Java基础复习笔记08数据结构-二叉树和二叉树的遍历
1. 二叉树
一般的树限制比较少,所以才提出了具有特色的二叉树的概念。二叉树顾名思义,每个节点最多有两个子节点,分别叫做左子节点和右子节点。有了这个限定性后,就可以干很多树不能干的事情了。如果树的所有层,除了最后一层的节点外都是两个子节点,那么称这个树为满二叉树。如下图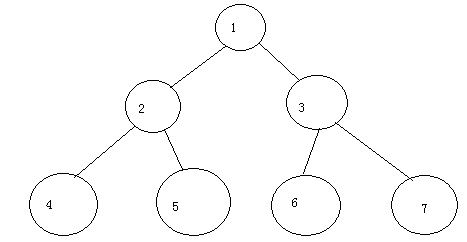
若设二叉树的高度为h,除第 h 层外,其它各层 (1~h-1) 的结点数都达到最大个数,第 h 层所有的节点都连续集中在最左边,这就是完全二叉树。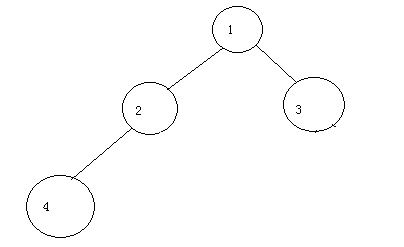
2. 二叉树的操作
二叉树具有为指定节点增加子节点操作、判断树是否为空、返回根节点、返回指定节点的父节点,返回指定节点的左子节点、返回指定节点的右子节点、返回树的深度、返回指定节点的位置。
3. 二叉树的延伸
其实二叉树只是一个引子,计算机界很多的算法都是根据二叉树所展开的,比如排序二叉树、红黑树、哈夫曼树、线索二叉树等等。
4. 顺序实现二叉树
下面我们来看看二叉树的顺序实现方式,顺序实现二叉树就是利用数组存储所有的二叉树的节点。代码如下
package dateStructer.tree.binaryTree;
/**
* 顺序二叉树
*
* @author liuyan
*/
public class ArrayBinaryTree<T> {
// 树的默认深度
private static final int DefTreeDeep = 4;
// 节点数组
private Object[] datas;
// 指定的树的深度
private int treeDeep;
// 实际的数组个数
private int arraySize;
/**
* 默认构造函数
*/
public ArrayBinaryTree() {
// 设置默认的树深度
treeDeep = DefTreeDeep;
// 2的DefTreeDeep次方-1个数组元素
arraySize = (int) Math.pow(2, DefTreeDeep) - 1;
datas = new Object[arraySize];
}
/**
* 指定深度构建二叉树
* @param deep
*/
public ArrayBinaryTree(int deep) {
// 按指定深度
treeDeep = deep;
arraySize = (int) Math.pow(2, treeDeep) - 1;
datas = new Object[arraySize];
}
/**
* 指定深度和指定根节点构建二叉树
* @param deep
* @param data
*/
public ArrayBinaryTree(int deep, T data) {
// 按指定深度
treeDeep = deep;
arraySize = (int) Math.pow(2, treeDeep) - 1;
datas = new Object[arraySize];
datas[0] = data;
}
/**
* 为指定节点索引增加子节点
* @param index
* @param data
* @param isLeft
* @return
*/
public boolean addNode(int index, T data, boolean isLeft) {
if (index * 2 + 2 > arraySize || datas[index] == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("标记无效");
}
if (isLeft) {
datas[index * 2 + 1] = data;
} else {
datas[index * 2 + 2] = data;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 判断二叉树是否为空
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return arraySize == 0;
}
/**
* 返回根节点
*
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T getRoot() {
return (T) datas[0];
}
/**
* 返回指定节点的父节点
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T getParent(int index) {
if (index > arraySize || datas[index] == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("标记无效");
}
if (datas[(index - 1) / 2] == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("无父节点");
}
return (T) datas[(index - 1) / 2];
}
/**
* 返回左子节点
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T getLeftNode(int index) {
if (index * 2 + 2 > arraySize || datas[index] == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("标记无效");
}
return (T) datas[index * 2 + 1];
}
/**
* 返回右子节点
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T getRightNode(int index) {
if (index * 2 + 2 > arraySize || datas[index] == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("标记无效");
}
return (T) datas[index * 2 + 2];
}
/**
* 返回树的深度
* @return
*/
public int getTreeDeep() {
return treeDeep;
}
/**
* 返回指定节点的索引位置
* @param data
* @return
*/
public int getNodeIndex(T data) {
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) {
if (data == datas[i]) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer("[");
for (int i = 0; i < datas.length; i++) {
str.append("[" + datas[i] + "],");
}
if (datas.length > 0) {
return str.substring(0, str.lastIndexOf(",")) + "]";
}
return str.append("]").toString();
}
}
测试代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayBinaryTree<String> arrayBinaryTree = new ArrayBinaryTree<String>(4,"汉献帝");
System.out.println(arrayBinaryTree);
arrayBinaryTree.addNode(0, "刘备", true);
arrayBinaryTree.addNode(0, "曹操", false);
arrayBinaryTree.addNode(1, "关羽", true);
arrayBinaryTree.addNode(1, "张飞", false);
arrayBinaryTree.addNode(2, "张辽", true);
arrayBinaryTree.addNode(2, "许褚", false);
System.out.println(arrayBinaryTree);
System.out.println(arrayBinaryTree.getLeftNode(1));
System.out.println(arrayBinaryTree.getRightNode(0));
System.out.println(arrayBinaryTree.isEmpty());
System.out.println(arrayBinaryTree.getParent(4));
}
测试效果如下
顺序实现是比较浪费资源的,可以看到数组没有元素的位置都是null。如果将测试代码稍微变更一下,如下因为树本身就是具有递归性质的结构。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayBinaryTree<String> arrayBinaryTree = new ArrayBinaryTree<String>(4,"汉献帝");
System.out.println(arrayBinaryTree);
arrayBinaryTree.addNode(0, "刘备", true);
arrayBinaryTree.addNode(0, "曹操", false);
arrayBinaryTree.addNode(2, "张辽", true);
arrayBinaryTree.addNode(2, "许褚", false);
arrayBinaryTree.addNode(6, "李典", true);
arrayBinaryTree.addNode(6, "乐进", false);
System.out.println(arrayBinaryTree);
System.out.println(arrayBinaryTree.getLeftNode(2));
System.out.println(arrayBinaryTree.getRightNode(0));
System.out.println(arrayBinaryTree.isEmpty());
System.out.println(arrayBinaryTree.getParent(14));
}
5. 二叉链表实现二叉树
为了弥补顺序实现的空间浪费问题,可以使用链表方式实现二叉树,但是链表又分为两种情况,一种是二叉链表,另一种稍后再说。二叉链表的思想就是构造一个对象,记住它的两个子节点,所谓记住两个子节点可以是子节点的位置,可以是子节点的实体对象。如果记录了位置,其实是离不开数组的帮助的。如果记录了整个子节点对象,那么就可以完全脱离数组,完完全全,真真正正的链表离散式存储。这次使用记录节点位置,算法如下
package dateStructer.tree.binaryTree;
/**
* 二叉链表二叉树
*
* @author liuyan
*/
public class TwoLinkedBinaryTree<T> {
// 树的默认深度
private static final int DefTreeDeep = 4;
// 节点数组
private TwoLinkNode<T>[] datas;
// 指定的树的深度
private int treeDeep;
// 实际的数组个数
private int arraySize;
//节点个数
private int nodeSize;
/**
* 二叉节点
*/
@SuppressWarnings("hiding")
class TwoLinkNode<T> {
public int leftChildIndex;
public int rightChildIndex;
public int index;
public T data;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public TwoLinkedBinaryTree() {
treeDeep = DefTreeDeep;
arraySize = (int) Math.pow(2, treeDeep) - 1;
datas = new TwoLinkNode[arraySize];
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public TwoLinkedBinaryTree(int deep, T data) {
treeDeep = DefTreeDeep;
arraySize = (int) Math.pow(2, treeDeep) - 1;
datas = new TwoLinkNode[arraySize];
TwoLinkNode<T> twoLinkNode = new TwoLinkNode<T>();
twoLinkNode.data = data;
twoLinkNode.leftChildIndex = 1;
twoLinkNode.rightChildIndex = 2;
twoLinkNode.index = 0;
datas[0] = twoLinkNode;
nodeSize = 1;
}
/**
* 为指定节点索引增加子节点
*
* @param index
* @param data
* @param isLeft
* @return
*/
public boolean addNode(int index, T data, boolean isLeft) {
if (index + 1 > arraySize || datas[index] == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("标记无效");
}
for (int i = index + 1; i < arraySize; i++) {
if (datas[i] == null) {
TwoLinkNode<T> twoLinkNode = new TwoLinkNode<T>();
twoLinkNode.data = data;
twoLinkNode.index = i;
datas[i] = twoLinkNode;
if (isLeft) {
datas[index].leftChildIndex = i;
} else {
datas[index].rightChildIndex = i;
}
nodeSize ++;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判断二叉树是否为空
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return nodeSize == 0;
}
/**
* 返回根节点
*
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T getRoot() {
return (T) datas[0];
}
/**
* 返回指定节点的父节点
*
* @return
*/
public T getParent(int index) {
if (index > arraySize || datas[index] == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("标记无效");
}
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) {
if (datas[i] != null) {
if (datas[i].leftChildIndex == index
|| datas[i].rightChildIndex == index) {
return datas[i].data;
}
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 返回左子节点
*
* @return
*/
public T getLeftNode(int index) {
if (index + 2 > arraySize || datas[index] == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("标记无效");
}
return (T) datas[datas[index].leftChildIndex].data;
}
/**
* 返回右子节点
*
* @return
*/
public T getRightNode(int index) {
if (index + 2 > arraySize || datas[index] == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("标记无效");
}
return (T) datas[datas[index].rightChildIndex].data;
}
/**
* 返回树的深度
*
* @return
*/
public int getTreeDeep() {
return treeDeep;
}
/**
* 返回指定节点的索引位置
*
* @param data
* @return
*/
public int getNodeIndex(T data) {
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) {
if (data == datas[i]) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer("[");
for (int i = 0; i < nodeSize; i++) {
if(datas[i].data != null){
str.append("[" + datas[i].data + "],");
}
}
if (datas.length > 0) {
return str.substring(0, str.lastIndexOf(",")) + "]";
}
return str.append("]").toString();
}
}
使用这种实现其实是想利用好数组的空间。别让中间任何的节点空间白白浪费了。但是可以发现找父节点的时候比较麻烦。还得遍历一下整个节点。三叉链表就不必遍历,因为三叉链表比二叉链表多了记录了一个节点,那就是此节点的父节点。无论是父节点的位置或者父节点实体,都是一样的思想。
6. 三叉链表实现二叉树
下面我们基于上面的二叉链表形式编写三叉链表。代码如下
package dateStructer.tree.binaryTree;
/**
* 三叉链表的实现
*
* @author liuyan
*/
public class ThreeLinkedBinaryTree<T> {
// 树的默认深度
