MVVC模式并不是ExtJS首先提出的,其实ExtJS也是模仿微软的WPF中应用的MVVC设计模式。ExtJS在4.0时引入了MVC模式,在5.0时代又引入了MVVC模式。MVC模式对于大家来说应该不陌生了,MVVC是什么?要理解MVVC还是必须先了解MVC是什么?先来张MVC的结构图感受下:
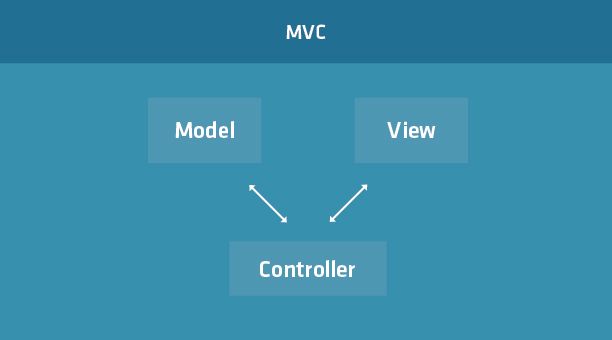
MVC是一种用来更好组织架构软件的设计模式,它把应用程序划分为3部分,各部分各司其责。
Model:是用来表示应用程序中需要用到的数据,当然Model层中也可以包含业务逻辑和数据验证规则,以及其他各种功能接口。
View:是用来展示数据给最终用户的视图,不同的视图可能会以不同的方式展示相同的数据给用户,比如 图表和表格都可以用来展示数据。
Controller:它是应用程序的控制中心,它监听着应用程序中的各种事件,代理处理Model和View之间的各种命令。比如Model中数据改变了,需要通过Controller来改变View。
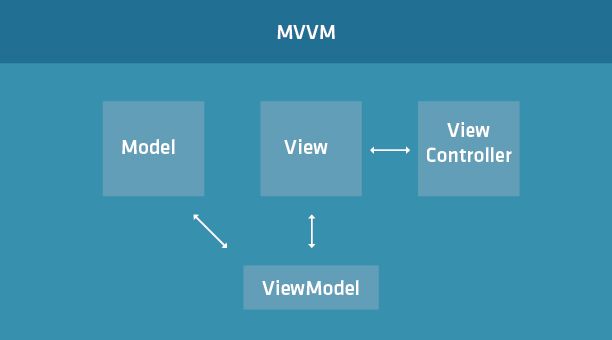
那什么是MVVC呢?MVVC其实是基于MVC设计模式的一种延伸,它与MVC最关键的不同点在于它引入了ViewModel概念,ViewModel提供了Model和View之间的数据绑定,至于数据(Model)更新到视图(View)则是通过ViewController来完成。来张图感受下
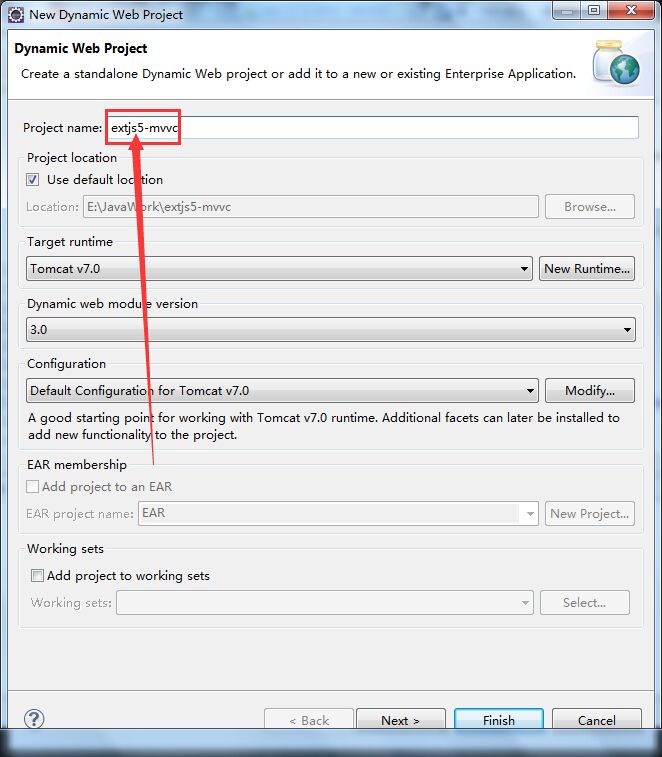
打开Eclipse,新建一个Web project,准备采用最新的MVVC设计模式来编写一个ExtJS5的Grid和Form的数据双向绑定的demo

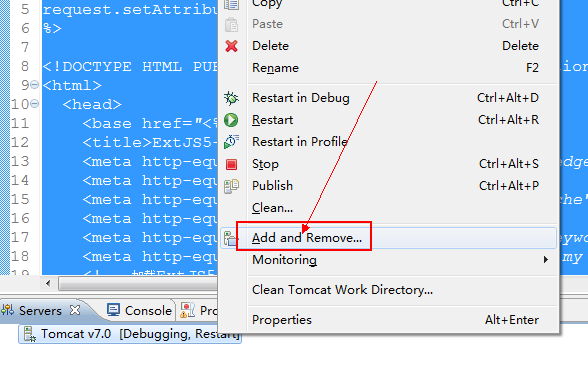
如图导入ExtJS5
如果主题皮肤文件不知道怎么导入的话,请查看我的第一篇博文《ExtJS5学习之Hello World篇》
开发环境搭好了,开始编写测试代码

请如图搭好项目结构
首先需要定义一个Application类,当然也可以不用定义,直接Ext.application({name: "appName"});这样写其实就是让ExtJS默认帮我们new一个Application实例,这里说的定义一个Application类其实就是继承ExtJS的Ext.app.Application类,进行一些我们自定义配置来覆盖默认配置,默认配置其实也是可以在Ext.application()创建application实例的运行时去覆盖的,但为了迎合面向对象的开发思想,还是定义一个Application类装装逼吧,显得高大上点。
Application.js
Ext.define('MyApp.Application', {
extend: 'Ext.app.Application',
autoCreateViewport: true,
enableQuickTips: true,
launch: function () {
}
});
Ext.define()定义一个类,类似于Java里的public class XXXX,
extend:继承,你懂的
autoCreateViewport即自动帮我们创建ViewPort画布,autoCreateViewport的详细用法,我第一篇博客有详细说明,这里就不累赘了。
enableQuickTips: true 表示启用气泡提示,比如表单验证时,在文本框旁边用气泡方式显示提示信息。
在ExtJS3.x时代,只能这样写Ext.QuickTips.init();来启用,当然ExtJS5.x还是两种写法都兼容的,怎么写看各自喜好,建议采用新的写法,以免在API升级过程中旧的用法会被抛弃。
autoCreateViewport自动创建Viewport,所以我们得定义一个Viewport,
app/view/Viewport.js
/*********************全局视图容器类************************/
Ext.define("MyApp.view.Viewport",{
