玩转Android---UI篇---ListView之SampleAdapter(列表)---1
ListView是列表组件,这个ListView是我接触的目前所有Android UI控件中最为麻烦的控件,之所以麻烦就是因为它的各种的适配器Adapter特别麻烦,Adapter的组织结构图如下

在ListView中,以内不同的Adapter不同,所以也会有不同的效果,其中比较常用的是SampleAdapter,SimpleCursorAdapter,ArrayAdapter,BaseAdapter等,
万事开头难,还是从最简单的SimpleAdapter说起,以后再一点点学习
simpleAdapter的扩展性最好,可以定义各种各样的布局出来,可以放上ImageView(图片),还可以放上Button(按钮),CheckBox(复选框)等等。下面的代码都直接继承了ListActivity,ListActivity和普通的Activity没有太大的差别,不同就是对显示ListView做了许多优化,方面显示而已。
先看看一个实例,是由SimpleAdapter与ListView绑定后的一个小例子。
ListViewone.java文件
package org.hualang.simpleadapter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import android.app.ListActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class ListViewone extends ListActivity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
private Toast toast;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
ArrayList<HashMap<String,String>> list=new ArrayList<HashMap<String,String>>();
HashMap<String,String> map1=new HashMap<String,String>();
HashMap<String,String> map2=new HashMap<String,String>();
HashMap<String,String> map3=new HashMap<String,String>();
map1.put("name", "凝墨");
map1.put("phone", "13699452790");
map2.put("name", "小棕");
map2.put("phone", "15827980910");
map3.put("name", "花郎");
map3.put("phone", "18678091166");
list.add(map1);
list.add(map2);
list.add(map3);
SimpleAdapter listAdapter=new SimpleAdapter(this,
list,
R.layout.info,
new String[] {"name","phone"},
new int[] {R.id.name,R.id.phone});
setListAdapter(listAdapter);
}
protected void onListItemClick(ListView l,View v,int position,long id)
{
super.onListItemClick(l,v,position,id);
if(l.getItemIdAtPosition(position)==0)
{
toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "我是凝墨", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}else if(l.getItemIdAtPosition(position)==1)
{
toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "我是小棕", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}else if(l.getItemIdAtPosition(position)==2)
{
toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "我是花郎", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
}
main.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/linearlayout"
android:orientation="vertical"
>
<ListView
android:id="@id/android:list"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:drawSelectorOnTop="false"
android:scrollbars="vertical"
/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
info.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:paddingLeft="10dip" android:paddingRight="10dip" android:paddingTop="1dip" android:paddingBottom="1dip" > <TextView android:id="@+id/name" android:layout_width="180dip" android:layout_height="30dip" android:textSize="10pt" android:singleLine="true" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/phone" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:gravity="right" android:textSize="10pt" /> </LinearLayout>
使用simpleAdapter的数据用一般都是HashMap构成的List,list的每一节对应ListView的每一行。HashMap的每个键值数据映射到布局文件中对应id的组件上。因为系统没有对应的布局文件可用,我们可以自己定义一个布局info.xml。下面做适配,new一个SimpleAdapter参数一次是:this,布局文件(info.xml)。布局文件的组件name,phone。布局文件的各组件分别映射到HashMap的各元素上,完成适配。
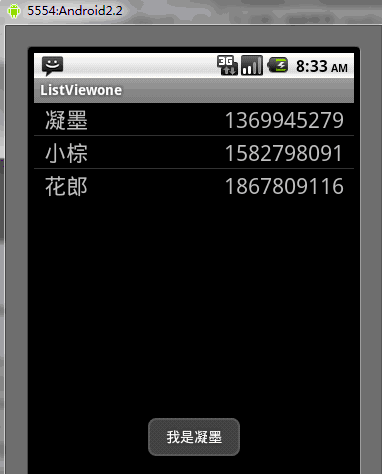
运行结果如下:
当点击了第一行
实例2:显示一个带图片的ListView,使用适配器SampleAdapter
ListViewone.java
package org.hualang.simpleadapter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import android.app.ListActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
public class ListViewone extends ListActivity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
SimpleAdapter adapter = new SimpleAdapter(this,getData(),R.layout.info,
new String[]{"name","phone","img"},
new int[]{R.id.name,R.id.phone,R.id.img});
setListAdapter(adapter);
}
private List<Map<String, Object>> getData() {
List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("name", "凝墨");
map.put("phone", "13699782346");
map.put("img", R.drawable.pic1);
list.add(map);
map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("name", "小棕");
map.put("phone", "15899034671");
map.put("img", R.drawable.pic2);
list.add(map);
map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("name", "花郎");
map.put("phone", "18677656526");
map.put("img", R.drawable.pic3);
list.add(map);
return list;
}
}
info.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <ImageView android:id="@+id/img" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_margin="5px"/> <LinearLayout android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView android:id="@+id/name" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF" android:textSize="22px" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/phone" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textColor="#FFFFFFFF" android:textSize="13px" /> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
这里,就不做事件处理了,运行结果如下: