android TAb分页菜单实现总结
首先说明的是,我们做APP开发,Tab分页不管是顶部还是底部,都是必不可少的,网上也有太多太多的实现方式了,我在这里总结一下:
第一种方式:TabHost原始方式:(链接另一篇文章)
这里实现的是底部菜单:
布局文件:(我们通过RelativeLayout 可以把TabWidget定位在底部)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TabHost xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@android:id/tabhost"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="3dp" >
<FrameLayout
android:id="@android:id/tabcontent"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" >
</FrameLayout>
<TabWidget
android:id="@android:id/tabs"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignBottom="@android:id/tabcontent"
android:background="@drawable/tabbar_bg" />
</RelativeLayout>
</TabHost>
在这里我们将说明一下:之前我是获取到TabWidget的view试图及内部icon和title,然后控制实现其效果,但是我们也可以用另外一种方式,也就是我们调用TabHost.TabSpec 的setIndicator(View view);这个方法,我们可以定制显示的view,
代码片段:
/***
* 创建footerview
*/
public void createFooterView() {
tabHost = getTabHost(); // The activity TabHost
view = new TabView(this, R.drawable.tabbar_icon_home,
R.drawable.tabbar_icon_home_selecotr);
view.setBackgroundDrawable(this.getResources().getDrawable(
R.drawable.footer_view_selector));
intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, HomeActivity.class);
spec = tabHost.newTabSpec("num1").setIndicator(view).setContent(intent);
tabHost.addTab(spec);
view = new TabView(this, R.drawable.tabbar_icon_search,
R.drawable.tabbar_icon_search_selecotr);
view.setBackgroundDrawable(this.getResources().getDrawable(
R.drawable.footer_view_selector));
intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, HomeActivity.class);
spec = tabHost.newTabSpec("num2").setIndicator(view).setContent(intent);
tabHost.addTab(spec);
view = new TabView(this, R.drawable.tabbar_icon_cart,
R.drawable.tabbar_icon_cart_selector);
view.setBackgroundDrawable(this.getResources().getDrawable(
R.drawable.footer_view_selector));
intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, HomeActivity.class);
spec = tabHost.newTabSpec("num3").setIndicator(view).setContent(intent);
tabHost.addTab(spec);
view = new TabView(this, R.drawable.tabbar_icon_more,
R.drawable.tabbar_icon_more_selecotr);
view.setBackgroundDrawable(this.getResources().getDrawable(
R.drawable.footer_view_selector));
intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, HomeActivity.class);
spec = tabHost.newTabSpec("num4").setIndicator(view).setContent(intent);
tabHost.addTab(spec);
}
/***
* 自定义view
*
*/
class TabView extends LinearLayout {
ImageView imageView;
public TabView(Context c, int drawable, int drawableselec) {
super(c);
imageView = new ImageView(c);
// 可以定制点击后状态
StateListDrawable listDrawable = new StateListDrawable();
// 未选
listDrawable.addState(SELECTED_STATE_SET, this.getResources()
.getDrawable(drawableselec));
// 选择
listDrawable.addState(ENABLED_STATE_SET, this.getResources()
.getDrawable(drawable));
imageView.setImageDrawable(listDrawable);// 引用 StateListDrawable
setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
addView(imageView);
}
}
这样我们就实现想要的效果了.( 建议使用这种方法,我的项目就是用的这个实现的.)
如果我是图标和文字分开的,我们也可以用(RadioButton代替,也许大家都不陌生,一会我简单介绍下)
这个源码是因为项目里面用的。有时间整理下上传上去,不过我相信大家看过都会做出来的.
第二种方法:GridView+ActivityGroup (图片 ,文字)
(为了省事,我把上下tab分页整理到一个demo里面了.)
这个的布局文件我就不显示了,因为比较简单,我们还是来看代码吧.