extend:'Ext.container.Viewport',
requires:['Ext.container.Viewport','MyApp.view.MainPanel'],
alias : 'widget.baseviewport',
alternateClassName: ["MyApp.Viewport"],
layout: 'fit',
loadMask:{msg : '正在加载,请稍候...'},
items: [
{
xtype: 'mainpanel'
}
]
});
viewport容器里就放了一个mainpanel,mainpanel是别名,下面继续定义一个MainPanel类
app/view/MainPanel.js
Ext.define("MyApp.view.MainPanel", {
extend:'Ext.panel.Panel',
alias : 'widget.mainpanel',
alternateClassName: ["MyApp.MainPanel"],
requires: [
"Ext.layout.container.Fit",
"MyApp.controller.PersonController",
"MyApp.viewmodel.PersonViewModel",
"MyApp.view.PersonGridPanel",
"MyApp.view.PersonFormPanel"
],
layout: 'hbox',
border: 0,
defaults: {
flex: 1
},
controller: "personController",
viewModel: {
type: "personViewModel"
},
initComponent: function () {
var me = this;
me.items = [
{
xtype: "personGridPanel"
},
{
xtype: "personFormPanel"
}
];
me.callParent(arguments);
}
});
MainPanel里采用hbox水平布局,即从左到右这样水平摆放,里面放了两个子组件,personGridPanel和personFormPanel,即左边一个Grid表格右边一个FormPanel表单。
requires即导入当前类依赖的其他类,跟Java里的import导包差不多的意思。
controller:这个配置是5.x的MVVC模式里新引入的,其实就是MVC模式里的Controller,只不过这里的Controller的父类不再是Ext.app.Controller,变成了Ext.app.ViewController,
viewModel即当前视图的viewModel实例是什么,viewModel的参数值可以是viewMode的别名字符串,也可以是ViewModel带完整命名空间的类路径的字符串形式,也可以是viewModel的配置实例对象,比如我代码里写的那样,personViewModel是ViewModel类的别名。
app/view/PersonGridPanel.js
Ext.define("MyApp.view.PersonGridPanel",{
extend:'Ext.grid.Panel',
requires:[
"Ext.grid.plugin.CellEditing",
"MyApp.controller.PersonController",
"MyApp.viewmodel.PersonViewModel",
"MyApp.store.PersonStore"
],
alias : 'widget.personGridPanel',
alternateClassName: ["MyApp.personGridPanel"],
uses: [
"Ext.form.field.Text",
"Ext.form.field.Number"
],
plugins: [
{
ptype: "cellediting",
clickToEdit: 2,
pluginId: "cellediting"
