Android RoboGuice 使用指南(2):第一个例子Hello World
首先介绍一下如果将Guice 和RoboGuice 的库添加到项目中。
- 下载RoboGuice和guice-2.0-no_aop.jar(not guice-3.0),或者下载
- 创建一个新Android项目,比如GuiceDemo,目标平台Android1.5以上。
- 一般可以在该项目下添加一个lib目录,将两个jar文件拷到lib目录下,然后通过: Project > Properties > Java Build Path > Libraries > Add External JARs
添加了对应guice 和roboguice库的引用之后,就可以开始编写第一个使用roboguice 的例子。
使用roboguice 的步骤:
1. 创建一个RoboApplication 的子类GuiceApplication,GuiceApplication为Appliacation的子类,因此需要修改AndroidManifest.xml,将Application 的name 指向这个类。可以参见Android简明开发教程九:创建应用程序框架
<application android:name=”GuiceApplication”
android:icon=”@drawable/icon” android:label=”@string/app_name”>
<activity android:name=”.GuiceDemo”
android:label=”@string/app_name”>
<intent-filter>
< action android:name=”android.intent.action.MAIN” />
<category android:name=”android.intent.category.LAUNCHER” />
< /intent-filter>
< /activity>
</application>
2. 在这个简单的例子中,它使用的Layout 定义如下:
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”utf-8″?>
< LinearLayout xmlns:android=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”
android:orientation=”vertical”
android:layout_width=”fill_parent”
android:layout_height=”fill_parent”
>
<TextView
android:id=”@+id/hello”
android:layout_width=”fill_parent”
android:layout_height=”wrap_content”
android:text=”@string/hello”
/>
< /LinearLayout>
我们定义了一个TextView ,它的id为hello.
假定这个应用使用一个IGreetingService ,它有一个方法getGreeting() 返回一个字符串,至于IGreetingService 如何实现,GuideDemo 不需要关心。
Dependency injection 设计模式的一个核心原则为: Separate behavior from dependency resolution. 也就说将应用需要实现的功能和其所依赖的服务或其它对象分离。 对本例来说GuiceDemo只要知道它依赖于IGreetingService 服务,至于IGreetingService有谁实现GuiceDemo并不需要知道。
在Roboguice 中使用@Inject 来表示这种依赖关系。
public class GuiceDemo extends RoboActivity {
@InjectView (R.id.hello) TextView helloLabel;
@Inject IGreetingService greetingServce;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
helloLabel.setText(greetingServce.getGreetings());
}
}
代码中没有创建greetingServce 对象的代码(如 new xxx()) 和为helloLabel 赋值的代码。这些值都可以Roboguice 自动创建和赋值注入(Inject)到变量中。
为了说明问题,我们在代码中添加两个对getGreetings的实现,一个为HelloWorld, 一个为HelloChina:
public class HelloChina implements IGreetingService{
@Override
public String getGreetings() {
return "Hello,China";
}
}
public class HelloWorld implements IGreetingService{
@Override
public String getGreetings() {
return "Hello,World";
}
} 3. 到这里,你可能有些困惑,RoboGuice怎么知道使用那个类(HelloWorld或是HelloChina)为GuiceDemo中的greetingServce 赋值呢?这是通过在Module 中定义binding 来实现的。
在项目中添加一个GreetingModule (从AbstractAndroidModule 派生)重载configure方法:
public class GreetingModule extends AbstractAndroidModule{
@Override
protected void configure() {
bind(IGreetingService.class).to(HelloWorld.class);
//bind(IGreetingService.class).to(HelloChina.class);
}
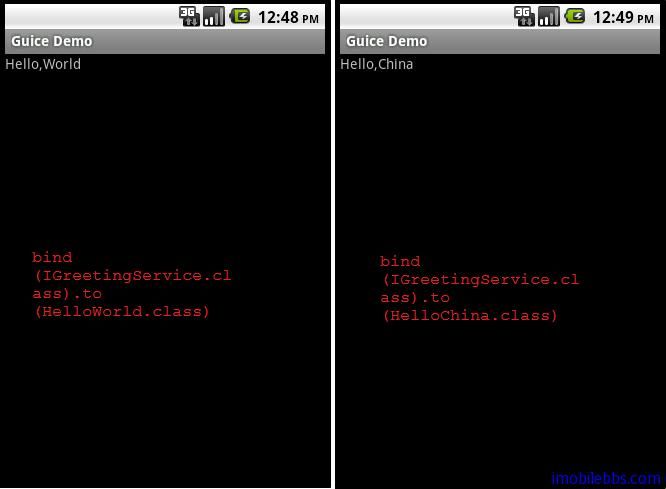
} 将IGreetingService 绑定到HelloWorld 类。
然后在GuiceApplication 的addApplicationModules 添加上述模块:
public class GuiceApplication extends RoboApplication {
protected void addApplicationModules(List<Module> modules) {
modules.add(new GreetingModule());
}
} 可以将GreetingModule 绑定改为HelloChina ,对比一下:
通过改变binding ,GuiceDemo 显示了不同的结果,GuiceDemo不依赖于具体的实现,可以非常方便的改变接口的实现而无需更改GuiceDemo的代码。大大降低了类于类之间的耦合性。
后面将逐个介绍Guice和RoboGuice支持的Binding类型和用法(Guice)以及与android 平台相关的Dependency injection (RoboGuice)