private static final int DefTreeDeep = 4;
// 节点数组
private ThreeLinkNode<T>[] datas;
// 指定的树的深度
private int treeDeep;
// 实际的数组个数
private int arraySize;
// 节点个数
private int nodeSize;
/**
* 三叉节点
*/
@SuppressWarnings("hiding")
class ThreeLinkNode<T> {
public int parentIndex;
public int leftChildIndex;
public int rightChildIndex;
public int index;
public T data;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public ThreeLinkedBinaryTree() {
treeDeep = DefTreeDeep;
arraySize = (int) Math.pow(2, treeDeep) - 1;
datas = new ThreeLinkNode[arraySize];
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public ThreeLinkedBinaryTree(int deep, T data) {
treeDeep = DefTreeDeep;
arraySize = (int) Math.pow(2, treeDeep) - 1;
datas = new ThreeLinkNode[arraySize];
ThreeLinkNode<T> threeLinkNode = new ThreeLinkNode<T>();
threeLinkNode.data = data;
threeLinkNode.leftChildIndex = 1;
threeLinkNode.rightChildIndex = 2;
threeLinkNode.index = 0;
threeLinkNode.parentIndex = -1;
datas[0] = threeLinkNode;
nodeSize = 1;
}
/**
* 为指定节点索引增加子节点
*
* @param index
* @param data
* @param isLeft
* @return
*/
public boolean addNode(int index, T data, boolean isLeft) {
if (index + 1 > arraySize || datas[index] == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("标记无效");
}
for (int i = index + 1; i < arraySize; i++) {
if (datas[i] == null) {
ThreeLinkNode<T> threeLinkNode = new ThreeLinkNode<T>();
threeLinkNode.data = data;
threeLinkNode.index = i;
threeLinkNode.parentIndex = index;
datas[i] = threeLinkNode;
if (isLeft) {
datas[index].leftChildIndex = i;
} else {
datas[index].rightChildIndex = i;
}
nodeSize++;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判断二叉树是否为空
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return nodeSize == 0;
}
/**
* 返回根节点
*
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T getRoot() {
return (T) datas[0];
}
/**
* 返回指定节点的父节点
*
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T getParent(int index) {
if (index > arraySize || datas[index] == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("标记无效");
}
return (T) datas[datas[index].parentIndex];
}
/**
* 返回左子节点
*
* @return
*/
public T getLeftNode(int index) {
if (index + 2 > arraySize || datas[index] == null
|| datas[datas[index].leftChildIndex] == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("标记无效");
}
return (T) datas[datas[index].leftChildIndex].data;
}
/**
* 返回右子节点
*
* @return
*/
public T getRightNode(int index) {
if (index + 2 > arraySize || datas[index] == null
|| datas[datas[index].rightChildIndex] == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("标记无效");
}
return (T) datas[datas[index].rightChildIndex].data;
}
/**
* 返回树的深度
*
* @return
*/
public int getTreeDeep() {
return treeDeep;
}
/**
* 返回指定节点的索引位置
*
* @param data
* @return
*/
public int getNodeIndex(T data) {
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) {
if (data == datas[i]) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer("[");
for (int i = 0; i < nodeSize; i++) {
if (datas[i].data != null) {
str.append("[" + datas[i].data + "],");
}
}
if (datas.length > 0) {
return str.substring(0, str.lastIndexOf(",")) + "]";
}
return str.append("]").toString();
}
}
可以看到基本上方法实现都一样,就是找寻父节点的时候更省事了。因为节点对象多存了父节点的信息,当然就省事了。
7. 二叉树的遍历
遍历二叉树实际上就是将一个非线性的二维结构给排列呈线性的过程。如果是顺序实现了二叉树的结构,自然底层就是线性的,无需转化。如果是纯链表实现呢,就需要将离散的节点重新组织组织了。
遍历也分为深度优先遍历、广度优先遍历。而对于深度优先遍历又分为三种模式:先根遍历、中根遍历、后根遍历。
深度优先遍历:就是优先访问树中最深层次的节点
广度优先遍历:就是从根往下一层一层遍历访问
先根遍历:先遍历根节点,之后处理其他子节点
中根遍历:先遍历根节点的左子树,之后遍历根节点,最后遍历右子树
后根遍历:先遍历根节点的左子树,之后遍历右子树,最后遍历根节点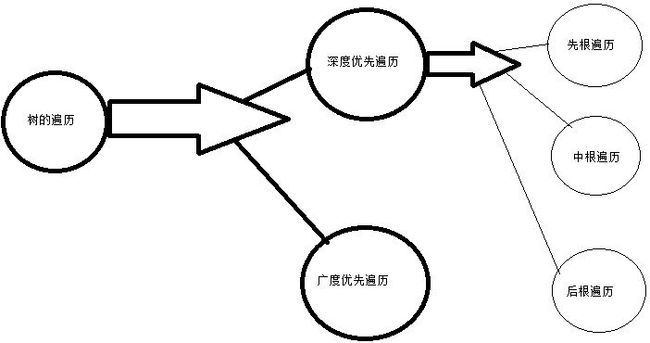
先根遍历算法如下
public List<TwoLinkNode<T>> firstRoot(TwoLinkNode<T> twoLinkNode) {
if (twoLinkNode == null) {
return null;
}
List<TwoLinkNode<T>> list = new ArrayList<TwoLinkNode<T>>();
list.add(twoLinkNode);
if (twoLinkNode.leftChildIndex > 0) {
list.addAll(firstRoot(datas[twoLinkNode.leftChildIndex]));
}
if (twoLinkNode.rightChildIndex > 0) {
list.addAll(firstRoot(datas[twoLinkNode.rightChildIndex]));
}
return list;
}
中根遍历算法如下
/**
* 中根遍历
*
* @param twoLinkNode
* @return
*/
public List<TwoLinkNode<T>> minRoot(TwoLinkNode<T> twoLinkNode) {
if (twoLinkNode == null) {
return null;
}
List<TwoLinkNode<T>> list = new ArrayList<TwoLinkNode<T>>();
if (twoLinkNode.leftChildIndex > 0) {
list.addAll(minRoot(datas[twoLinkNode.leftChildIndex]));
}
list.add(twoLinkNode);
if (twoLinkNode.rightChildIndex > 0) {
list.addAll(minRoot(datas[twoLinkNode.rightChildIndex]));
}
return list;
}
后根遍历
/**
* 后根遍历
*
* @param twoLinkNode
* @return
*/
public List<TwoLinkNode<T>> afterRoot(TwoLinkNode<T> twoLinkNode) {
if (twoLinkNode == null) {
return null;
}
List<TwoLinkNode<T>> list = new ArrayList<TwoLinkNode<T>>();
if (twoLinkNode.leftChildIndex > 0) {
list.addAll(afterRoot(datas[twoLinkNode.leftChildIndex]));
}
if (twoLinkNode.rightChildIndex > 0) {
list.addAll(afterRoot(datas[twoLinkNode.rightChildIndex]));
}
list.add(twoLinkNode);
return list;
}
广度优先遍历
/**
* 后根遍历
*
* @param twoLinkNode
* @return
*/
public List<TwoLinkNode<T>> deepFirst() {
List<TwoLinkNode<T>> list = new ArrayList<TwoLinkNode<T>>();
Queue<TwoLinkNode<T>> queue = new ArrayDeque<TwoLinkNode<T>>();
queue.add(datas[0]);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
list.add(queue.peek());
TwoLinkNode<T> twoLinkNode = queue.poll();
if (twoLinkNode.leftChildIndex > 0) {
queue.add(datas[twoLinkNode.leftChildIndex]);
}
if (twoLinkNode.rightChildIndex > 0) {
queue.add(datas[twoLinkNode.rightChildIndex]);
}
}
return list;
}
8. 二叉树、树、森林转换
其实这三个结构可以互相转换,具体参考
http://jpkc.nwu.edu.cn/sjjg/study_online/book/6/4_2.htm
9. 总结
这次总结学习了二叉树的概念、用法、实现细节、二叉树的遍历法。当然了这篇总结还不是很全面。回头再补上吧。