}
],
publishes: ["currentPerson"],
bind : {
currentPerson: "{currentPerson}",
store: "{personStore}",
title: "<strong>{currentPerson.personName}</strong>"
},
config: {
currentPerson: null
},
controller: "personController",
viewModel: {
type: "personViewModel"
},
listeners: {
scope: "this",
select: "onPersonSelect"
},
/**表格标题行**/
header: {
title: "Person Grid",
padding: "4 9 5 9",
items: [
{
text: "添加",
xtype: "button",
itemId: "add",
handler: "onGridButtonClick"
},
{
text: "撤消",
xtype: "button",
itemId: "reject",
handler: "onGridButtonClick",
tooltip: "撤消重填",
disabled: true,
margin: "0 0 0 15",
bind: {
disabled: "{!storeDirty}"
}
},
{
text: "提交",
xtype: "button",
itemId: "commit",
handler: "onGridButtonClick",
tooltip: "提交",
disabled: true,
margin: "0 0 0 15",
bind: {
disabled: "{!storeDirty}"
}
}
]
},
/**表格列头*/
columns:[
{
text: "姓名",
width: "50%",
dataIndex: "personName",
editor: {
xtype: "textfield",
bind: "{currentPerson.personName}"
}
},
{
text: "年龄",
width: 340,
dataIndex: "age",
editor: {
xtype: "textfield",
bind: "{currentPerson.age}"
}
}
],
onPersonSelect: function(grid,person) {
this.setCurrentPerson(person);
var formPanel = Ext.ComponentQuery.query('personFormPanel')[0];
formPanel.setCurrentPerson(person);
},
updateCurrentPerson: function(current,previous) {
var sm = this.getSelectionModel();
if(current) {
sm.select(current);
}
if(previous) {
sm.deselect(previous);
}
},
});
personGridPanel里代码关键点就几处,我一一说明
bind:即数据绑定,把Model数据绑以key-value形式暴露出去,view视图里可以采用{key}
这种表达式来引用Model里的数据。
config:就是把在这里定义的属性自动生成get/set函数,也就是说如果你类里面需要生成get/set函数的属性可以放到config里定义,extjs会自动帮你生成get/set,这个特性在ExtJS4.x时代就有了。
controller:即当前视图的controller是谁,同理这里可以配置成controller类的别名也可以是controller类包含完整命令空间的类路径字符串。不过要记住的是,在MVVC模式里,controller都指的是Ext.app.ViewController,不再是Ext.app.Controller.
ViewModel:即MVVC中的第二个V,ExtJS5.x里的数据双向绑定就是依赖ViewModel,
app/viewmodel/PersonViewModel.js
Ext.define("MyApp.viewmodel.PersonViewModel", {
extend : "Ext.app.ViewModel",
alias: "viewmodel.personViewModel",
requires:[
"MyApp.store.PersonStore",
"MyApp.model.PersonModel"
],
data: {
currentPerson: null
},
formulas: {
dirty: {
bind: {
bindTo: "{currentPerson}",
deep: true
},
get: function(data) {
console.log(data);
return data ? data.dirty : false;
}
},
storeDirty: {
bind: {
bindTo: "{currentPerson}",
deep: true
},
get: function() {
return this.getStore("personStore").isDirty();
}
}
},
stores: {
personStore: {
type: "personStore"
}
}
});
viewModel的关键点就是data,stores,
data即当前时刻Model的数据
stores即定义数据源,可以定义多个数据源,personStore数据源的引用别名,可以通过grid.getStore("store引用名")来获取这里的数据源,后面的type是PersonStore定义的别名,即表示这里的Store是哪个类的实例。如果有多个store你可以这样:
stores: {
aaa: {type: ""xx.xxxx.AA""},
bbb: {type: ""xx.xxxx.BB""}
}
外部通过getStore("aa"),getStore("bb")这样来获取Store对象,后面的xx.xxx.AA是Store类的完整类路径(包含命名空间)
至于formulas是里定义的是一些函数用于绑定按钮禁用状态。
app/view/PersonFormPanel.js
Ext.define("MyApp.view.PersonFormPanel", {
extend: "Ext.form.Panel",
alias: "widget.personFormPanel",
requires: [
"Ext.form.field.Number",
"MyApp.controller.PersonController",
"MyApp.viewmodel.PersonViewModel"
],
controller: "personController",
viewModel: {
type: "personViewModel"
},
publishes: ["currentPerson"],
/**自动生成get/set*/
config: {
currentPerson: null
},
bind : {
currentPerson: "{currentPerson}",
title: "<strong>{currentPerson.personName}</strong>"
},
bodyPadding: 10,
defaultType: "textfield",
defaults: {
anchor: "100%",
selectOnFocus: true
},
header: {
title: "Person Form",
padding: "4 9 5 9",
items: [
{
text: "撤消",
xtype: "button",
itemId: "reject",
handler: "onFormButtonClick",
tooltip: "撤消重填",
disabled: true,
margin: "0 0 0 15",
bind: {
disabled: "{!dirty}"
}
},
{
text: "提交",
xtype: "button",
itemId: "commit",
handler: "onFormButtonClick",
tooltip: "提交",
disabled: true,
margin: "0 0 0 15",
bind: {
disabled: "{!dirty}"
}
}
]
},
items: [
{
name: "id",
hidden: true,
fieldLabel: "",
bind: {
value: "{currentPerson.id}"
}
},
{
fieldLabel: "姓名",
//disabled: true,
bind: {
value: "{currentPerson.personName}",
disabled: "{!currentPerson}"
}
},
{
fieldLabel: "年龄",
//disabled: true,
bind: {
value: "{currentPerson.age}",
disabled: "{!currentPerson}"
}
}
],
height: 310
});
PersonFormPanel和PersonGridPanel代码差不多,唯一就是Grid需要绑定Store数据源。
app/store/PersonStore.js
Ext.define("MyApp.store.PersonStore", {
extend : "Ext.data.Store",
requires: ["MyApp.model.PersonModel"],
model: 'MyApp.model.PersonModel',
alias: "store.personStore",
storeId: "personStore",
pageSize: 10,
proxy: {
type: 'ajax',
url: MyApp.util.AppUtil.basePath + 'person.json',
reader: { rootProperty: 'items', totalProperty: 'total' }
},