代码片段:
/***
* 适配器
*
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class ImageAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private Context mContext;
private ImageTextButton[] imgItems;
private int selResId;
/***
*
* @param c
* @param picIds
* @param titles
* @param width
* @param height
* @param selResId
*/
public ImageAdapter(Context c, int[] picIds, String titles[], int width,
int height, int selResId) {
mContext = c;
this.selResId = selResId;
imgItems = new ImageTextButton[picIds.length];
for (int i = 0; i < picIds.length; i++) {
imgItems[i] = new ImageTextButton(mContext);
imgItems[i]
.setLayoutParams(new GridView.LayoutParams(width, height));// 设置ImageView宽高
imgItems[i].setPadding(2, 2, 2, 2);
// 显示图片与文本
imgItems[i].setImageResource(picIds[i], titles[i]);
}
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return imgItems.length;
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return position;
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
/***
* 设置选中后的效果
*/
public void SetFocus(int index) {
for (int i = 0; i < imgItems.length; i++) {
// 先把所有设为最初状态
if (i != index) {
imgItems[i].setBackgroundResource(0);// 回到最初样式
}
}
// 选中设置
imgItems[index].setBackgroundResource(selResId);
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
ImageTextButton imageView;
if (convertView == null) {
imageView = imgItems[position];
} else {
imageView = (ImageTextButton) convertView;
}
return imageView;
}
}
在这里我们用到了自定义控件,其实就是把imageview 和textview 整到一起了,
/***
* 自定义控件(图片文字)
*/
public class ImageTextButton extends LinearLayout {
private ImageView button = null;
private TextView text = null;
private Context context;
public ImageTextButton(Context context) {
this(context, null);
this.context = context;
}
public ImageTextButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.imagetextbutton, this,
true);
button = (ImageView) this.findViewById(R.id.button);
text = (TextView) this.findViewById(R.id.btnText);
text.setSingleLine(true);
}
public void setImageResource(int image_id, String title) {
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(context.getResources(),
image_id);
button.setBackgroundDrawable(new BitmapDrawable(bitmap));
text.setText(title);
}
public void setImageBitmap(Bitmap bitmap) {
if (button != null)
button.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
}
public void setBackgroundDrawable(Drawable drawable, int Width, int Hdight) {
if (button != null) {
button.setBackgroundDrawable(drawable);
button.setMinimumHeight(Hdight);
button.setMinimumWidth(Width);
}
}
public void setText(String title) {
if (text != null)
text.setText(title);
}
public void setText(int ResID) {
if (text != null)
text.setText(ResID);
}
public void setWidth(int width) {
button.setMaxWidth(width);
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
button.setMaxHeight(height);
}
}我们只需要在oncreate中调用即可:
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Navigation_Top_Bar = (GridView) this
.findViewById(R.id.Navigation_Top_Bar);
Navigation_Buttom_Bar = (GridView) this
.findViewById(R.id.Navigation_Buttom_Bar);
// 获取显示宽度
int width = this.getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getWidth()
/ topbar_image_array.length;
topImgAdapter1 = new ImageAdapter(this, topbar_image_array, titles,
width, 100, R.drawable.cover);
Init(Navigation_Top_Bar, topImgAdapter1);
ButtomImgAdapter2 = new ImageAdapter(this, topbar_image_array, titles,
width, 100, R.drawable.cover);
Init(Navigation_Buttom_Bar, ButtomImgAdapter2);
}
这个实现起来有点复杂,不过用习惯了会觉得别有一翻风味的.我之前就一直用这个方法.在这里我要说明一点:
imgItems[i].setLayoutParams(new GridView.LayoutParams(width, height));// 设置ImageView宽高
其他的都是细节上的问题,我想你们看过都会ok的.
