.net/cutesource/schema/people http://blog.csdn.net/cutesource/schema/people.xsd" >
< cutesource:people id ="cutesource" name ="test1" age ="27" />
</ beans >
其中xmlns:cutesource="http://blog.csdn.net/cutesource/schema/people"是用来指定自定义schema,xsi:schemaLocation用来指定xsd文件。<cutesource:people id="cutesource" name="zhijun.yuanzj" age="27"/>是一个具体的自定义配置使用实例。
最后就可以在具体程序中使用基本的bean载入方式来载入我们的自定义配置对象了,如:
People p = (People)ctx.getBean( " cutesource " );
System.out.println(p.getId());
System.out.println(p.getName());
System.out.println(p.getAge());
会输出:
cutesource
test1
27
以上就是一个基于Spring可扩展Schema提供自定义配置支持实战过程,一些复杂应用和技巧还有待挖掘
原文地址:http://yjhexy.iteye.com/blog/828737
spring 可以基于schema 扩展,自定义 schema。参考文档自己搭了个应用试验了一下:
首先看下自己写的 myns.xsd
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <xsd:schema xmlns="http://www.yjhexy.com/schema/myns"
- xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- targetNamespace="http://www.yjhexy.com/schema/myns" elementFormDefault="qualified"
- attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
- <xsd:import namespace="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" />
- <xsd:element name="dateformat">
- <xsd:complexType>
- <xsd:complexContent>
- <xsd:extension base="beans:identifiedType">
- <xsd:attribute name="lenient" type="xsd:boolean" />
- <xsd:attribute name="pattern" type="xsd:string" use="required" />
- </xsd:extension>
- </xsd:complexContent>
- </xsd:complexType>
- </xsd:element>
- </xsd:schema>
然后看下我的applicationContxt.xml配置:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xmlns:myns="http://www.yjhexy.com/schema/myns"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
- http://www.yjhexy.com/schema/myns http://www.yjhexy.com/schema/myns/myns.xsd
- ">
- <myns:dateformat id="dateFormat" pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm"
- lenient="true" />
- </beans>
很明显实现了个自定义的bean ,这个bean有两个属性,一个是时间的格式,另外一个不知道啥东西。
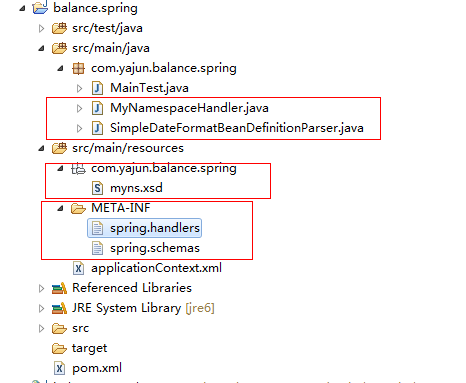
然后在META-INF下面写了两个文件,
spring.handlers:用来描述如何处理自定义的namespace
- http\://www.yjhexy.com/schema/myns=com.yajun.balance.spring.MyNamespaceHandler
spring.schemas:描述schema的位置
- http\://www.yjhexy.com/schema/myns/myns.xsd=com/yajun/balance/spring/myns.xsd
然后是需要两个类,一个处理namespace,一个处理beanDefinition
- package com.yajun.balance.spring;
- import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.NamespaceHandlerSupport;
- public class MyNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
- public void init() {
- registerBeanDefinitionParser("dateformat", new SimpleDateFormatBeanDefinitionParser());
- }
- }
- package com.yajun.balance.spring;
- import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
- import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
- import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser;
- import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
- import org.w3c.dom.Element;
- public class SimpleDateFormatBeanDefinitionParser extends AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser {
- protected Class getBeanClass(Element element) {
- return SimpleDateFormat.class;
- }
- protected void doParse(Element element, BeanDefinitionBuilder bean) {
- // this will never be null since the schema explicitly requires that a value be supplied
- String pattern = element.getAttribute("pattern");
- bean.addConstructorArgValue(pattern);
- // this however is an optional property
- String lenient = element.getAttribute("lenient");
- if (StringUtils.hasText(lenient)) {
- bean.addPropertyValue("lenient", Boolean.valueOf(lenient));
- }
- }
- }
最后main输出试试:
- package com.yajun.balance.spring;
- import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
- import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
- import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
- public class MainTest {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
- SimpleDateFormat f = (SimpleDateFormat) ctx.getBean("dateFormat");
- System.out.println(f);
- }
- }
===========================
xsd 基础 常用的简单 类型
- xs:string
- xs:decimal
- xs:integer
- xs:boolean
- xs:date
- xs:time
- xs:positiveInteger