reader: {type: 'json'},
sorters: [{
property: 'id',
direction: 'asc'
}],
autoLoad: true,
isDirty: function() {
var dirty = this.getModifiedRecords().length;
dirty = dirty || this.getNewRecords().length;
dirty = dirty || this.getRemovedRecords().length;
return !!dirty;
}
});
Store就没有什么好说的,关键点就是配置Model类和proxy,proxy数据代理那里我为了简便起见,就没有编写访问数据库代码了,而仅仅是访问一个json文件,store需要的数据都以json字符串的形式定义在person.json文件里。Store是依赖于Model的,所以requires里需要引入PersonModel类。
下面贴出person.json里定义的测试数据:
webContent\person.json
{
"total": 12,
"items": [
{
"id": 1,
"personName": "益达1",
"age": 28
},
{
"id": 2,
"personName": "益达2",
"age": 28
},
{
"id": 3,
"personName": "益达3",
"age": 28
},
{
"id": 4,
"personName": "益达4",
"age": 28
},
{
"id": 5,
"personName": "益达5",
"age": 28
},
{
"id": 6,
"personName": "益达6",
"age": 28
},{
"id": 7,
"personName": "益达7",
"age": 28
},
{
"id": 8,
"personName": "益达8",
"age": 28
},
{
"id": 9,
"personName": "益达9",
"age": 28
},
{
"id": 10,
"personName": "益达10",
"age": 28
},
{
"id": 11,
"personName": "益达11",
"age": 28
},
{
"id": 12,
"personName": "益达12",
"age": 28
}
]
}
PersonModel就是一个普通实体类,就好比Java里的一个普通的JavaBean,仅仅是一些类属性声明;
app/model/PersonModel.js
Ext.define("MyApp.model.PersonModel", {
extend : "Ext.data.Model",
fields : [
{name: 'id', type: 'int'},
{name: 'personName', type: 'string'},
{name: 'age', type: 'int'}
]
});
编写app.js来创建ExtJS的Application实例对象来运行我们的应用程序,这个文件存放路径没有什么规范约束,不像MVVC模式那样,controller类必须放controller目录下,Store类必须放store目录下。
webContent\app.js
Ext.Loader.setConfig({
enabled : true
});
Ext.Loader.setPath({
'Ext.ux' : 'extjs/ux',
'MyApp.util' : 'app/util'
});
/**
* 加载ExtJS插件文件
*/
Ext.require(
[
'Ext.ux.PageSizePaging',
'MyApp.util.AppUtil'
]
);
Ext.application({
requires: ['Ext.container.Viewport','MyApp.view.Viewport'],
//项目名称简称
name: 'MyApp',
appFolder: 'app',
autoCreateViewport: true,
launch: function () {
//Ext.create('MyApp.view.Viewport');
}
});
OK,最后新建一个JSP页面,测试一把,就完事儿了。
webContent\index.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
request.setAttribute("basePath", basePath);
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>ExtJS5-MVVC设计模式学习</title>
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!-- 加载ExtJS5 默认的经典蓝主题皮肤样式文件 -->
<link href="${basePath}extjs/theme/ext-theme-classic/ext-theme-classic-all.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"/>
<script type="text/javascript" src="${basePath}extjs/bootstrap.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="${basePath}extjs/ext-locale-zh_CN.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="${basePath}app.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
启动Tomcat,打开浏览器,输入http://localhost:8080/extjs5-mvvc/访问页面,你将会看到如图效果: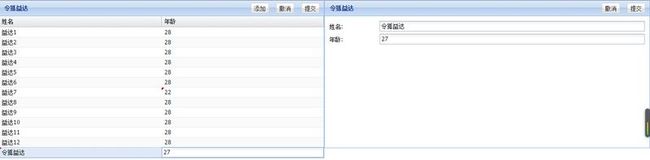
OK,今天就写到这儿,如果有什么问题请加我Q-Q:736031305,
或者加裙:![]() 一起交流学习
一起交流学习