效果图:

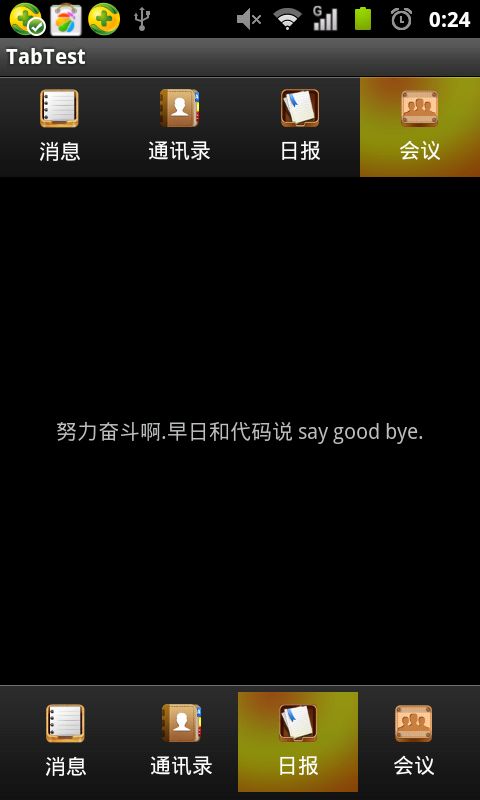
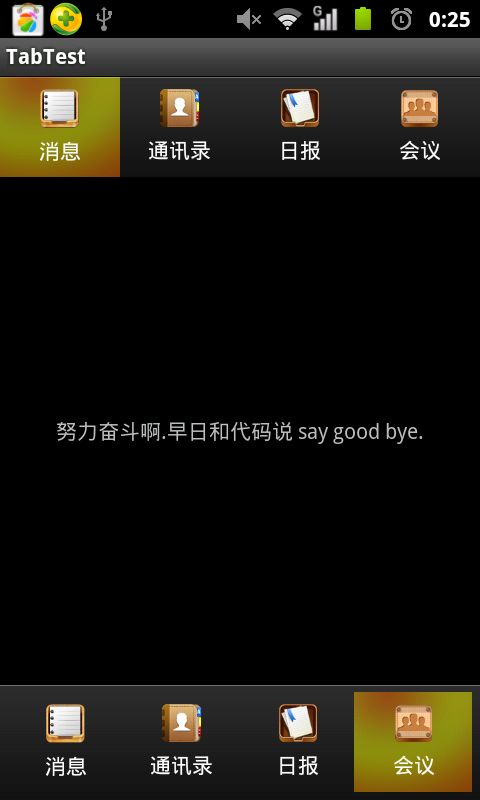
(怎么样,效果还不错吧。就是实现起来有点负责,不过习惯就好.)
第三种方法:ActivityGroup+一些TextView布局.(在这里我们自定实现动态滚动效果)
详情请查看前面一片文章:android 分页Title栏滑块效果--ActionBar(模拟网易 腾讯等动态效果)
分页Tab的实现方法和上面方法类是,都是运用ActivityGroup的性质,而上面是通过GridView生成,而我们这边是我们自定义View控件实现.
这里我主要说一下怎样实现ActionBar:
代码片段:
/***
* 自定义控件
*
* @author zhangjia
*
* 在这里我要说明一点 我们在创建RectF矩形的时候,
*
* 参照物原点是所在"父控件的左上角".
*
*/
public class ActionBar extends LinearLayout implements OnClickListener {
private ImageView tv1;
private ImageView tv2;
private ImageView tv3;
private ImageView tv4;
private Paint paint;// 画笔
private RectF curRectF;// draw当前bar
private RectF tarRectF;// draw被点击bar
private final int space_x = 0;// 相当于pading.
private final int space_y = 0;// 相当于pading
private final double step = 32;// 速度step.
public ActionBar(Context context) {
super(context);
}
/***
* 构造方法
*
* @param context
* @param attrs
*/
public ActionBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
setWillNotDraw(false);
LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.action_bar, this, true);
paint = new Paint();
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
tv1 = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.tv1);
tv2 = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.tv2);
tv3 = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.tv3);
tv4 = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.tv4);
tv1.setOnClickListener(this);
tv2.setOnClickListener(this);
tv3.setOnClickListener(this);
tv4.setOnClickListener(this);
curRectF = null;
tarRectF = null;
}
/***
* invalidate():调用这个方法会执行onDraw()方法,但是前提是:自己把invalidate()方法执行结束在进行执行.
*/
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
canvas.drawColor(Color.BLACK);
paint.setColor(Color.RED);
// 如果当前curRectF=null,也就是第一次访问,则默认为draw第一个bar
if (curRectF == null)
curRectF = new RectF(tv1.getLeft() + space_x, tv1.getTop()
+ space_y, tv1.getRight() - space_x, tv1.getBottom()
- space_y);
// 第一次方位tarRectF=null,默认为draw
if (tarRectF == null)
tarRectF = new RectF(tv1.getLeft() + space_x, tv1.getTop()
+ space_y, tv1.getRight() - space_x, tv1.getBottom()
- space_y);
/***
* 作用:如果在这个范围内则,以这个为最终位置,(不明的白的话,你可以把这个注释运行下你就知道why了.)
*/
if (Math.abs(curRectF.left - tarRectF.left) < step) {
curRectF.left = tarRectF.left;
curRectF.right = tarRectF.right;
}
/***
* 说明目标在当前的左侧,需要向左移动(每次矩形移动step,则进行invalidate(),从新进行移动...)
*/
if (curRectF.left > tarRectF.left) {
curRectF.left -= step;
curRectF.right -= step;
invalidate();// 继续刷新,从而实现滑动效果,每次step32.
}
/***
* 说明目标在当前的右侧,需要向右移动(每次矩形移动step,则进行invalidate(),从新进行移动...)
*/
else if (curRectF.left < tarRectF.left) {
curRectF.left += step;
curRectF.right += step;
invalidate();
}
// canvas.drawRect(curRectF, paint);
// 参数,矩形,弧度,画笔
canvas.drawRoundRect(curRectF, 5, 5, paint);
}
/****
* 这里要记录目标矩形的坐标
*/
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
tarRectF.left = v.getLeft() + space_x;
tarRectF.right = v.getRight() - space_x;
invalidate();// 刷新
System.out.println("tarRectF.top=" + tarRectF.top + ",v.getTop()="
+ v.getTop() + ", v.getBottom()" + v.getBottom());
}
}上面已经讲的很详细了,就不啰嗦了.
效果图:


大致就这么多了。
额外:还有一点就是有的会用到RadioButton这个控件,其实就是对其进行了一些调整,这里我简单说明一下应用:
可以取消button样式,用android:drawableTop显示图片,从而达到想要的效果.
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<RadioGroup
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
android:background="@drawable/maintab_toolbar_bg"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@drawable/home_btn_bg"
android:button="@null"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/icon_1_n"
android:gravity="center"
android:paddingTop="5dp"
android:text="首页"
android:textSize="12sp" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@drawable/home_btn_bg"
android:button="@null"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/icon_2_n"
android:gravity="center"
android:paddingTop="5dp"
android:text="短信"
android:textSize="12sp" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@drawable/home_btn_bg"
android:button="@null"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/icon_3_n"
android:gravity="center"
android:paddingTop="5dp"
android:text="联系人"
android:textSize="12sp" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@drawable/home_btn_bg"
android:button="@null"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/icon_4_n"
android:gravity="center"
android:paddingTop="5dp"
android:text="搜索"
android:textSize="12sp" />
</RadioGroup>
</RelativeLayout>这里我们还需要selector.xml
实现点击效果.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:drawable="@drawable/home_btn_bg_s" android:state_enabled="true" android:state_focused="true" android:state_pressed="false"/>
<item android:drawable="@drawable/home_btn_bg_s" android:state_enabled="true" android:state_pressed="true"/>
<item android:drawable="@drawable/home_btn_bg_d" android:state_checked="true" android:state_enabled="true"/>
</selector>
示例图:
就说这么多了,情况因人而异.




